Biocompatible magnetic rare earth nanoparticles, their preparation and magnetic resonance imaging applications
A technology of magnetic nanoparticles and biocompatibility, which is applied in the fields of material chemistry, nanoscience and biomedicine, can solve the problems of low colloidal stability, poor binding force, and insufficient coordination ability of nanoparticles, and achieve the goal of overcoming colloids. The effect of low stability and high crystallinity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
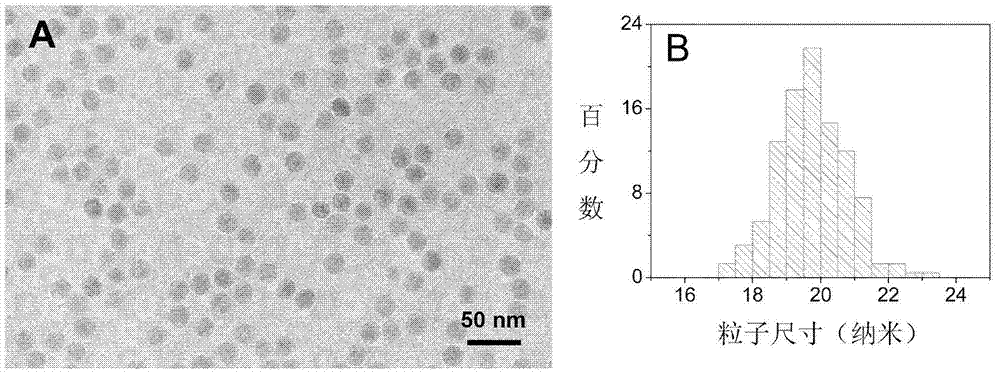
[0064] Dissolve 0.742g of gadolinium chloride hexahydrate and 6mL of oleic acid in 30mL of octadecene, then transfer the above solution into a 100mL three-necked flask, heat and dehydrate under vacuum (90°C) for 5 hours, and cool the reaction solution to room temperature. Dissolve 0.45 g of sodium hydroxide and 0.6 g of ammonium fluoride in 10 mL of methanol, and add them to the above reaction solution. The reaction was stopped after passing nitrogen gas and heating to 350°C for 10 hours. After the reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, NaGdF was precipitated with ethanol 4 The nanoparticles were washed three times, and the nanoparticles were obtained by centrifugation. The resulting crystals were dissolved in toluene and characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). figure 1 NaGdF 4 TEM photo of paramagnetic nanoparticles (A) and histogram of particle size distribution (B). It can be seen from electron microscope photos that the biocompatible magneti...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Dissolve 0.742g of gadolinium chloride hexahydrate and 6mL of oleic acid in 30mL of octadecene, then transfer the above solution into a 100mL three-necked flask, heat and dehydrate under vacuum (90°C) for 5 hours, and cool the reaction solution to room temperature. Dissolve 0.45 g of sodium hydroxide and 0.6 g of ammonium fluoride in 10 mL of methanol, and add them to the above reaction solution. The reaction was stopped after passing nitrogen gas and heating to 280°C for 10 hours. All the other operations are with embodiment 1, gained NaGdF 4 The average particle size of the nanoparticles is 14.8 nm. attached image 3 NaGdF 4 TEM photo of paramagnetic nanoparticles (A) and histogram of particle size distribution (B).
Embodiment 3
[0068] Dissolve 0.742g of gadolinium chloride hexahydrate and 6mL of oleic acid in 30mL of octadecene, then transfer the above solution into a 100mL three-necked flask, heat and dehydrate under vacuum (90°C) for 5 hours, and cool the reaction solution to room temperature. Dissolve 0.45 g of sodium hydroxide and 0.6 g of ammonium fluoride in 10 mL of methanol, and add them to the above reaction solution. The reaction was stopped after passing nitrogen gas and heating to 250°C for 10 hours. All the other operations are with embodiment 1, gained NaGdF 4 The average particle size of the nanoparticles is 5.4 nm. attached Figure 4 NaGdF 4 TEM photo of paramagnetic nanoparticles (A) and histogram of particle size distribution (B).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| solubility (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com