Free-range breeding method capable of promoting development of digestive organ of lamb
A technology for digestive organs and lambs, which is applied in the field of sheep feeding and grazing management, and achieves the effects of simple and easy technology, convenient use, and promotion of digestion and absorption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
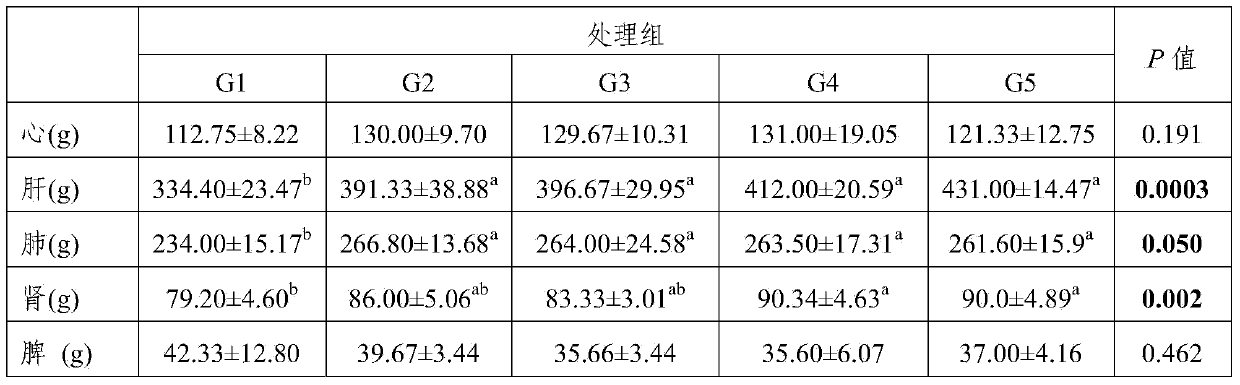
[0019] Example 1: Effects of grazing plus supplementary feeding on the development of lamb internal organs
[0020] Divide 30 weaned local fat-tailed sheep (average weight 22kg) from 3 to 4 months into 5 groups: house feeding group (G1, no grazing), 2-hour grazing group (G2, 7:00-9:00 grazing), 4-hour grazing group (G3, 7:00-11:00 grazing), 8-hour grazing group (G4, 7:00-15:00 grazing), all-day grazing group (G5, 7:00-17:00 grazing) . The trial period is from June to October. The house-feeding group was reared in captivity, fed with 550g of concentrated feed every day, and had free access to natural pastures and hay. Groups G2, G3, G4, and G5 were supplemented with 450, 300, 250, and 150 g of concentrate in 4 different pens after grazing, and they also ate grass and hay ad libitum in natural pastures. The concentrated feed is fed twice a day, and the hay is cut into 5-10cm long sections with a guillotine before feeding. All lambs were slaughtered after the grazing experime...
Embodiment 2
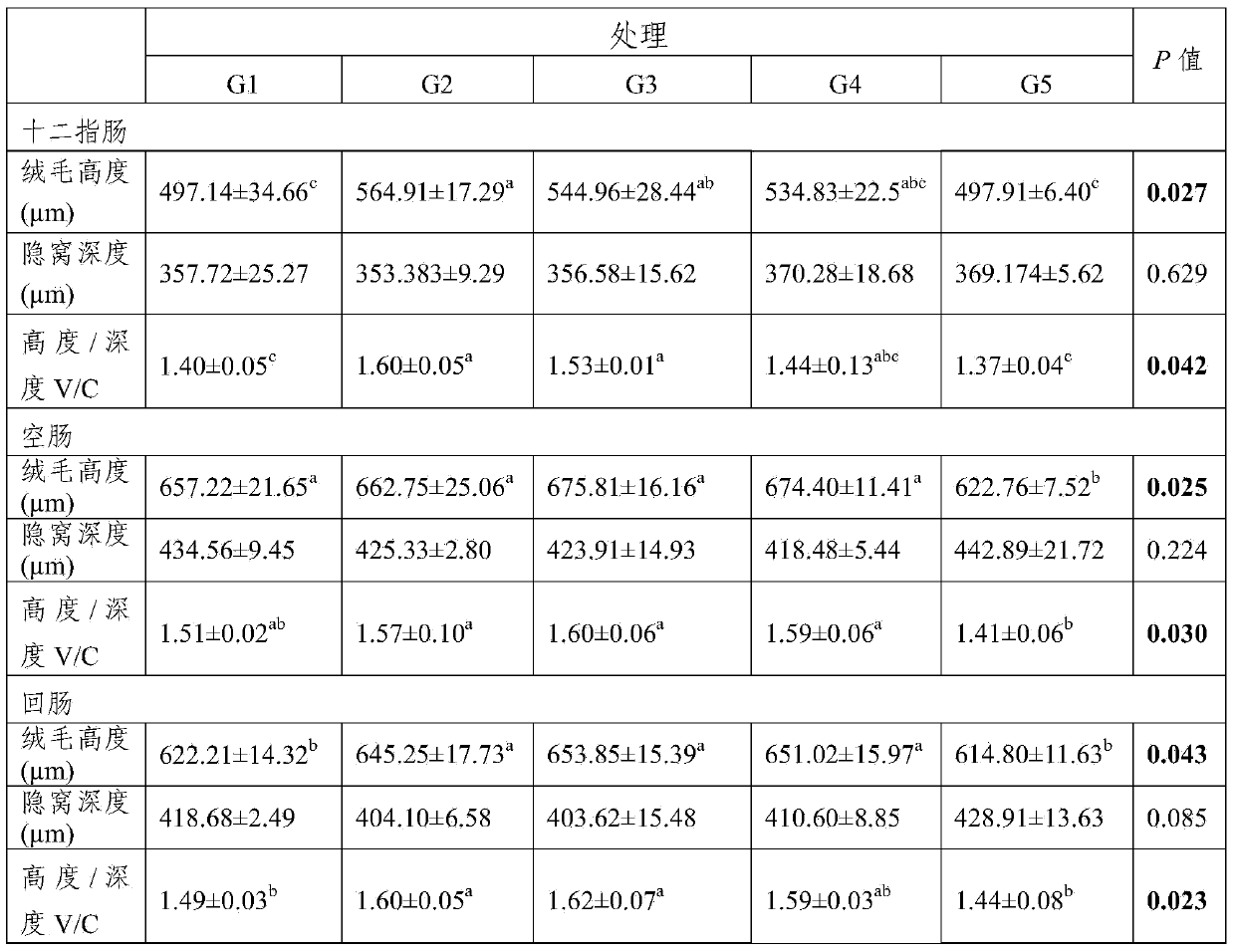
[0026] Example 2: Effects of grazing plus supplementary feeding on the development of lamb small intestinal villi
[0027] On the basis of Example 1, the small intestine samples of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum were collected at the slaughtering site to make paraffin sections according to conventional histological analysis methods, stained with HE, observed with an optical microscope, and took pictures to analyze the villus height and crypt depth . The test results show (Table 2):
