Lithium-ion electrode material and lithium-ion power battery
A technology for electrode materials and power batteries, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, non-aqueous electrolyte battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of low battery power density, achieve the effects of extended safety, long cycle life, and improved safety performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
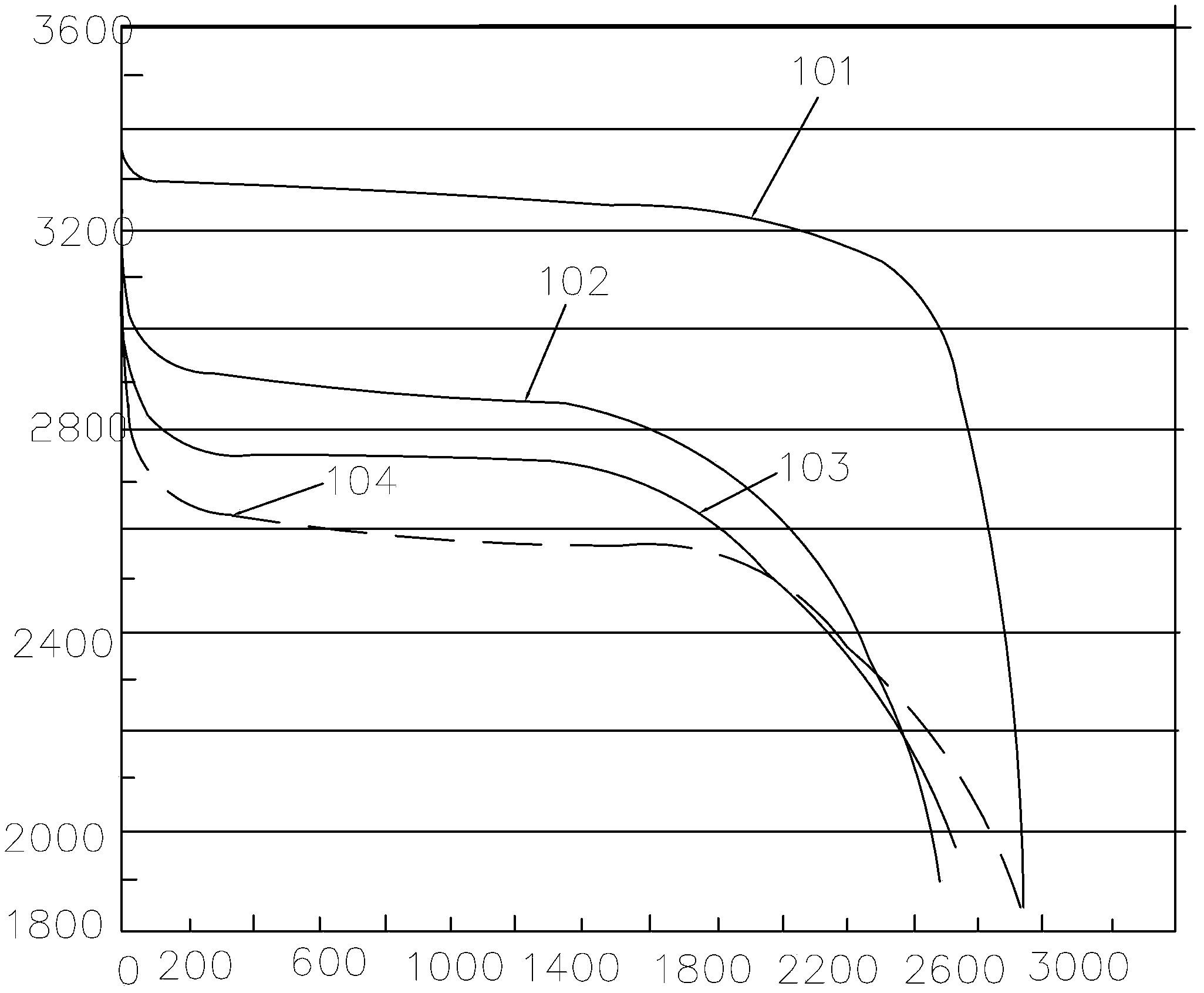
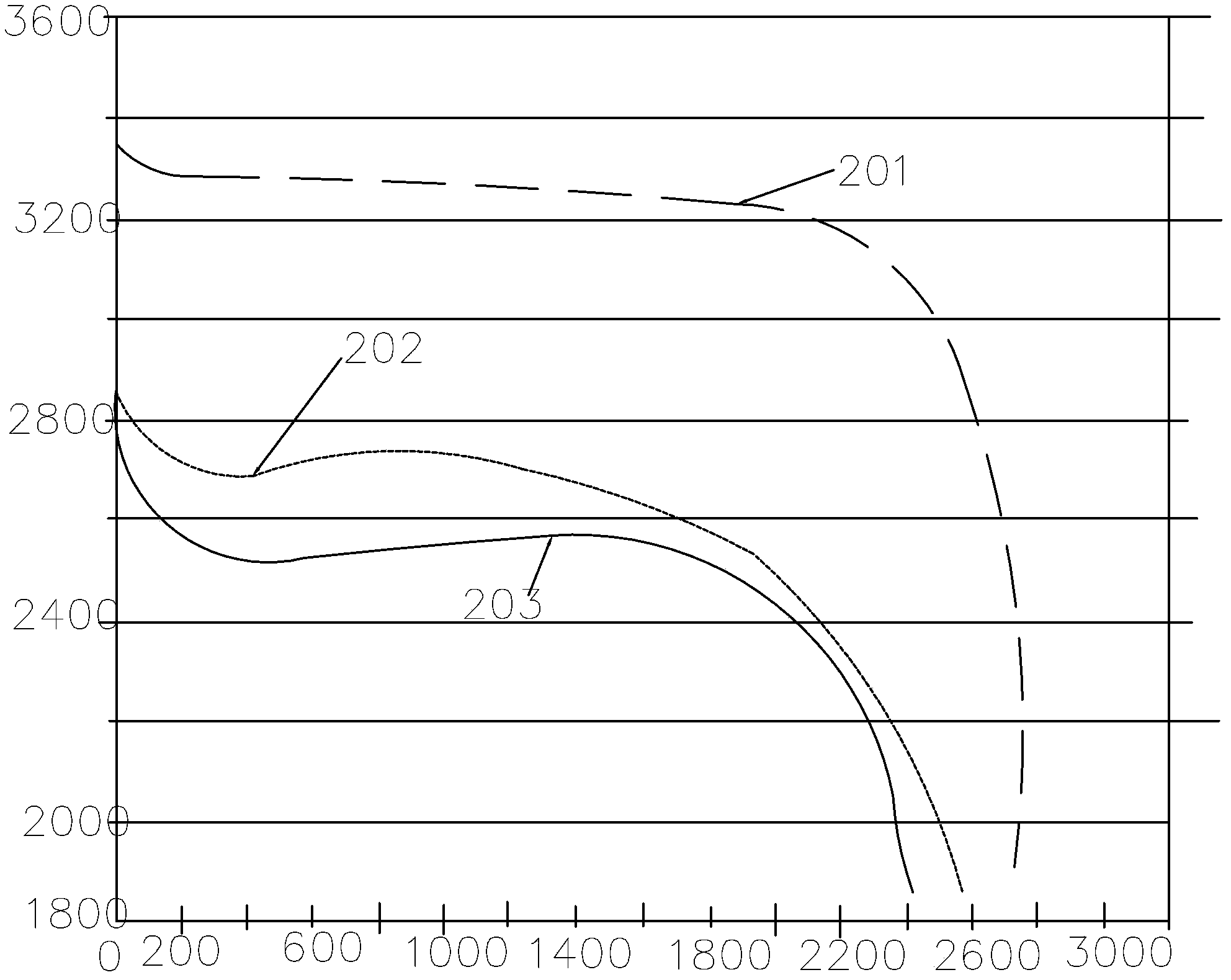
[0045] This embodiment provides a lithium-ion battery, which includes a battery core, an electrolyte, and a casing. Wherein, the electric core body and the electrolyte are packaged in the casing, and the electric core body is soaked in the electrolyte.
[0046] The cell body is composed of a positive electrode sheet, a negative electrode sheet and a separator, and the separator is spaced between any adjacent positive electrode sheet and negative electrode sheet.
[0047] The positive electrode material is respectively coated and fixed on the surface of each positive electrode sheet of the cell body, and the positive electrode material is composed of lithium iron phosphate, a conductive binder, polyvinylidene fluoride, and carbon nanotubes. The mass percentage of each component is as follows: lithium iron phosphate: 93%, conductive binder (sulfonic acid-based conductive polymer is selected): 1.5%, polyvinylidene fluoride: 2.5%, carbon nanotube: 3%.
[0048] The negative electr...
Embodiment 2
[0054] This embodiment provides a lithium-ion battery, the structure of which is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and the main difference from Embodiment 1 is that the components of the positive electrode material and negative electrode material coated on the positive electrode sheet and the negative electrode sheet are different.
