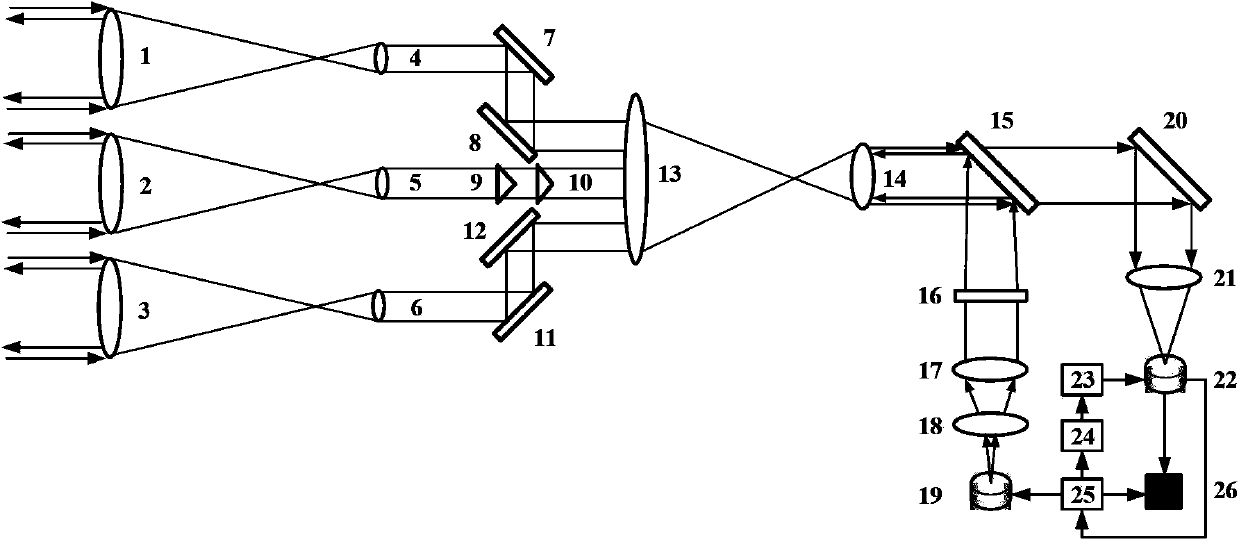
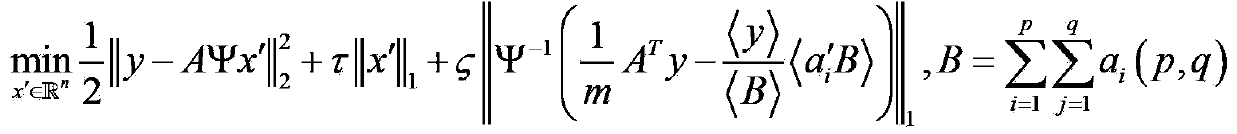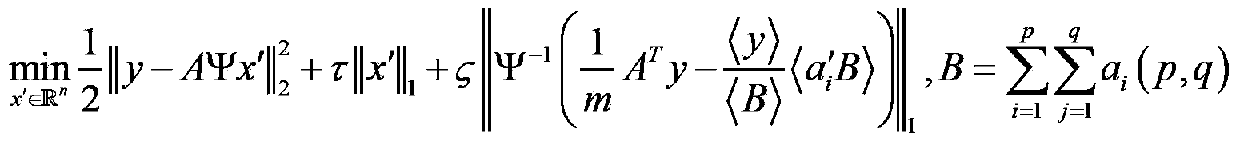Three-dimensional imaging system and method for calculating correlation flight time by means of sparse aperture compression
A sparse aperture and time-of-flight technology, applied in radio wave measurement systems, electromagnetic wave re-radiation, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of inability to balance the accuracy of spatial resolution and depth information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The present invention will be further described now in conjunction with accompanying drawing.
[0036] Before describing the present invention in detail, the concepts involved in the present invention will be introduced first.
[0037] Correlative imaging, or ghost imaging (GI), refers to the ability to generate an image of an object on an optical path that does not contain an object, and is one of the frontiers and hotspots in the field of quantum optics in recent years. The concept of ghost imaging was first demonstrated using spatially entangled photon pairs generated by parametric down-conversion. Ordinary ghost imaging, in the object arm, there is an object, but it is detected by a barrel (single pixel) detector without spatial resolution, in the reference arm, there is no object, but a spatially resolved detector is used at the same optical path as the object The detector with the ability detects the changing light field information, and the image can be obtained...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com