Waste treatment method
A treatment method and waste technology, applied in the field of environmental governance, can solve the problems of not being able to treat waste at the same time, not being able to deal with sludge containing copper and nickel, and having a single treatment object
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Example 1: Waste bricks with a total copper content of 25%
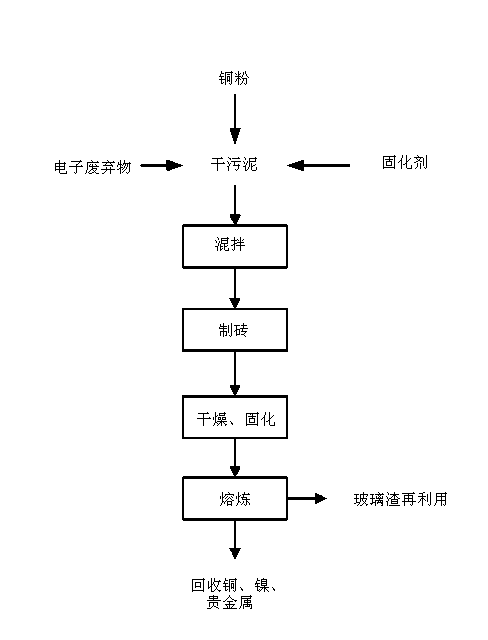
[0022] 1. Process for preparing waste bricks:
[0023] a) Ingredients: E-waste with a copper content of 20% and a particle size of less than 30 mm, copper-nickel sludge and other materials, 8% curing agent (lime: cement: water glass = 8:15:10);
[0024] b) According to the above ratio, mix 5% copper powder with the above raw materials evenly;
[0025] c) Brick making: “waste bricks” are made from mixed raw materials manually or mechanically;
[0026] d) Drying: place the finished product in a cool place to dry and solidify naturally to form a "waste brick" with compressive strength;
[0027] 2. Furnace smelting treatment process:
[0028] Put the dry and solidified waste bricks with compressive strength into the melting furnace for smelting. When the temperature in the melting furnace is 1100°C, after 3 hours of smelting, the harmful industrial waste such as sludge, circuit boards, and connecting wires will...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: Waste bricks with a total copper content of 30%
[0030] 1. Process for preparing waste bricks:
[0031] a) Ingredients: Electronic waste with a particle size of less than 30mm and copper-nickel sludge with a copper content of 15%, 5% curing agent (lime: cement: water glass = 5:20:10);
[0032] b) According to the above ratio, mix 15% copper powder with the above raw materials evenly;
[0033] c) Brick making: "waste bricks" are made from mixed raw materials manually or mechanically;
[0034] d) Drying: Place the finished product in a cool place to dry and solidify naturally to form a "waste brick" with compressive strength
[0035] 2. Furnace smelting treatment process:
[0036] Put dry and solidified waste bricks with compressive strength into a melting furnace or a blast furnace for smelting. When the temperature in the melting furnace is 1300°C, after 2.5 hours of smelting, harmful industrial waste such as sludge, circuit boards, and connecting wires w...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Waste bricks with a total copper content of 35%
[0038] 1. Process for preparing waste bricks:
[0039] a) Ingredients: materials such as electronic waste with a particle size of 30mm or less and copper-nickel sludge with a copper content of 30%, 10% curing agent (lime: cement: water glass = 3:25:10);
[0040] b) According to the above ratio, mix 5% copper powder with the above raw materials evenly;
[0041] c) Brick making: the mixed raw materials are made into "waste bricks" of appropriate size by manual or mechanical means;
[0042] d) Drying: Place the finished product in a cool place to dry and solidify naturally to form a "waste brick" with compressive strength
[0043] 2. Furnace smelting treatment process:
[0044] Put dry and solidified waste bricks with compressive strength into a melting furnace or a blast furnace for smelting. When the temperature in the melting furnace is 1400°C, after 2 hours of smelting, harmful industrial waste such as slu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com