Paste-like bone cement
A free-radical, monomeric technology, applied in prosthesis, surgery, tissue regeneration, etc., can solve problems such as the contribution to the mechanical stability of pasty cement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
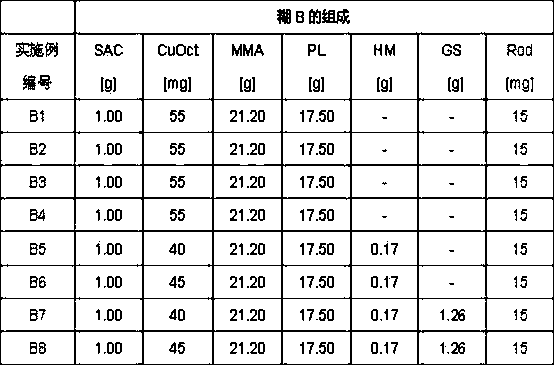
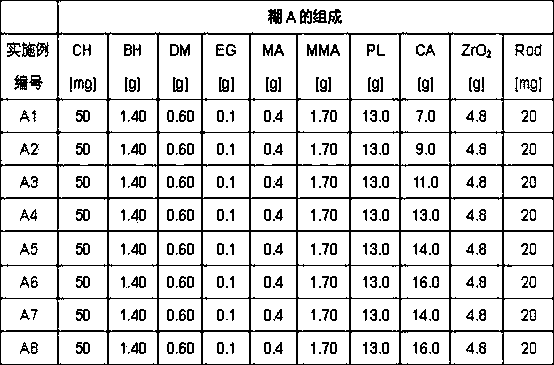
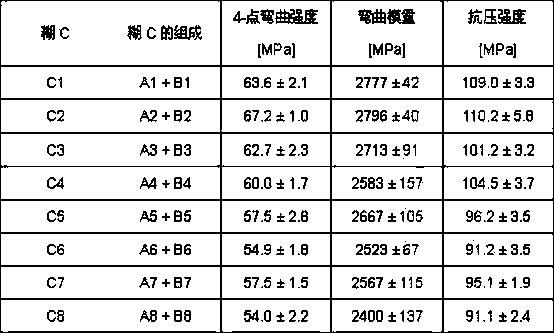
[0014] The present invention is based on the discovery that well-formed and formed bone cements can be prepared by using particulate inorganic calcium salts from molecular sieve fractions smaller than 63 μm (according to DIN 66165-1 / -2), With methyl methacrylate bone cement, that was an accident. The surprise is that the hitherto customary crosslinked polymer particles which are insoluble in methacrylate monomers can be completely or partially replaced by particulate inorganic calcium salts. Inorganic calcium salts are considerably cheaper than crosslinked polymer particles and can thus be used economically and advantageously in the production of pasty polymethylmethacrylate bone cements. Surprisingly, it was found that calcium carbonate, in particular from molecular sieve fractions smaller than 63 μm, is particularly suitable as filler.
[0015] Inorganic calcium salts such as calcium carbonate have relatively low hardness. Calcium carbonate (calcite) is therefore character...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com