Recombinant production of steviol glycosides
A technology of stevia and recombinant host, which is applied in the direction of sugar derivatives, bulk chemical production, recombinant DNA technology, etc., and can solve problems such as odor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
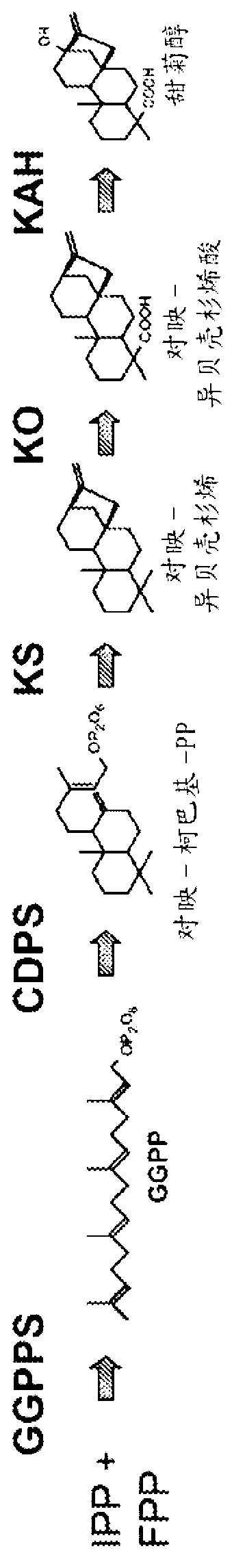
[0223] Example 1--Construction of Kaurene Biosynthetic Pathway Gene
[0224] The nucleotide sequence encoding a truncated baker's yeast HMG CoA reductase was cloned into a yeast high copy episomal plasmid vector such that the coding sequence is operably linked to a promoter that is repressed by the amino acid methionine and transcription is regulated by its regulation. See US Patents 5,460,949 and 5,306,862.
[0225] The nucleotide sequence encoding the GGPPS enzyme shown in Table 1 is modified to adapt to expression in yeast (see SEQ ID NOs: 18-25), and cloned into the E. coli vector so that the coding sequence can be operably linked A yeast promoter that is repressed by the amino acid methionine and that regulates transcription. Also shown in Table 1 is the name of each plasmid ("entry vector") containing the expression cassette. SEQ ID NOs: 26-33 give the nucleotide sequences from the source organism from which the polypeptide was originally identified. Using the unmo...
Embodiment 3
[0255] The construction of embodiment 3-yeast strain
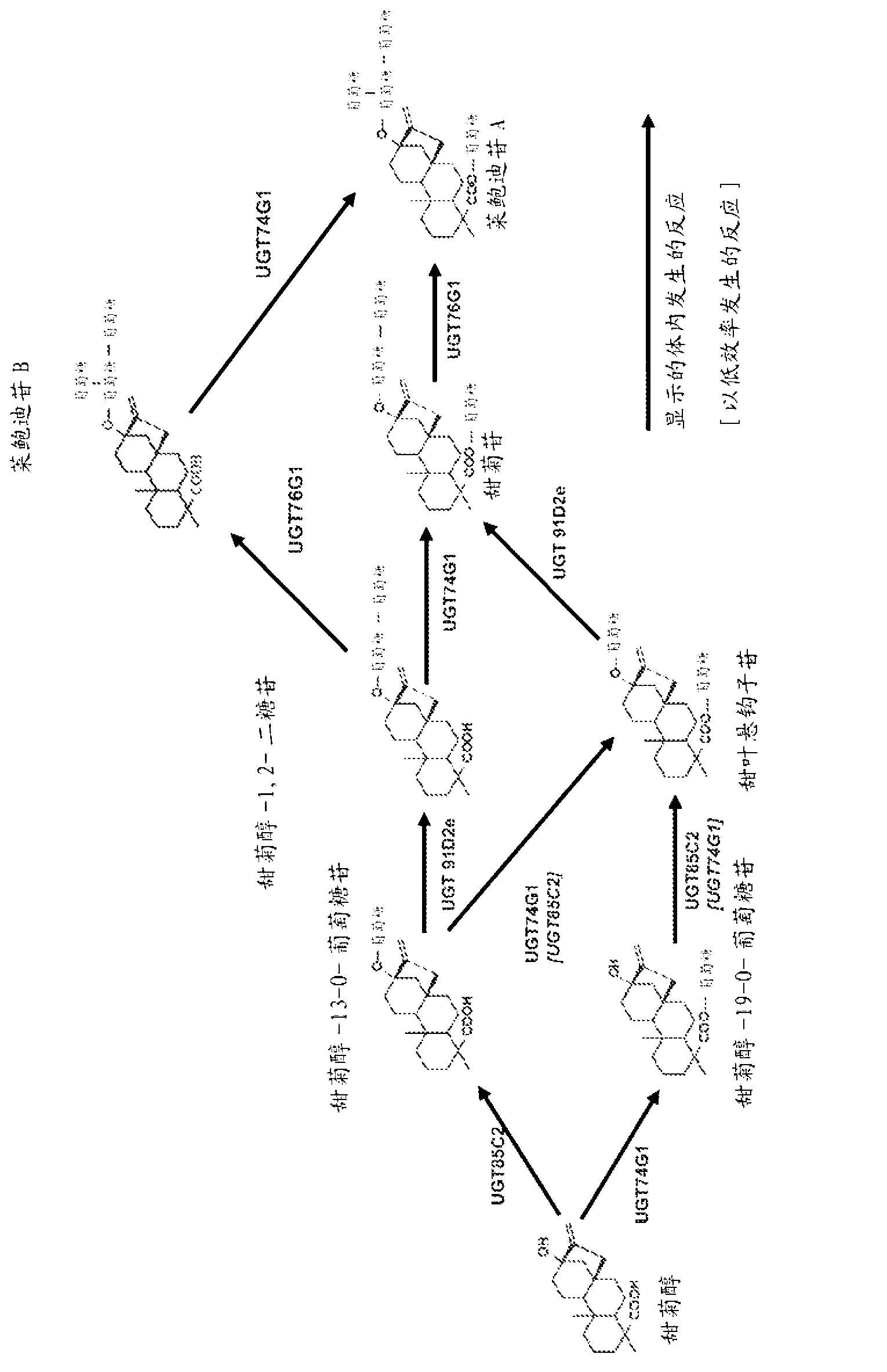
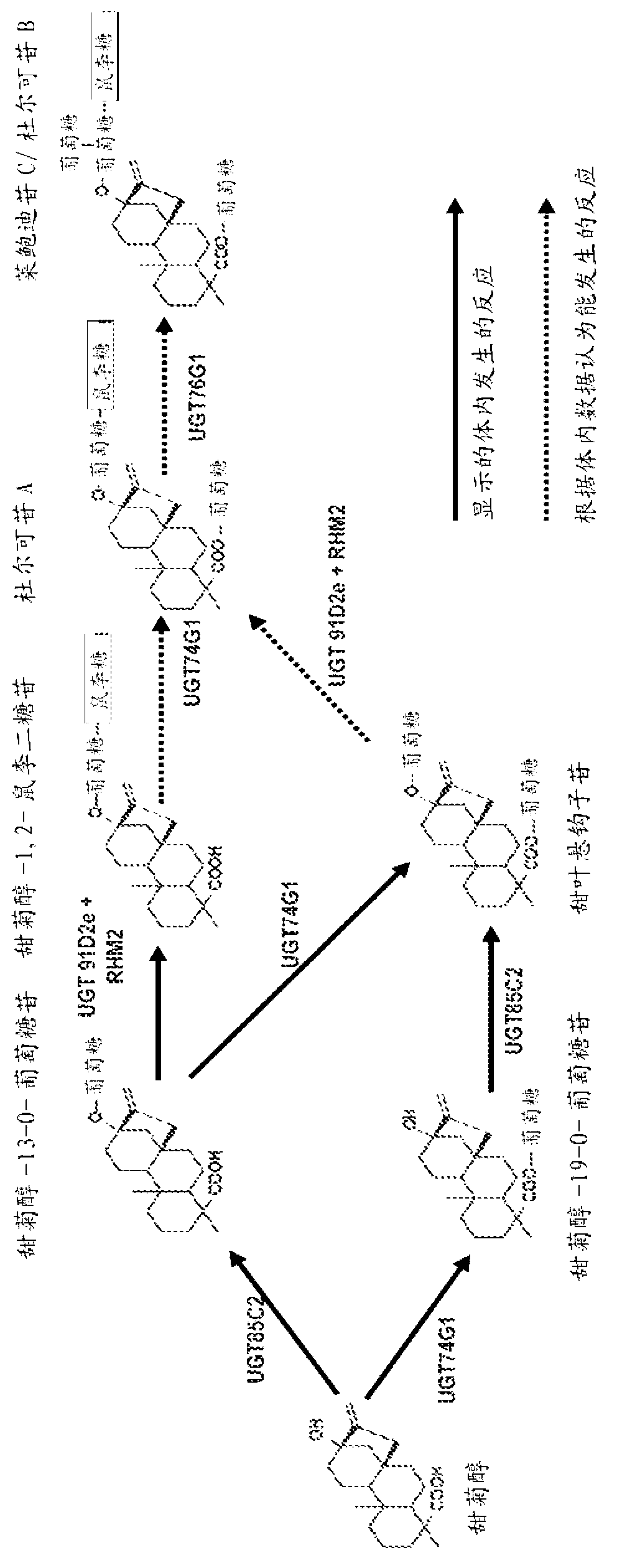
