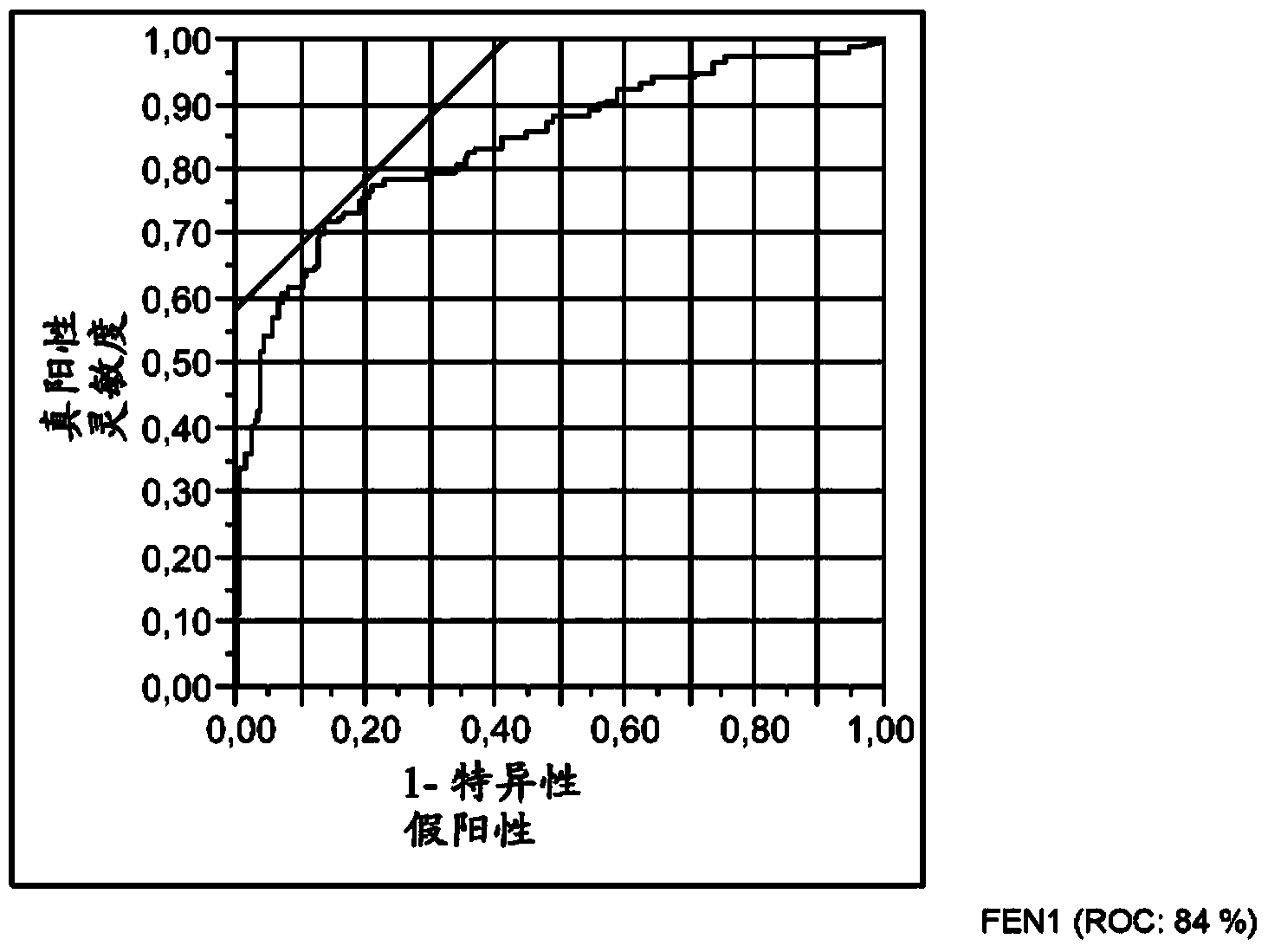
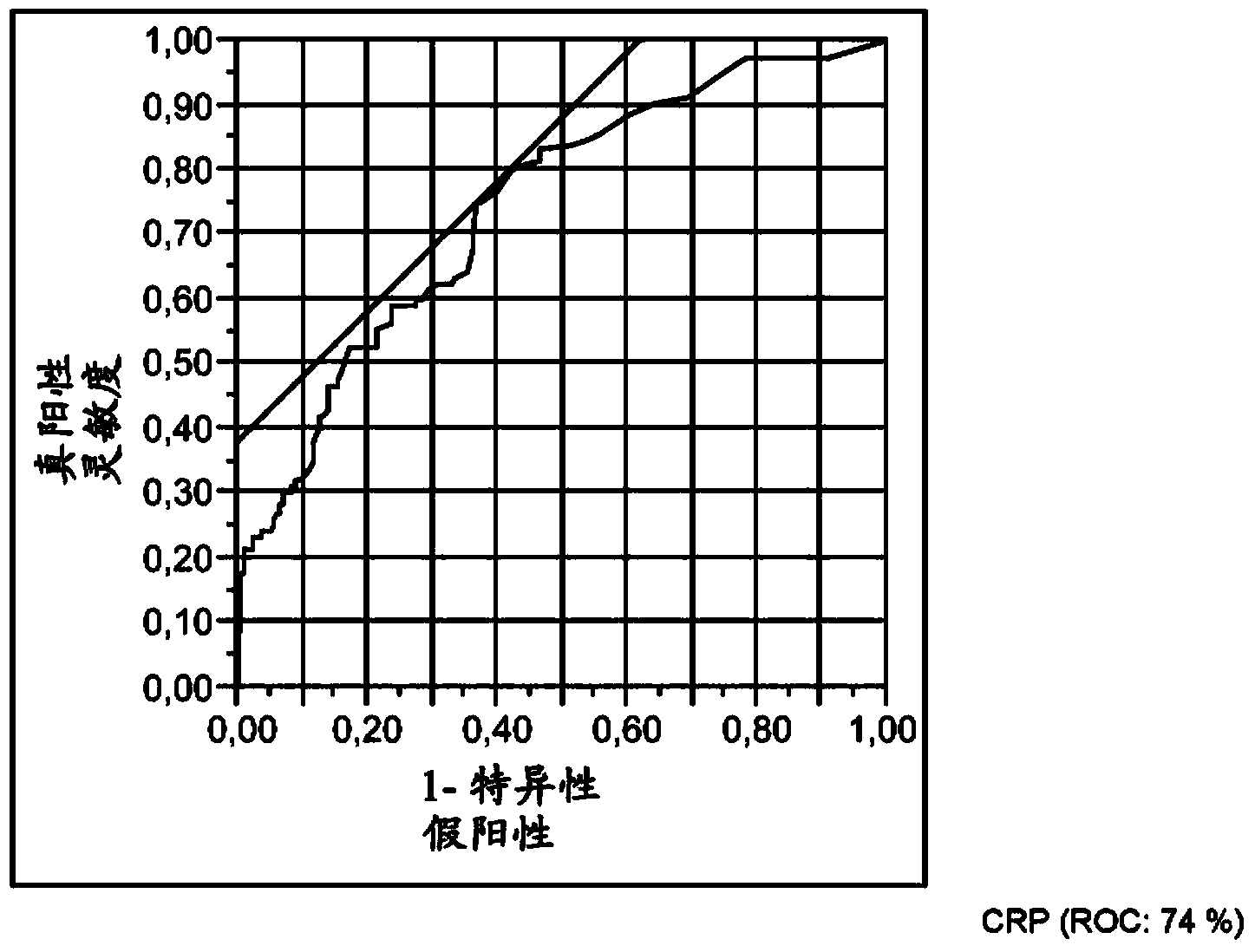
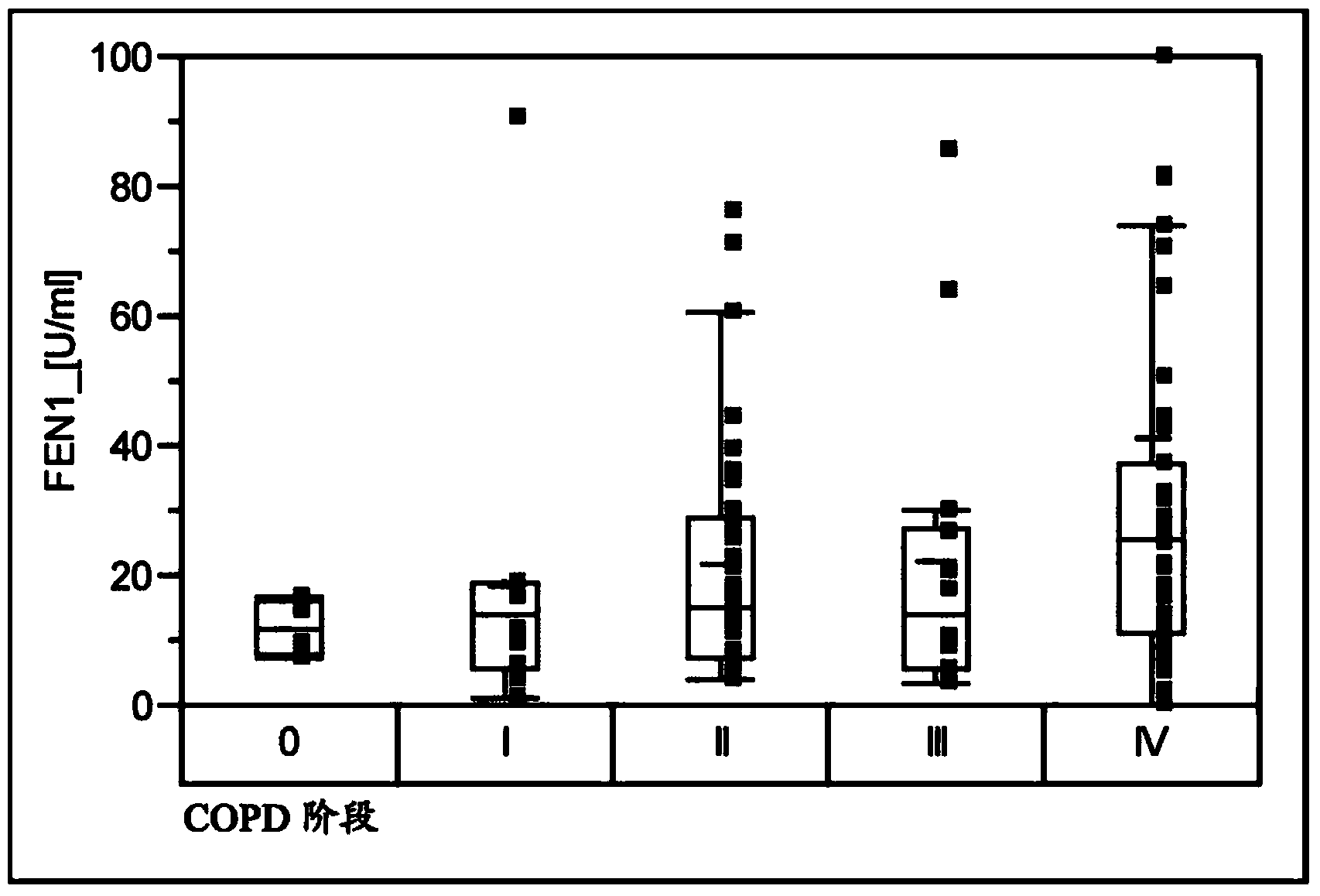
Fen1 as marker for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (copd)
By measuring the protein FEN1 concentration in body fluid samples, it solves the problem in the existing technology that COPD evaluation is expensive and relies on patient cooperation, achieves early diagnosis and the ability to distinguish COPD from other respiratory diseases, and provides an economical and reliable diagnostic method. .
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0219] Example 1: COPD Study Population
[0220] Source of serum samples:
[0221] To identify COPD-specific proteins as potential diagnostic markers of COPD, serum samples were derived from well-characterized COPD patients (according to the ATS classification system in Table 1) in a national multicenter study. From each sample