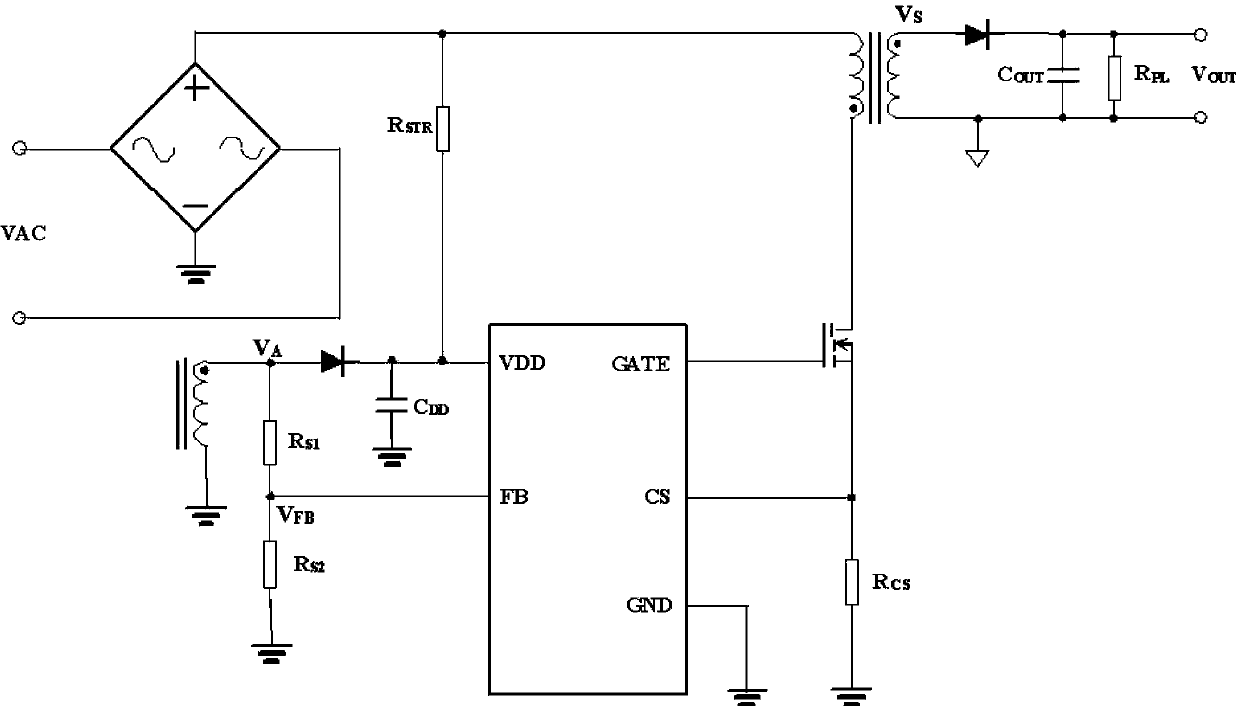
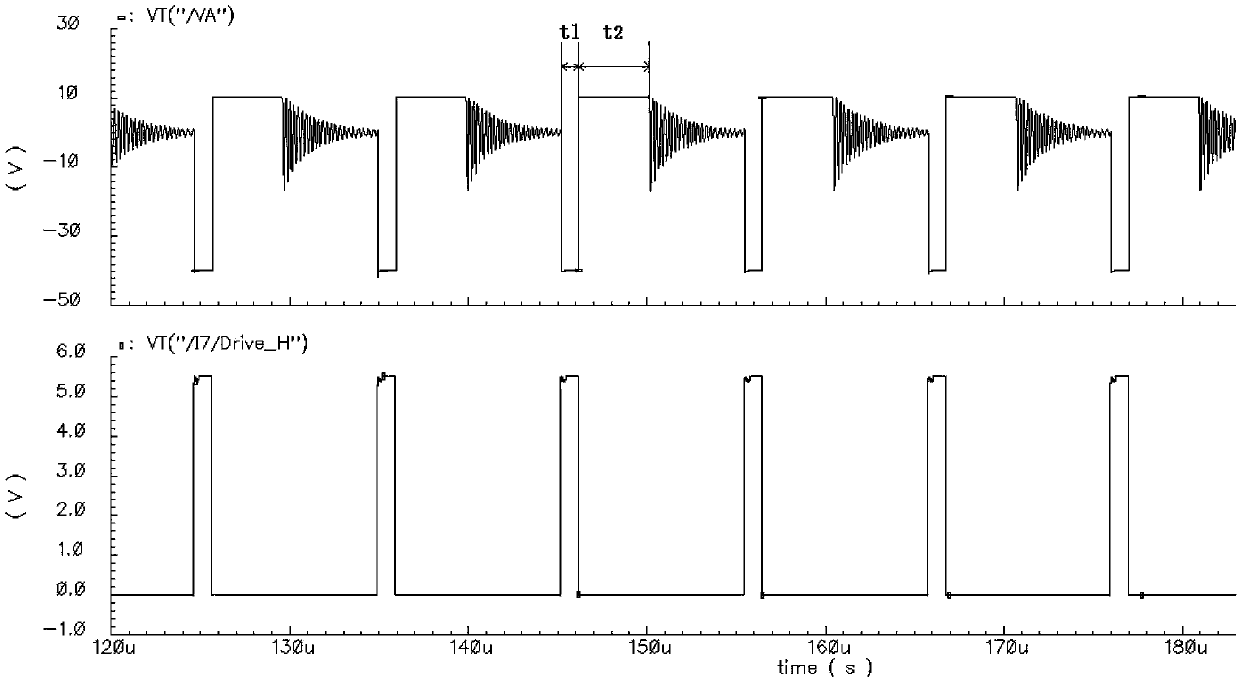
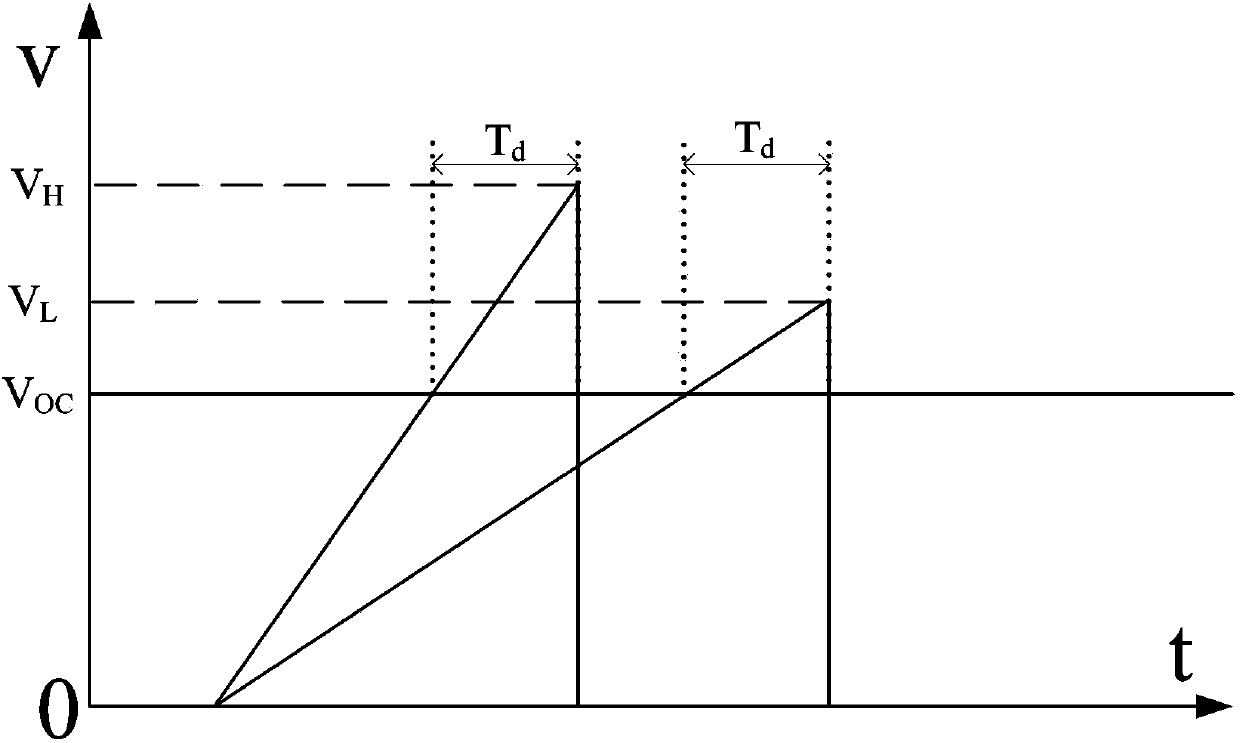
Input voltage sampling compensating circuit
A compensation circuit and input voltage technology, applied in the field of compensation circuits, can solve the problems of large temperature coefficient and affect sampling accuracy, and achieve the effects of good compensation effect, low power consumption, and simple power supply peripheral circuits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] A high-precision input voltage sampling circuit with self-compensation, comprising a first resistor R1, a second resistor R2, an operational amplifier amp, a bias resistor R2, a first logic NOT gate not1, and a first N-channel MOS transistor MN1 ,, the first transistor Q1, the second transistor Q2, the first P-channel MOS transistor MP1, the second P-channel MOS transistor MP2, the third P-channel MOS transistor MP3, and the P-type MOS transistor MP1, MP2 and MP3 form a feed-forward current mirror current mirror.
[0042] Such as Figure 7 Shown is the circuit diagram of the first embodiment of the present invention: VCC is the low-voltage power supply terminal of the chip; the output terminal of the bias current source Iref, the first port of the resistor R1, the drain terminal of the PMOS transistor MP2, and the positive input of the operational amplifier The terminals are connected together to form the first node; the second port of the resistor R1, the collector an...