[0028]The duodenal villi height and villus height / crypt depth in G2 and G3 groups were significantly higher (P0.05); the crypt depth of the ileum in the G5 group tended to be greater than that of the other groups (P=0.085). The small intestine is the main site for digestion and absorption of nutrients, and its function depends on the structure of the small intestinal mucosa (Kagnoff, Mucosal immunology: New frontiers. Immunology Today, 1996, 17(2):57–59.), such as villi and crypts, Mucous memb...
Embodiment 3
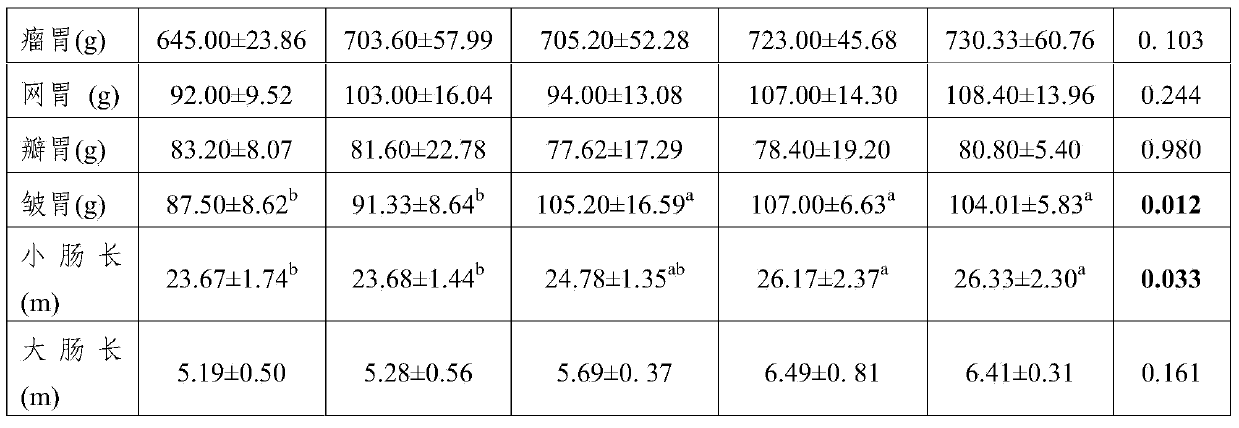
[0031] Example 3: Effect of grazing plus supplementary feeding on feed digestibility of lambs
[0032] On the basis of Example 1, the excrement volume and dry matter digestibility (DMD) of lambs in each group were analyzed through digestion tests, and the test results showed (Table 4):
[0033] The excretion of DM in feces was not significantly different among the groups (P>0.05), but the DMD in the house-fed, G2, and G3 groups was significantly higher than that in the G5 group (P=0.021), while there was no significant difference between the house-fed group and the G2, G3 groups. Significant difference (P>0.05), there was no significant difference between G4 and G5 groups (P>0.05). This example proves from the perspective of dietary DM digestibility that grazing for 2-4 hours is more conducive to the digestion and utilization of nutrients than grazing for 8-12 hours. Combining the weight of digestive organs, the development of small intestinal villi and feed digestibility, gr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com