Water-in-oil emulsion and method of producing the same
A manufacturing method and emulsification technology, which are applied in food science, edible oil/fat, edible oil/fat, etc., can solve the problems of easy separation of water phase and poor emulsion stability, and achieve the effect of excellent emulsion stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~6
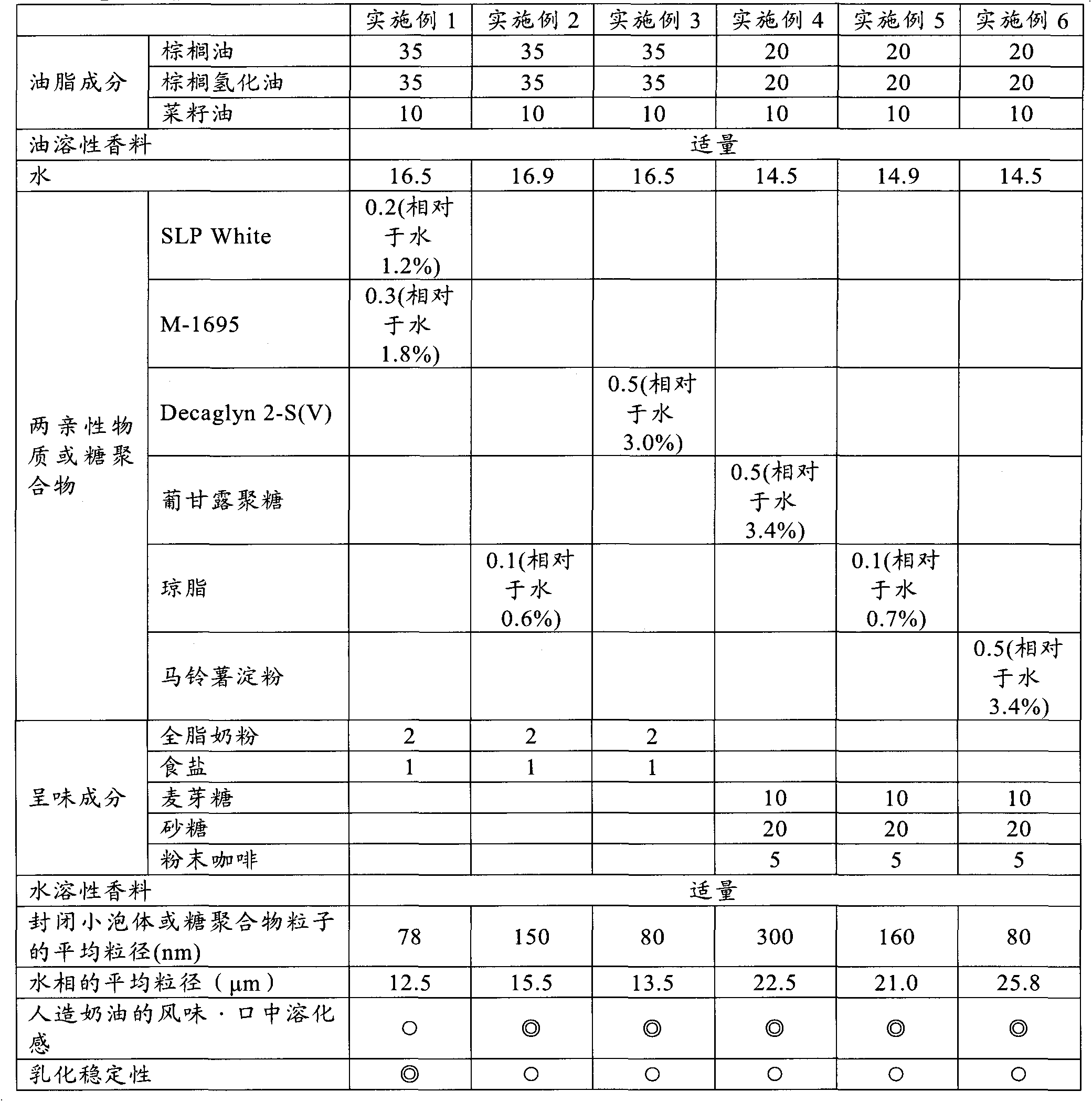
[0058] According to the compounding shown in Table 1 (the unit in the table is mass %), margarine was manufactured. Specifically, the oil phase was prepared by placing a mixture of fat and oil components shown in Table 1 at 70°C. In addition, the water phase is obtained by adding an amphiphilic substance or sugar polymer to water to form a hydrated state, and at 90°C, the hydrated amphiphilic substance or sugar polymer molecules are formed into particles dispersed at least partly. , Temporarily cooled to 20°C, added taste ingredients and water-soluble flavors, and heated again at 70°C to dissolve it. Stir and mix the water phase and the oil phase with a homomixer, and cool and solidify with a Perfector to obtain margarine. It should be noted that SLP White in Table 1 is soybean phospholipid (made by True Lecithin Co., Ltd.), M-1695 is sucrose fatty acid ester (made by Mitsubishi Chemical Food Co., Ltd.), and Decaglyn 2-S(V) is polyglycerol fat Ester (manufactured by Nikko Che...
