Pure entire foetal genome DNA isolation method
A whole-genome, fetal technology, applied in the medical field, can solve the problems of unidentified fetuses, amniotic membrane rupture, intrauterine death, etc., and achieve the effects of accurate and reliable diagnosis results, short life cycle, and large storage capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1, Separation and Obtaining Pure Fetal Complete Genome
[0031] 1.1. Separation of nucleated red blood cells from maternal peripheral blood
[0032] Take 10ml of peripheral venous blood from mothers (pregnant women) from 9 to 38 weeks of pregnancy, anticoagulate with 4mmol / L EDTA, and then dilute 1:1 with phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH7.4). In a 15ml Falcon centrifuge tube, add 5ml cell separation solution (Sigma Company), slowly add 10ml of the above-mentioned diluted pregnant woman's blood along the wall of the centrifuge tube, so that the blood is covered in the cell separation solution Centrifuge at 400×g for 30 minutes at room temperature. absorbed in plasma and The mononuclear cell layer in between was washed once with PBS buffer (containing 5mmol / L EDTA and 0.5% BSA by volume fraction), approximately every 10 7 A mononuclear cell suspension was prepared by adding 80 μL of PBS buffer (pH 7.4) to each cell.
[0033] Add CD71 immunomagnetic beads...
Embodiment 2-6
[0047] Embodiment 2-6, application
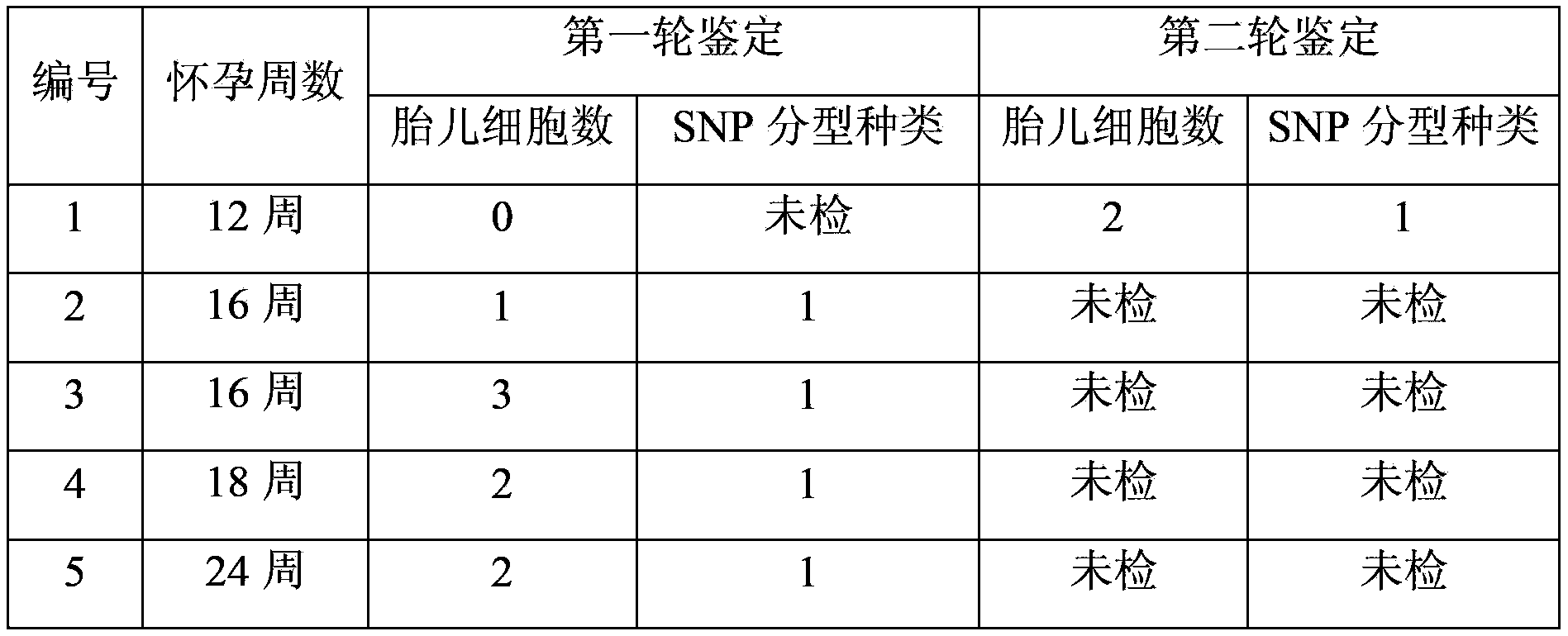
[0048] According to the method described in Example 1, 5 pregnant women who were pregnant for 12-24 weeks were selected, and 20 ml of peripheral blood from the pregnant women were respectively collected to separate nucleated red blood cells. 10 nucleated erythrocytes isolated from each pregnant woman were selected for whole-genome amplification, and then individual identification was carried out with the mother's somatic cells as a control to determine the fetal genome in the amplified genome. Among them, 4 pregnant women identified 1 -3 fetal cells, 1 pregnant woman was not detected for the first time. Another 10 nucleated erythrocytes were taken from the undetected pregnant woman for the second round of whole-genome amplification and identification, and 2 of them were found to be fetal cells. The above 5 volunteers only identified the SNP type of one fetus, which means that there is only one fetus. Since then, the fetuses have been born ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com