Remotely-excited fluorescent polycarbonate composite material and preparation method thereof
A polycarbonate, remote excitation technology, applied in the field of polymer fluorescent materials, can solve problems such as energy dissipation, slow progress, and technical difficulty, and achieve the effects of extending service life, delaying color temperature shift, and reducing maintenance costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
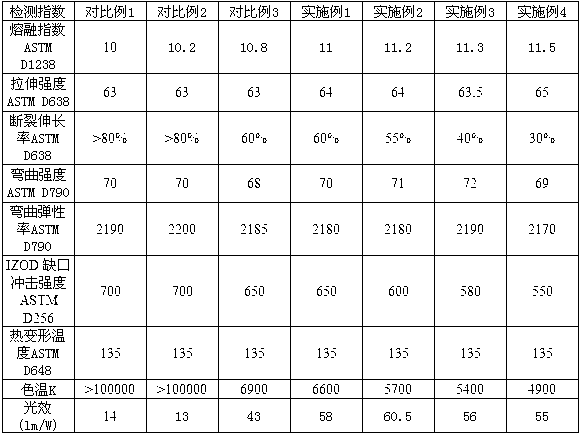
Embodiment 1
[0051] Step 1: Mix 0.5 parts of silicone diffusing agent, 0.1 parts of (2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl)phosphite triester, 0.1 parts of octadecyl-3,5-bis(1,1- Dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxyphenylpropionate, 0.2 parts of octadecanoic acid-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-[[(1-oxoctadecyl)oxy]methyl ]-1,3-propanediyl ester and 0.4 parts of 2-hydroxy-4-n-octyloxybenzophenone were stirred with a high-speed mixer at a stirring speed of 100 r / min for 2 minutes.
[0052] Step 2: Put 95.7 parts of polycarbonate and the material mixed in step 1 together in a high-speed mixer and stir evenly. The stirring speed is to start stirring at a speed of 20r / min for 1min, and then stir at a speed of 100r / min for 1min. Stir for 1 min at a speed of 20 r / min.
[0053] Step 3: Add the homogeneously mixed material in step 2 into the main feeding method, and add 3 parts of the fluorescent powder into the twin-screw extruder through the side feeding method to extrude and granulate. The extrusion temperature of the pellet feedi...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Step 1: Mix 0.7 parts of silicone diffusing agent, 0.2 parts of (2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl)phosphite triester, 0.2 parts of octadecyl-3,5-bis(1,1- Dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxyphenylpropionate, 0.1 parts of octadecanoic acid-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-[[(1-oxoctadecyl)oxy]methyl ]-1,3-propanediyl ester and 0.3 parts of 2-hydroxy-4-n-octyloxybenzophenone were stirred with a high-speed mixer at a stirring speed of 100 r / min for 2 minutes.
[0056] Step 2: Put 94.4 parts of polycarbonate and the material mixed in step 1 together in a high-speed mixer and stir evenly. The stirring speed is to start stirring at a speed of 30r / min for 2min, and then stir at a speed of 150r / min for 2min. Stir at a speed of 30r / min for 2min.
[0057] Step 3: Add the homogeneously mixed material in step 2 into the main feeding method, and add 4 parts of the fluorescent powder into the twin-screw extruder through the side feeding method to extrude and pelletize. The extrusion temperature of the pellet feeding...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Step 1: Mix 0.9 parts of silicone diffusing agent, 0.1 parts of (2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl)phosphite triester, 0.1 parts of octadecyl-3,5-bis(1,1- Dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxyphenylpropionate, 0.2 parts of octadecanoic acid-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-[[(1-oxoctadecyl)oxy]methyl ]-1,3-propanediyl ester and 0.5 parts of 2-hydroxy-4-n-octyloxybenzophenone were stirred with a high-speed mixer at a stirring speed of 200 r / min for 3 minutes.
[0060] Step 2: Put 96 parts of polycarbonate and the material mixed in step 1 together in a high-speed mixer and stir evenly. The stirring speed is to start stirring at a speed of 40r / min for 3 minutes, and then stir at a speed of 200r / min for 3 minutes. Stir at a speed of 40r / min for 3min.
[0061] Step 3: Add the homogeneously mixed material in step 2 through the main feeding method, and add 4.5 parts of the fluorescent powder into the twin-screw extruder through the side feeding method to extrude and granulate. The extrusion temperature of the p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com