Quasi-single-stage high power factor circuit and device with primary side constant current control
A high power factor, constant current control technology, applied in the direction of output power conversion device, high-efficiency power electronic conversion, conversion equipment with intermediate conversion to AC, etc., can solve the problems of stroboscopic and inapplicable, and achieve simple circuit structure , reduce ripple current, and reduce circuit cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
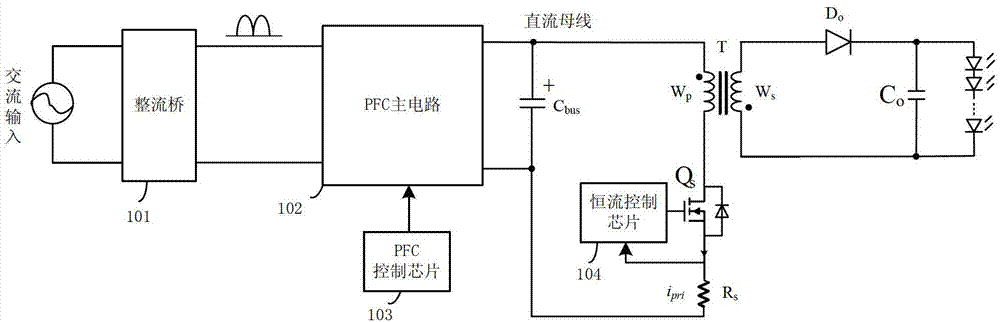
[0046] refer to image 3 , image 3 Shows the quasi-single-stage high power factor device of the first embodiment, including a quasi-single-stage high power factor circuit and a control circuit 300, wherein the quasi-single-stage high power factor circuit includes a rectifier bridge B1, an input capacitor C in , inductance L 1 , Bus capacitance C 1 , the first diode D 1 , switch tube Q 1 , the second diode D 2 , Sampling resistor R sen , Transformer T (including the primary winding W p , secondary winding W s and the auxiliary winding W a ), output diode D o and the output capacitor C o .
[0047] Further, the rectifier bridge B 1 The input terminal of the AC power supply signal is connected and rectified, and the rectifier bridge B 1 The positive output terminal is connected to the input capacitor C in The first end of the inductor L 1 The first end of the bridge rectifier B 1 The negative output terminal is connected to the input capacitor C in The second en...
no. 2 example
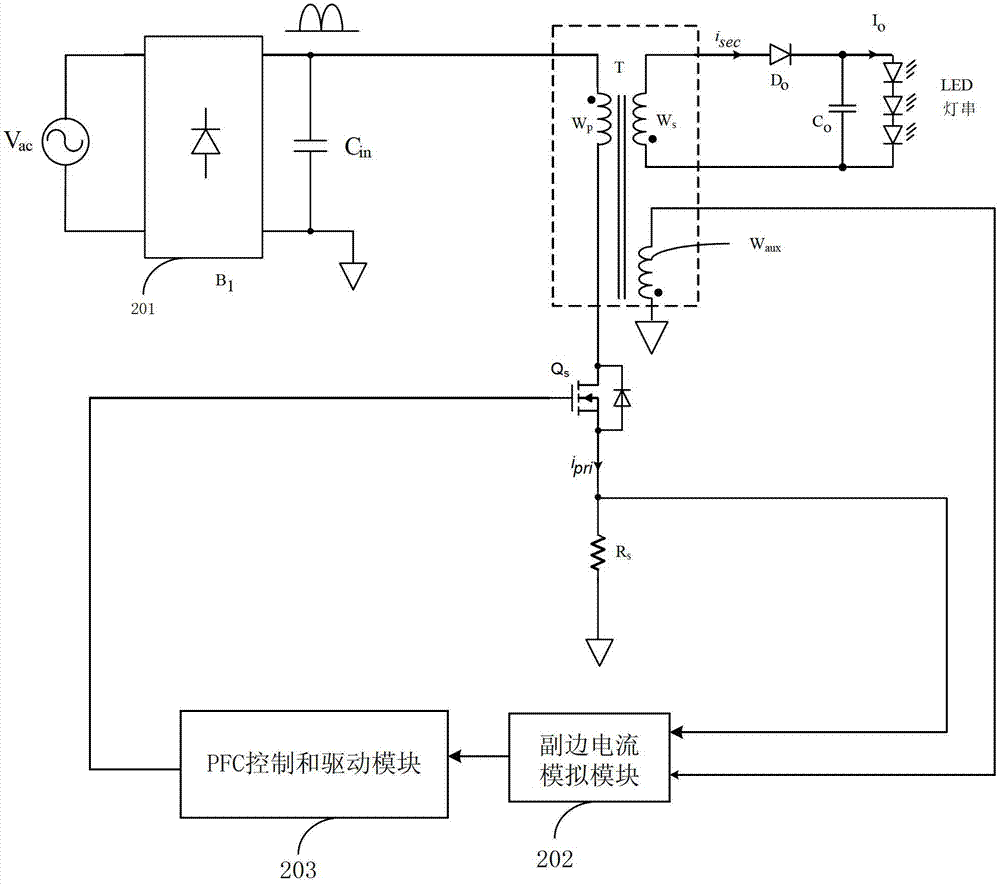