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Such as Figure 8 Shown is the circuit diagram of the second embodiment of the present invention: VCC is the low-voltage power supply terminal of the chip; the output terminal of the bias current source Iref, the first port of the resistor R1, the drain terminal of the PMOS transistor MP2, and the positive input of the operational amplifier The terminals are connected together to form the first node; the second port of the resistor R1, the collector and the base of the transistor Q1 are connected together to form the second node; the output terminal of the operational amplifier, the input negative terminal of the operational amplifier, and the input of the transmission gate T1 The ports are connected together to form the ③ node; the output terminal of the logic NOT gate not1, the input terminal of the logic NOT gate not2, the gate of the N-channel MOS transistor MN1, and the selection input negative terminal of the transmission gate T1 are connected together to form the ...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Such as Figure 9 As shown, compared with the second embodiment, the difference is that the sources and substrates of the current mirror MOS transistors MP1, MP2, and MP3 are all connected to the external high-voltage power supply VDD of the chip instead of the internal low-voltage power supply VCC of the chip. The advantage of doing this is: in some applications, a relatively large feed-forward current is required, that is, the current flowing through MP1, MP2, and MP3 is relatively large, and the internal power supply VCC is generated by the step-down of the external power supply VDD. The drive capability is limited, and this creates large power supply noise on the internal power supply. If the current of the current mirror is all absorbed from the external power supply VDD, the noise generated in the internal power supply VCC is very small.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com