Composite spinneret and method of manufacturing composite fiber
A composite spinneret and polymer technology, applied in spinneret assemblies, fiber processing, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to reach the nanometer level, the spacing between holes becomes larger, and the equipment cost is large, and it can prevent confluence. , the effect of high dimensional stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
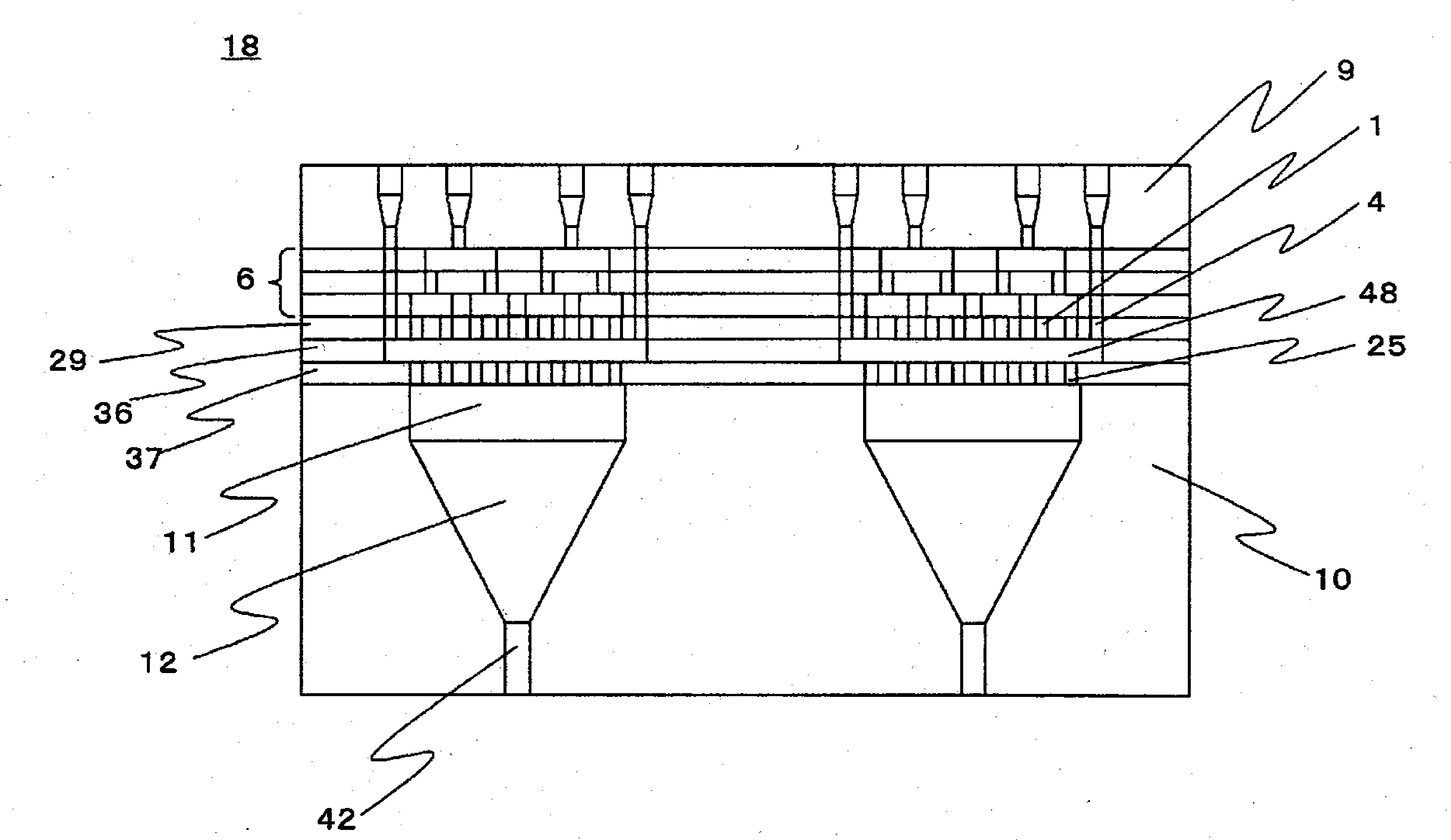
[0269] Polyethylene terephthalate (PET melt viscosity: 120 Pa?s) with an intrinsic viscosity (IV) of 0.63 dl / g as the island component and 5 with an IV of 0.58 dl / g as the sea component polymer -Sodium sulfonate isophthalic acid 5.0 mol% copolymerized PET (melt viscosity of copolymerized PET: 140Pa·s) was melted at 290°C respectively, measured, and flowed into the assembled Figure 6 In the spinning package of the composite spinneret according to this embodiment shown, a sea-island composite polymer stream is discharged from the spinneret discharge holes. In addition, 1,000 island component discharge holes were perforated at equal intervals in one discharge introduction hole for the island component polymer on the distribution plate of the lowest layer. The sea-island ratio is 50 / 50. After cooling and solidifying the discharged composite polymer stream, add an oil agent, and take it up at a spinning speed of 1500m / min, and obtain undrawn fibers of 150dtex-15 fibers (single hol...
