High-temperature-resistance optical fiber
A high-temperature, fiber-optic technology, applied in cladding fibers, optical waveguides and light guides, etc., can solve the problems of poor fiber performance, difficulty, and reliability degradation, and achieve the effect of superior temperature performance and good attenuation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
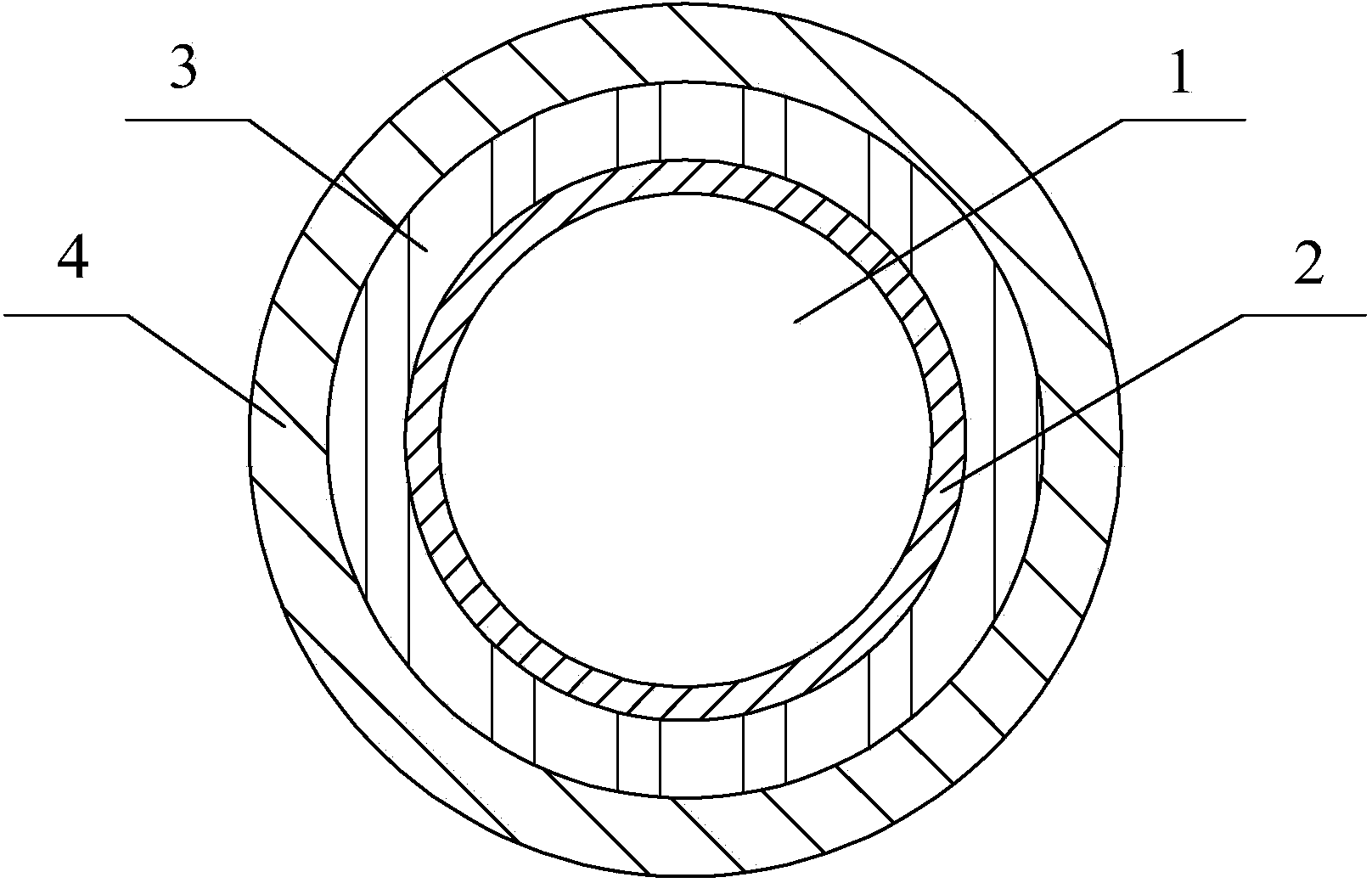
[0021] The first coating 2 is carbon with a thickness of 3 nm; the second coating 3 is polyimide with a Young's modulus of 0.8 GPa, and the thickness is 20 μm to 35 μm; the third coating 4 is a Young's modulus of 3.5 The polyimide of GPa, the thickness is 25μm~45μm.
[0022] The method for forming the high-temperature-resistant optical fiber in this embodiment is as follows: firstly, the quartz rod is melted and drawn into the optical fiber body 1 by using a high-temperature furnace, and a 3nm-thick fiber is deposited on its surface through a plasma chemical vapor deposition device arranged next to the lower furnace mouth of the high-temperature furnace. The carbon layer is the first coating 2 . Two more coats are then applied using the dry+wet method, first applying the second coat 3 by seal pressure coating, which is cured from liquid to solid using UV light; then applied again by seal pressure coating The third coating 4 is also cured from liquid to solid by using ultravio...
Embodiment 2
[0025] The first coating 2 is a polyacrylic resin with a Young's modulus of 1.2 MPa, and its thickness is 20 μm to 30 μm; the second coating 3 is a high temperature resistant polyacrylic resin with a Young's modulus of 1100 MPa, and its thickness is 20 μm to 35 μm; Coating 4 is polyimide with a Young's modulus of 4.0 GPa and a thickness of 10 μm to 30 μm.
[0026] The method for forming the high-temperature-resistant optical fiber in this embodiment is as follows: first, the quartz rod is fused and drawn into the optical fiber body 1 by using a high-temperature furnace, and the optical fiber diameter is 125 microns, and then the first coating 2 and the second coating 3 are applied by a wet-wet method. The first coating 2 and the second coating 3 are coated together by the sealing pressure coating method, and then the two coatings are cured from liquid to solid together with ultraviolet light, and the polyacrylic resin with Young's modulus of 1.2MPa is the first The first coati...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com