Method for improving viscosity of gelatin by using glutamine transaminase for catalyzing gelatin crosslinking
A transaminase catalyzed gelatin and glutamine technology, which is applied in the fields of food and medicine, can solve the problems of limiting the application of gelatin and the toxicity of cross-linking agents, and achieve the effects of cheap and easy-to-obtain raw materials, low production costs, and safe methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
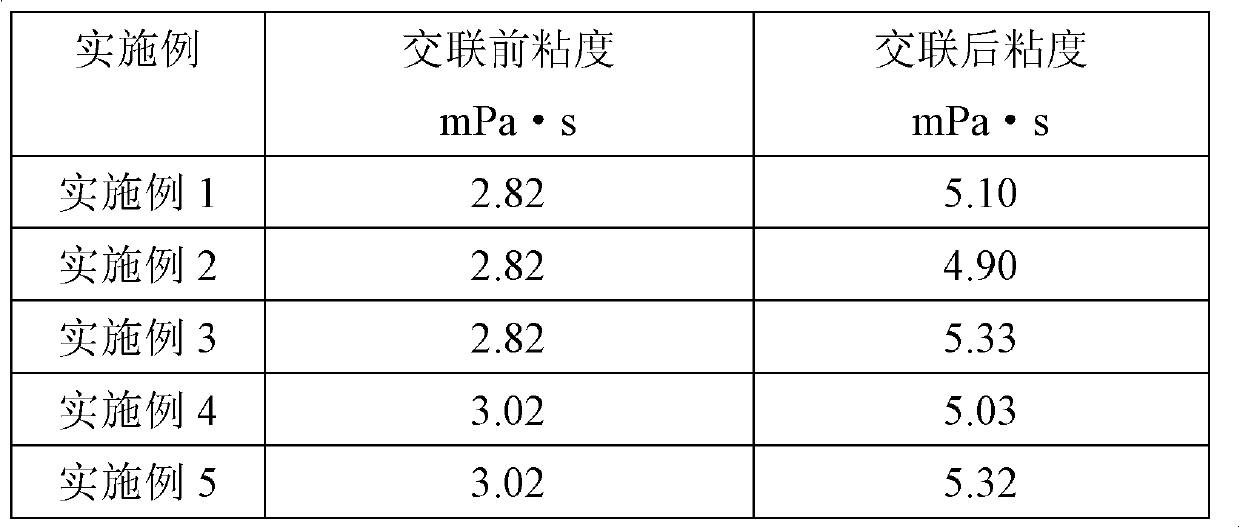
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] (1) Place 5 parts by weight of low-viscosity alkali-process bone gelatin in a reactor, add water to swell for 40 minutes, and stir at 50°C to dissolve the bone gelatin in the reactor to obtain a bone gelatin solution with a mass concentration of 5%. ;
[0024] (2) the pH value of the bone gelatin solution obtained by adjusting step (1) with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution is 7; according to the total amount of bone gelatin, add microbial transglutaminase, wherein the mass ratio of microbial transglutaminase to bone gelatin 1:2000; Stir at a temperature of 60°C for 6 hours to obtain a reaction solution;
[0025] (3) The temperature of the reaction solution obtained in step (2) was raised to 95° C., stirred for 15 minutes to inactivate the enzyme, and bone gelatin glue was obtained. The bone gelatin glue can be further freeze-dried or triple-effect evaporated, concentrated and then dried with a fourdrinier net to obtain a bone gelatin product. The product indexes of t...
Embodiment 2
[0027] (1) Put 10 parts by weight of low-viscosity alkali-process bone gelatin in a reaction kettle, add water to swell for 40 minutes, and stir at 50°C to dissolve the bone gelatin in the reaction kettle to obtain a bone gelatin solution with a mass concentration of 10%. ;
[0028] (2) the pH value of the bone gelatin solution that step (1) obtains with hydrochloric acid regulation is 5; According to the total amount of bone gelatin, add microorganism transglutaminase, wherein the mass ratio of microorganism transglutaminase and bone gelatin is 1: 1000; stirring at a constant temperature for 3 hours at a temperature of 37° C. to obtain a reaction solution;
[0029] (3) The temperature of the reaction solution obtained in step (2) was raised to 95° C., stirred for 15 minutes to inactivate the enzyme, and bone gelatin glue was obtained. The bone gelatin glue can be further freeze-dried or triple-effect evaporated, concentrated and then dried with a fourdrinier net to obtain a ...
Embodiment 3
[0031] (1) Put 10 parts by weight of low-viscosity alkali-process bone gelatin in a reaction kettle, add water to swell for 40 minutes, and stir at 50°C to dissolve the bone gelatin in the reaction kettle to obtain a bone gelatin solution with a mass concentration of 10%. ;
[0032] (2) the pH value of the bone gelatin solution that step (1) obtains with phosphoric acid adjustment is 5; According to the total amount of bone gelatin, add microorganism transglutaminase, wherein the mass ratio of microorganism transglutaminase and bone gelatin is 1: 4000; stirring at a constant temperature for 10 hours at a temperature of 50°C to obtain a reaction solution;
[0033] (3) The temperature of the reaction solution obtained in step (2) was raised to 100° C., stirred for 15 minutes to inactivate the enzyme, and the bone gelatin glue was obtained. The bone gelatin glue can be further freeze-dried or triple-effect evaporated, concentrated and then dried with a fourdrinier net to obtain ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com