Embodiment 2
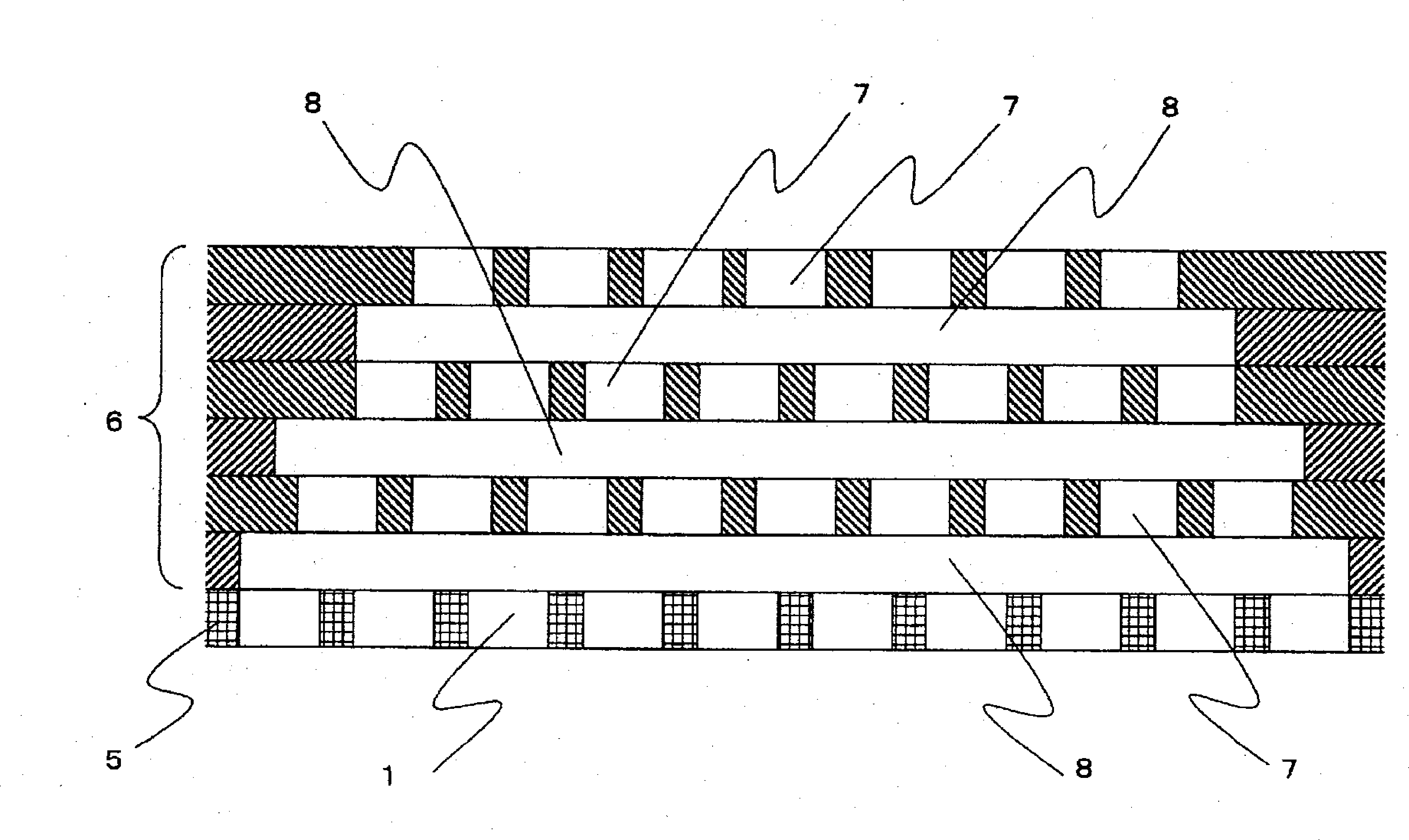
[0272] Such as figure 2 As shown, except that the arrangement of the island component discharge holes and the sea component discharge holes of the distribution plate at the lowest layer is changed to condition B of (2), the same composite spinneret as in Example 1 was used to make the island component polymer ratio ratio Example 1 was larger (the sea-island ratio was set to 20 / 80), but the same polymer as Example 1, the same fineness, and spinning conditions were spun to obtain 13,500 multifibers.