Embodiment 7~14、 comparative example 5~6
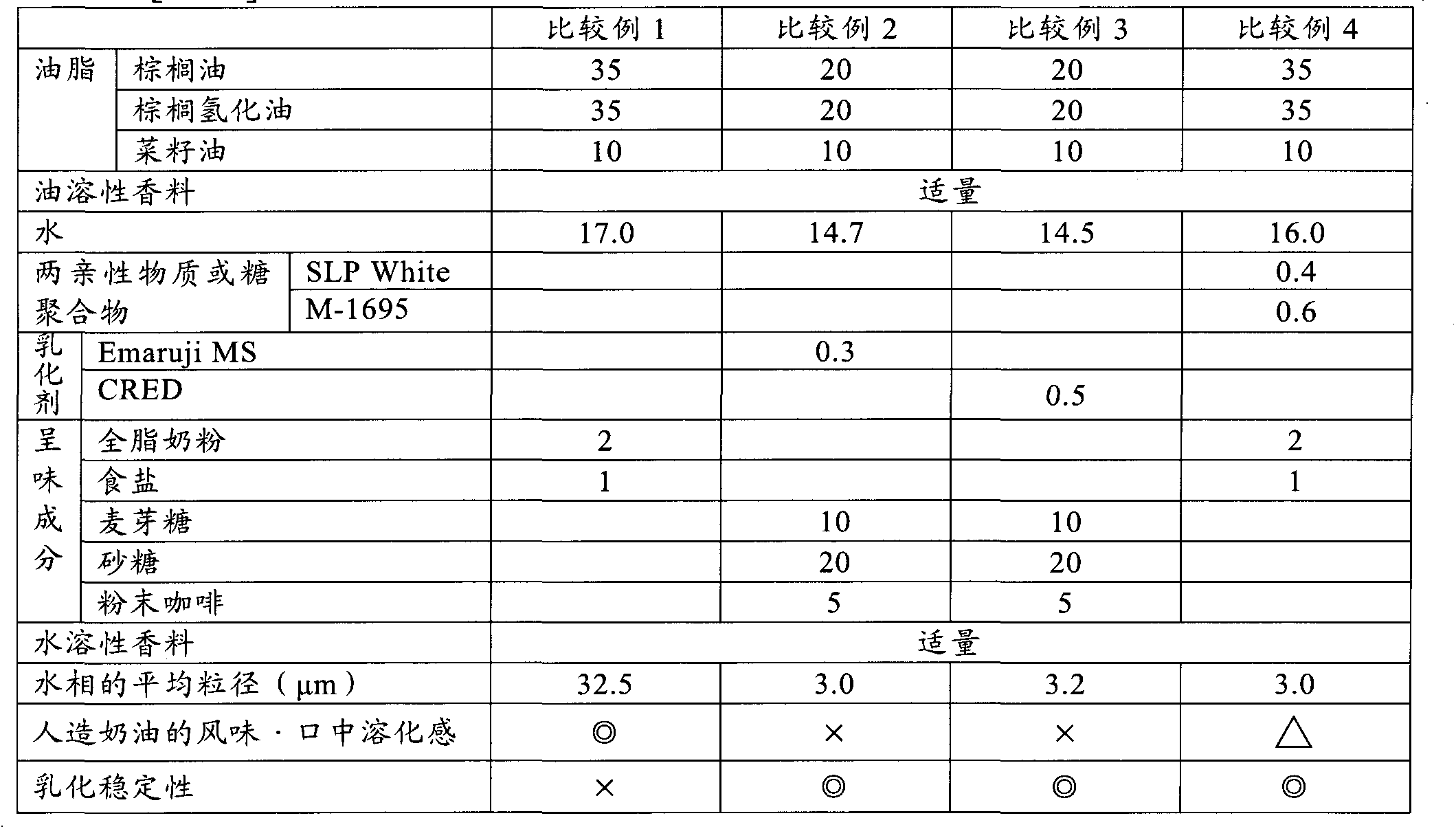
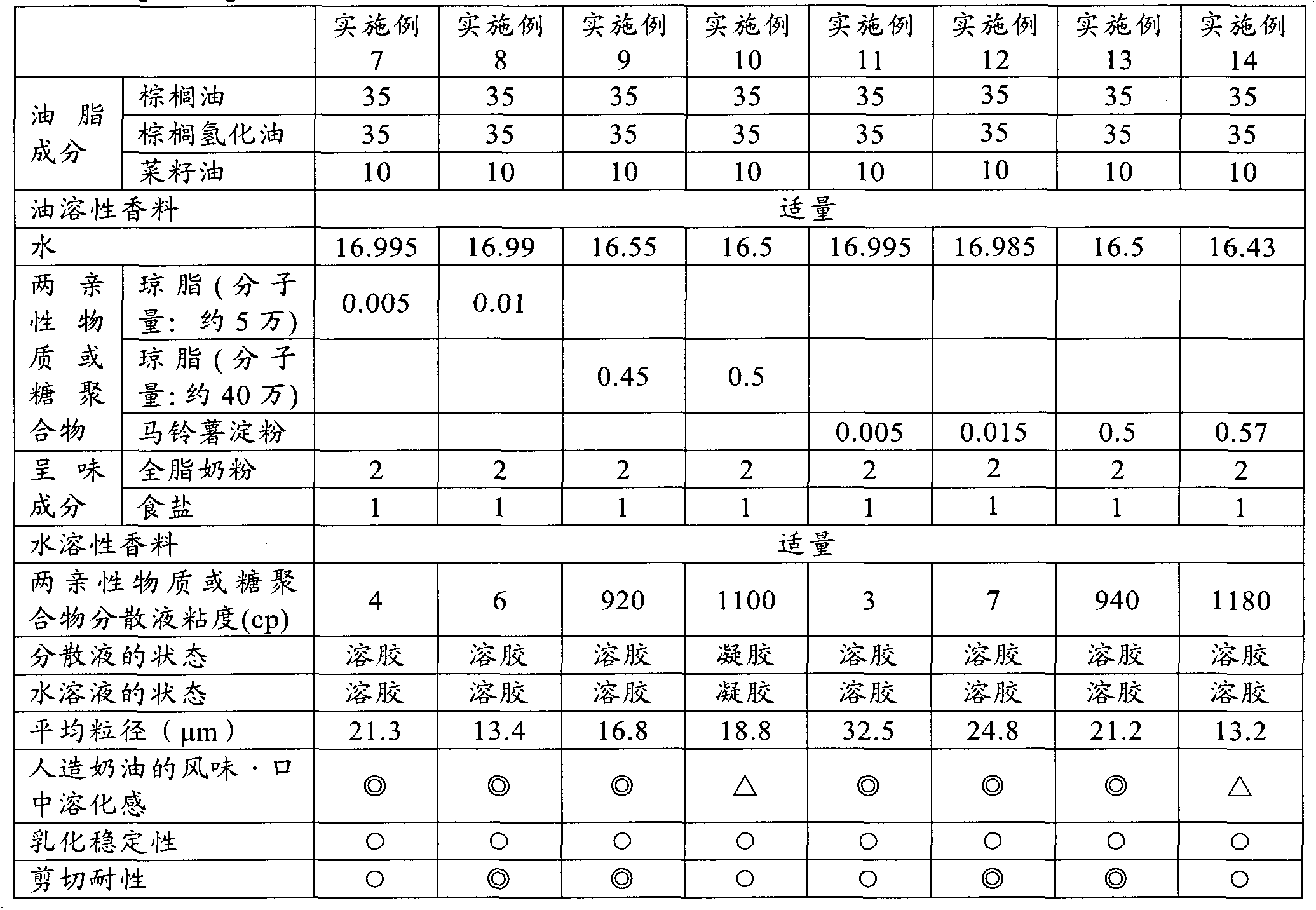
[0080] Except for the compounding shown in Tables 3 and 4, W / O type emulsions were prepared in the same procedure as in Examples 1 to 6 and Comparative Examples 1 to 4. The determination of the sol / gel state of the aqueous solution is as follows: In each example, a substance dispersed into particles from at least a part of a hydrated amphiphilic substance or sugar polymer molecule at 90° C. It is collected at the time when the temperature reaches 30°C during the cooling process and the time when the aqueous solution becomes 30°C after dissolving the flavor components and water-soluble fragrances. After standing at 30°C for 1 hour, the container will be fluid when tilted The case was judged to be a sol state, and the case of no fluidity was judged to be a gel state. The viscosity of the dispersion was measured as follows. That is, in each example, at least a part of the hydrated amphiphilic substance or sugar polymer molecule was formed into particles dispersed at 90°C, and the ...
Embodiment 15 and 16
[0088] Except for the compounding and cooling temperature shown in Table 5, the same procedure as in Examples 1 to 6 was followed to prepare W / O type emulsions.
[0089] [table 5]
[0090]
[0091] As shown in Table 5, after the closed vesicles or sugar polymer particles are formed, the cooling temperature is set to 35°C, thereby obtaining a W / O emulsion with better shear resistance compared with the case of 45°C. .
[0092] It should be noted that, in the examples and comparative examples of the present application, the amphiphilic substance or sugar polymer is added in advance to the water as the water phase to form particles and dispersed, and then the dispersion is mixed with the oil as the oil phase. , To obtain a W / O type emulsion, but it can also be reversed, that is, an amphiphilic substance or sugar polymer is added to the oil as the oil phase to form particles and dispersed to obtain a dispersion, or the previously obtained amphiphilic The sexual substance or sugar polyme...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com