[0055] The positive electrode material is composed of lithium iron phosphate, conductive binder, polyvinylidene fluoride, conductive carbon black, and carbon nanotubes.
[0056] The mass percentage of each component is as follows: lithium iron phosphate: 94%, conductive binder (select sulfonic acid-based conductive polymer): 1.0%, polyvinylidene fluoride: 2.0%, carbon nanotube: 2.5%; conductive carbon black : 0.5%.
[0057] The negative electrode material is coated and fixed on the negative electrode sheet, and the negative electrode material is composed of lithium titanate, conductive binder, polyvinylidene fluoride, conductive carbon black, and ca...
Embodiment 3
[0061] This embodiment provides a lithium ion battery, the structure of which is the same as that of Embodiment 1, and the difference from Embodiments 1 and 2 mainly lies in the different components of the positive electrode material and negative electrode material coated on the positive electrode sheet and the negative electrode sheet.
[0062] The positive electrode material is composed of lithium iron phosphate, conductive binder, polyvinylidene fluoride, conductive carbon black, and carbon nanotubes.
[0063] The mass percentage of each component is as follows: lithium iron phosphate: 95%, conductive binder: 0.5%, polyvinylidene fluoride: 1.5%, carbon nanotube: 0.5%; conductive carbon black: 2.5%.
[0064] The negative electrode material is coated and fixed on the negative electrode sheet, and the negative electrode material is composed of lithium titanate, conductive binder, polyvinylidene fluoride, conductive carbon black, and carbon nanotubes.
[0065] The mass percenta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com