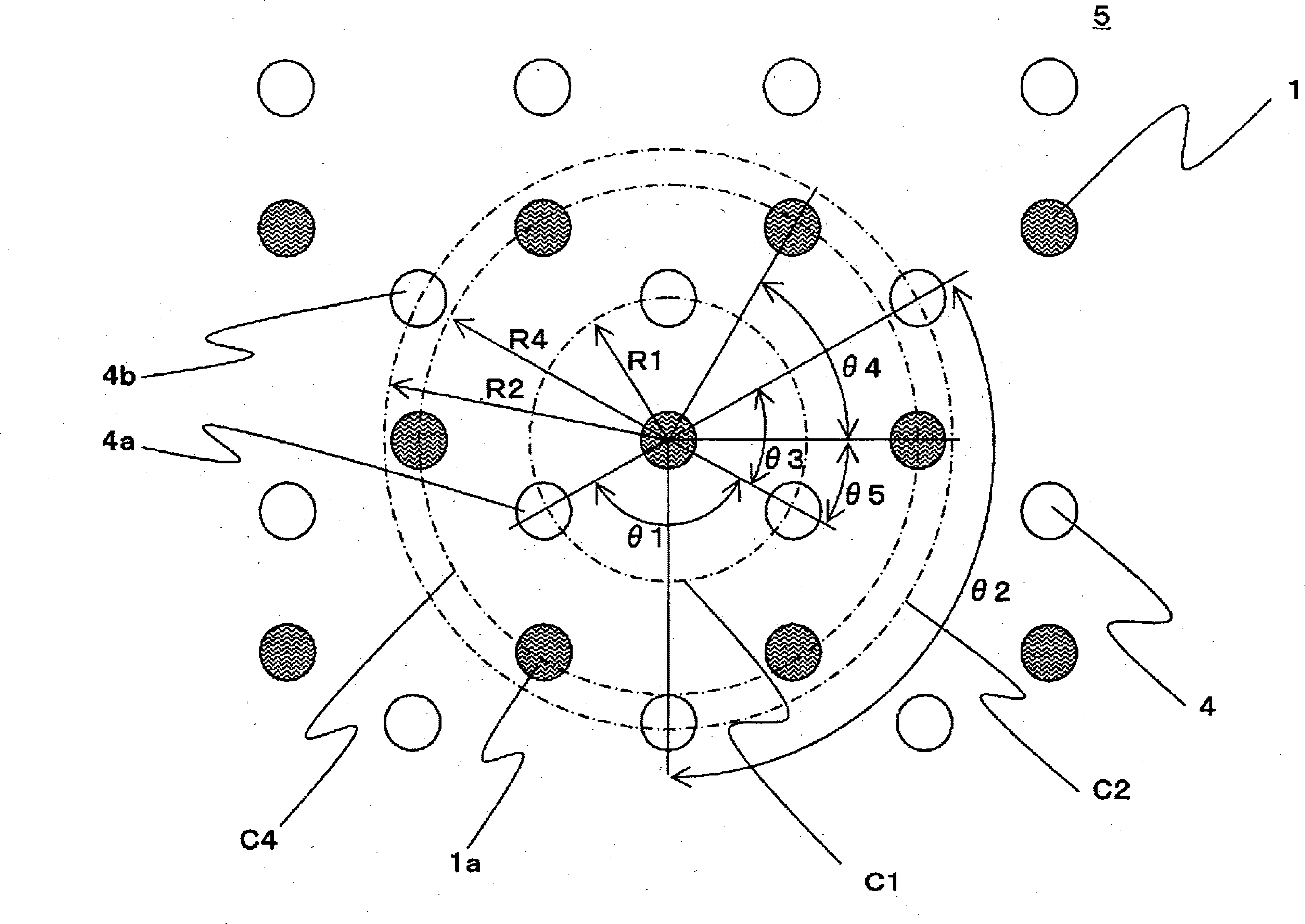
[0273] Here, in the composite spinneret used in Example 2, the radius R1 of the imaginary circumferential line C1 is 0.4 mm, the radius R2 of the imaginary circumferential line C2 is 0.8 mm, and the radius R4 of the imaginary circumferential line C4 is 0.8 mm. An island component discharge hole and a sea component discharge hole with a hole diameter of 0.2 mm were prepared. As described in Table 1, the island component has a triangular cross-section (the angle at the intersection...
Embodiment 3
[0275] Such as image 3 As shown, except that the arrangement of the island component discharge holes and sea component discharge holes of the distribution plate at the lowest layer is changed to condition C of (2), the same composite spinneret as in Example 1 is used, and the sea-island ratio is set to Other than 20 / 80, spinning was performed using the same polymer as in Example 1, the same fineness, and spinning conditions, and 15,000 multifibers were obtained.
[0276] Here, in the composite spinneret used in Example 3, the radius R1 of the imaginary circumferential line C1 is 0.4 mm, the radius R2 of the imaginary circumferential line C2 is 0.8 mm, and the radius R4 of the imaginary circumferential line C4 is 0.693 mm. An island component discharge hole and a sea component discharge hole with a hole diameter of 0.2 mm were prepared. As described in Table 1, the island component has a hexagonal cross-section (the angle at the intersection point of 6 straight lines is 120°)...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Plate thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fiber diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fiber diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com