[0057] refer to Figure 7 , shows the quasi-single-stage high power factor device with constant current control on the primary side of the second embodiment. The principle of the second embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment, except that it adopts a non-isolated structure. This embodiment includes a quasi-single-stage high power factor circuit and control circuit 300 . Among them, the quasi-single-stage high power factor circuit includes rectifier bridge B1, input capacitor C in , inductance L 1 , Bus capacitance C 1 , the first diode D 1 , switch tube Q 1 , the second diode D 2 , Sampling resistor R sen , Transformer T (including the primary winding L 2 and the auxiliary winding W aux ), the output diode Do and the output capacitor C o .
[0058] Further, the rectifier bridge B 1 The input terminal receives the AC power signal, and the rectifier bridge B 1 The positive output terminal of the input capacitor C in The first end of the inductor L 1T...
no. 3 example
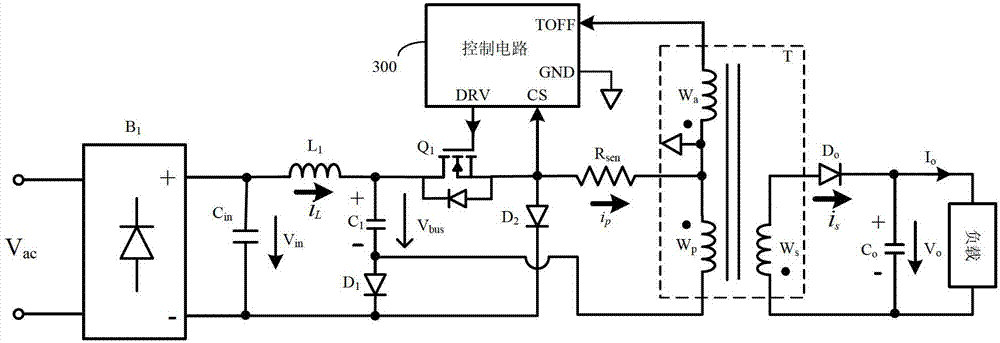
[0064] refer to Figure 10 , shows the quasi-single-stage high power factor device of the primary side constant current control of the third embodiment. The main circuit of this embodiment is basically the same as that of the aforementioned first embodiment, and the working principle is also basically the same, so it will not be described in detail. The main circuit of this embodiment and image 3 The difference of the first embodiment shown is that the contact between the control circuit 400 and the main circuit changes. In this embodiment, the sampling resistor R sen The first terminal of the sampling resistor Rsen is grounded, and the second terminal of the sampling resistor Rsen is connected to the current sampling terminal CS of the control circuit 400. Therefore, the current information sent to the control circuit 400 is the negative current information of the primary winding Wp of the transformer. After the reverse, the same can be achieved with image 3 The basic fu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com