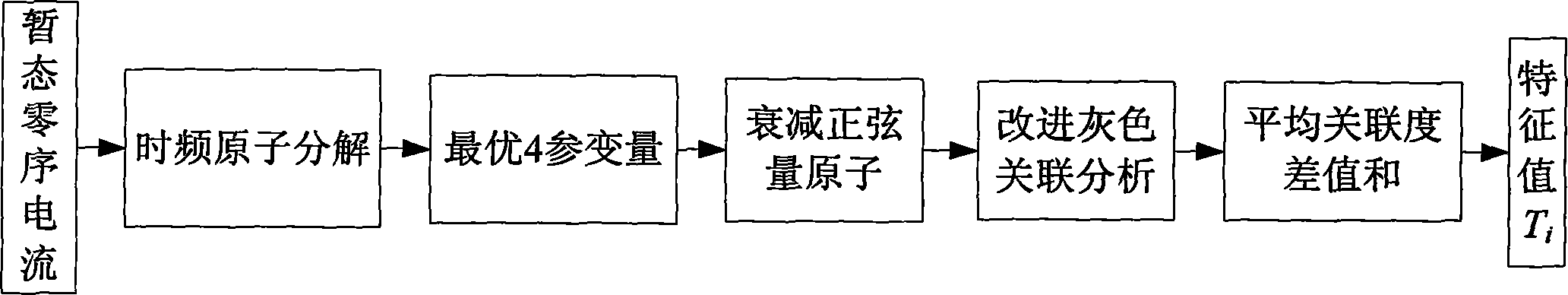
Small current earth fault line selection method for radial distribution network
A technology of small current grounding and fault line selection, applied in the fault location and other directions, can solve problems such as poor convergence, limited reliability, and inability to give exact distribution probability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
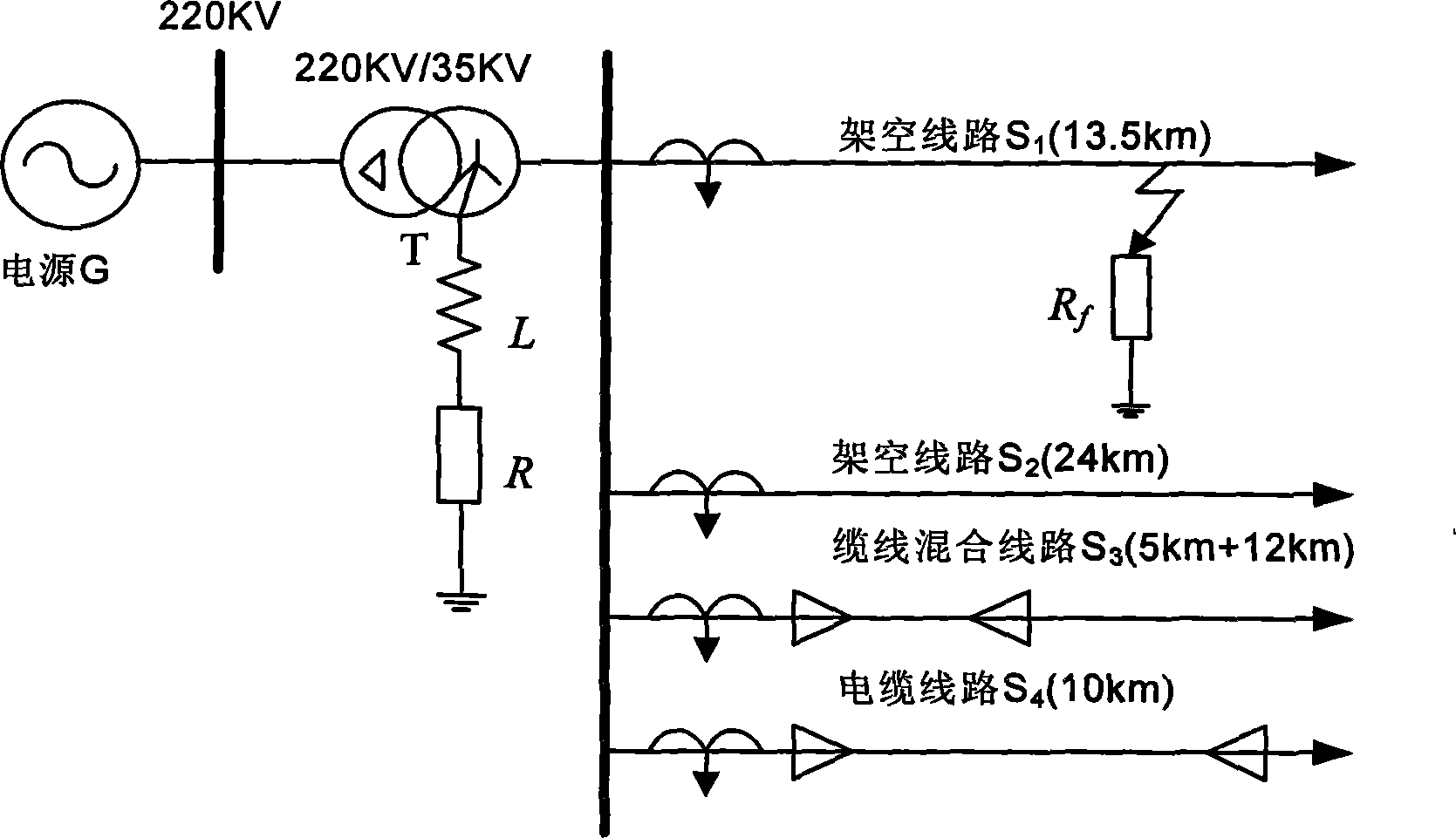
[0169] Line S 1 , S 2 It is an overhead line, the line lengths are 13.5km and 24km respectively, and the line positive sequence parameter is R 1 = 0.17Ω / km, L 1 = 1.2mH / km, C 1 =9.697nF / km, the zero sequence parameter is R 0 = 0.23Ω / km, L 0 =5.48mH / km, C 0 = 6nF / km; line S 4 It is a cable line with a length of 10km and the positive sequence parameter of the line is R 1 = 0.193Ω / km, L 1 =0.442mh / km, C 1 =143nF / km, the zero sequence parameter is R 0 =1.93Ω / km, L 0 =5.48mH / km, C 0 = 143nF / km. Line S 3 It is a cable-line hybrid line, in which the cable length is 5km, and the overhead line length is 12km; the overcompensation degree of the arc suppression coil is 10%, and the inductance value of the arc suppression coil is calculated to be 1.574H. Among them, the resistance value of the arc suppression coil is 10% of the reactance value, which is calculated as 48.576Ω. Simulation model such as image 3 shown.
[0170] take line S 1 When a single-phase ground fault...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com