donor, spirometry was performed. Pulmonary function, other diagnostic tests, and cause, diagnosis, and comorbidities of transferal were documented in a dedicated case report form (CRF). COPD samples have been evaluated in comparison to control samples obtained from Control Groups 1-4, as shown in Table 2.
[0222] Serum sample preparation:
[0223]Serum samples were collected into serum tubes and allowed to clot for at least 60 minutes and up to 120 minutes at room temperature. After centrifugation (10 min, 2000 g), the supernatant was divided into 1 ml aliquots and frozen at -70°C. Samples were thawed, aliquoted into smaller volumes suitable for t...
Embodiment 21
[0224] Example 2.1: Generation of antibodies against the marker protein FEN1
[0225] Generation of polyclonal antibodies against the marker protein FEN1 for further use of the antibodies to measure serum and plasma levels of FEN1 or concentrations in other bodily fluids by immunodetection assays such as Western blot and ELISA.
[0226] Recombinant protein expression in E. coli:
[0227] To generate antibodies against FEN1, the recombinant antigen was generated in E. coli: therefore, PCR was performed from a full-length cDNA clone (obtained from the German Resource Center for Genome Research (RZPD, Berlin, Germany)) using the following primers Amplification of the FEN1 coding region.
[0228] Forward primer (SEQ ID NO:8):
[0229] 5'-cacaca caattg attaaagaggagaaattaactATGAGAGGATCGCATCACCATCACCATCACATTGAAGGCCGTGGAATTCAAGGCCTGGCC-3' (MunI site is underlined, coding nucleotides are capital letters),
[0230] Reverse primer (SEQ ID NO:9):
[0231] 5'-acgtacgt aagctt TCATTA...
Embodiment 22
[0247] Example 2.2: CRP
[0248] The marker protein CRP was measured using a homogenous assay (Hitachi) distributed by Roche Diagnostics (Mannheim, FRG).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com