Blood separation system and method for a dry test strip
A technology for test strips and blood, applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, specific-purpose bioreactors/fermenters, analytical materials, etc., can solve problems such as limited production needs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
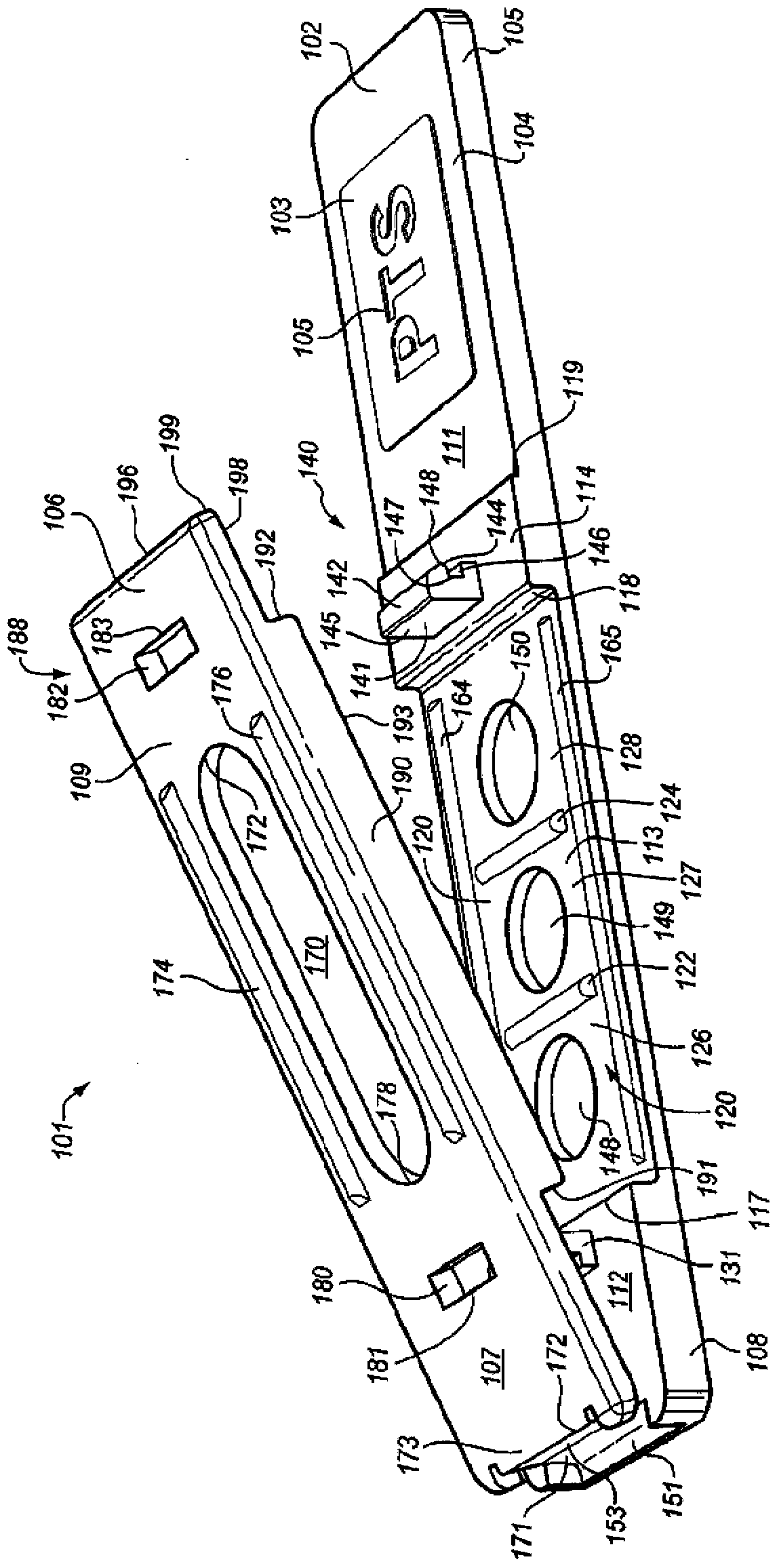
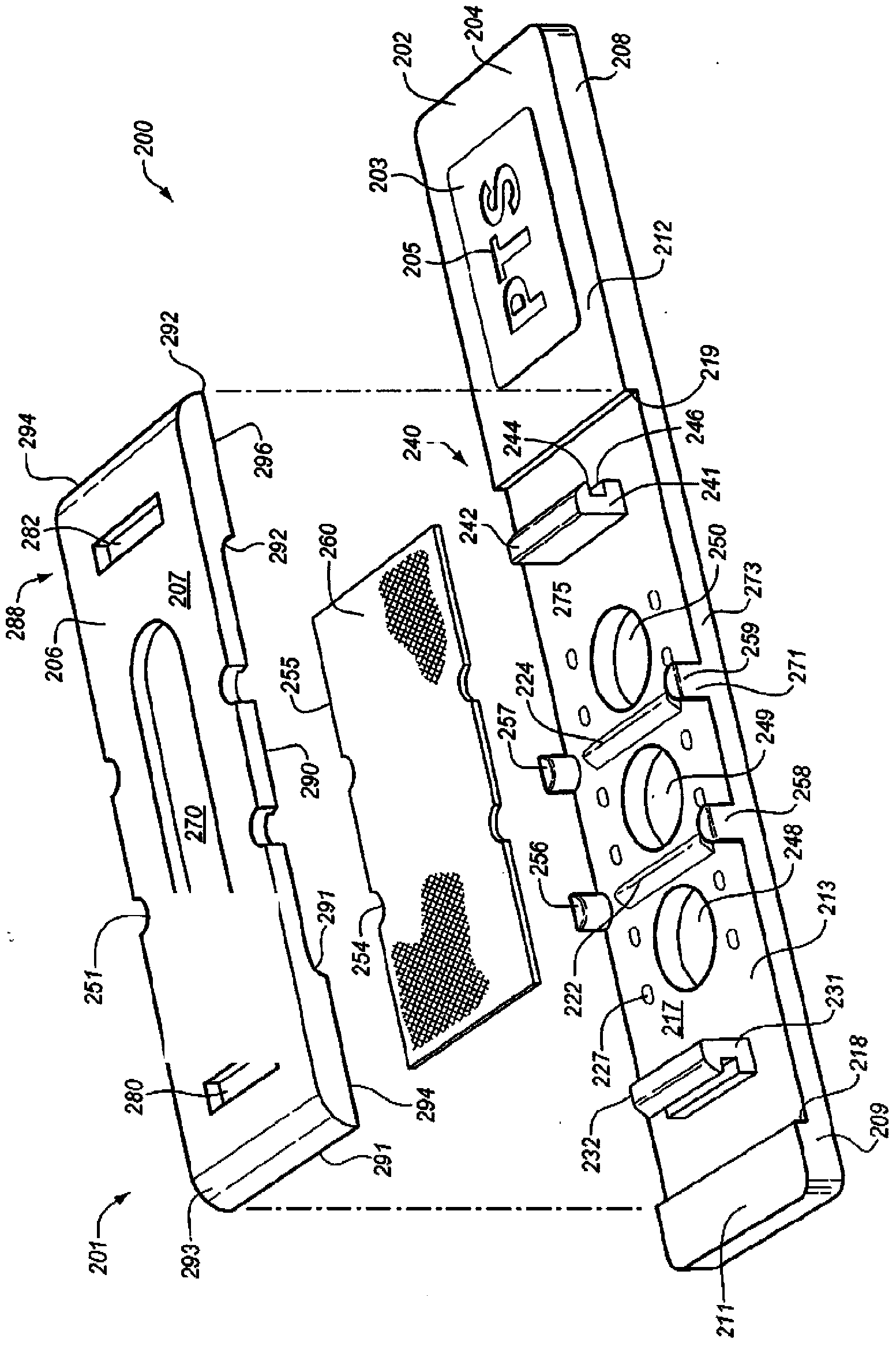
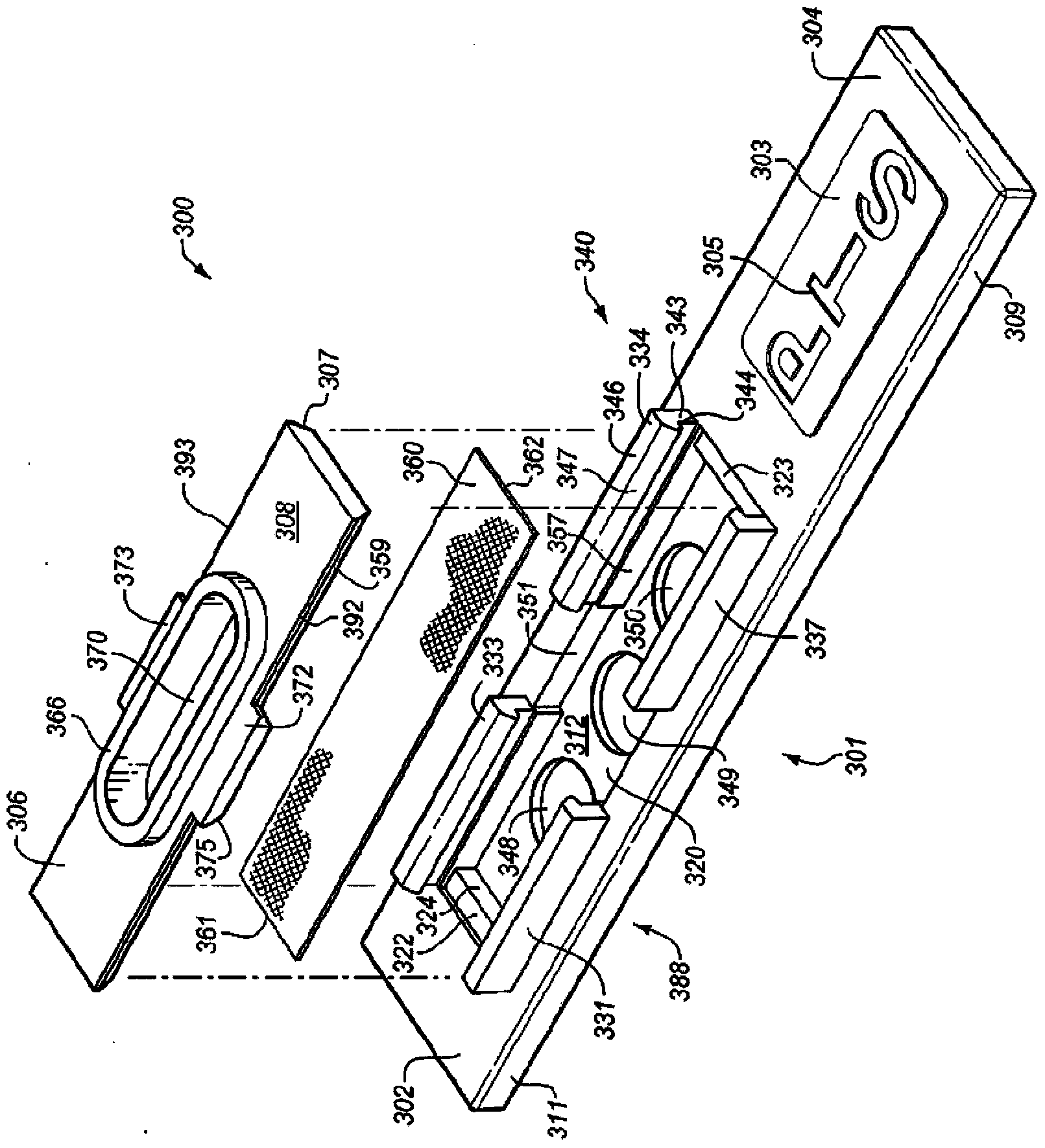
[0027]Embodiments include the use of PHA-P lectin (phase bean agglutinin) to slow the flow of red blood cells. The concentration of PHA-P was initially 100mg / 100ml solution, and then decreased to 50mg / 100ml because D-23 slowed down the plasma flow. Applicants note that D-23 has never been used as an erythrocyte separation layer. D-23 is strongly hydrophobic, and thus the sample does not readily penetrate D-23. To facilitate sample flow, the D-23 layer must be made more hydrophilic. Applicants have tested various other red blood cell separation layers for analyte strips, but none provided the performance of the chemically enhanced D-23 layer described in this application. Separation layers attempted include: Whatman's Fusion5, Whatman's VF2, Ahlstrom Grade142 and Ahlstrom Grade144. When thus treated, other borosilicate glass fiber layers with similar properties will exhibit similar performance as described herein.
[0028] To increase the hydrophilicity of D-23, polyvinyl a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com