[0256] A yeast strain designated EFSC301 was engineered by replacing the endogenous ERG9 promoter with the copper-inducible CUP1 promoter. Strain EFSC301 is a derivative of EUROSCARF deposited yeast strain BY4742. See Internet uni-frankfurt.de / fb15 / mikro / euroscarf / data / by.html. Transcript levels of the ERG9 gene are very low in standard yeast growth media because of the low copper concentrations in such media. The decrease in ergosterol production in this strain resulted in an increase in the amount of isoprene units available for steviol biosynthesis. The yeast strain was also engineered to genomically integrate the Stevia UGT85C2 and UGT74G1 genes, each under the transcriptional control of the strong constitutive GPD1 promoter. See Table 8. The strain contained one copy each of the Stevia UGT85C2 and UGT74G1 genes integrated into the MUS1241 strain genome.
Embodiment 4
[0257] Example 4--Analysis of Steviol Glycoside Pathway Gene Expression in Yeast
[0258] To examine steviol glycoside biosynthesis in yeast, the expression cassettes of the 36 entry vectors in Tables 1-7 and Example 1 were randomly concatenated in ligation reactions to form artificial yeast chromosomes ("eYACs"). The process is as Figure 5 hint.
[0259] Two different sets of ligation reactions were performed. Connectome A included all the genes in Tables 1-7, but not the bifunctional CDPS-KS gene (Table 4). Connectome B included all the genes in Tables 1-7, but did not contain the single-function CDPS and KS genes (Tables 2-3).
[0260] Prepare 30-200 μg of DNA from each entry vector containing the expression cassette. Gene expression cassettes were released from each vector using the restriction enzyme AscI. The expression cassettes were then randomly concatenated into eYACs by a 3-hour ligation reaction using T4 ligase. Because tandem DNA is very viscous, the succ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com