A Real-time Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Method for Detecting the Pathogenic Bacteria of Verticillium Wilt in Chinese Cabbage
A real-time fluorescence quantitative and Chinese cabbage technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to use large batches of detection practices and effectively distinguish Verticillium dahliae related species of bacteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Embodiment 1, primer design
[0051] 1. Primer design
[0052] According to the specific rDNA-ITS sequence (NCBI accession number: JN564038) of Verticillium dahliae pathogenic bacteria, the specific amplification primers are designed as follows:
[0053] HW1-F: 5'-GTTACAGCTCGCATCGGAGT-3' (SEQ ID No. 1)
[0054] HW1-R: 5'-CAGCGGGTATTCCTACCTGA-3' (SEQ ID No. 2)
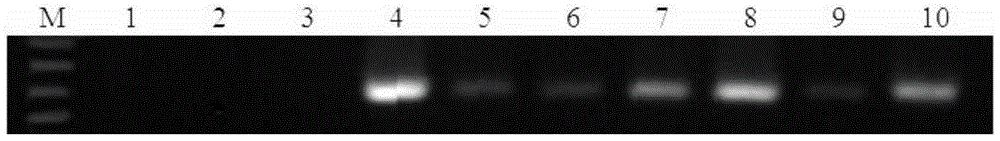
[0055] The length of the amplified target fragment is 100bp.
[0056] 2. Primer specificity and sensitivity detection
[0057] (1) Primer specificity detection
[0058] Extract the leaf tissue of Chinese cabbage not infected with the pathogen of Verticillium wilt of Chinese cabbage, the leaf tissue of Chinese cabbage infected with downy mildew of Chinese cabbage, the pathogen of Chinese cabbage Verticillium wilt BCHW10-2, the disease of Chinese cabbage infected with the pathogen of Verticillium wilt of Chinese cabbage DNA from leaves, diseased stems and roots, and expressed as ddH 2 O is a blank control.
...
Embodiment 2
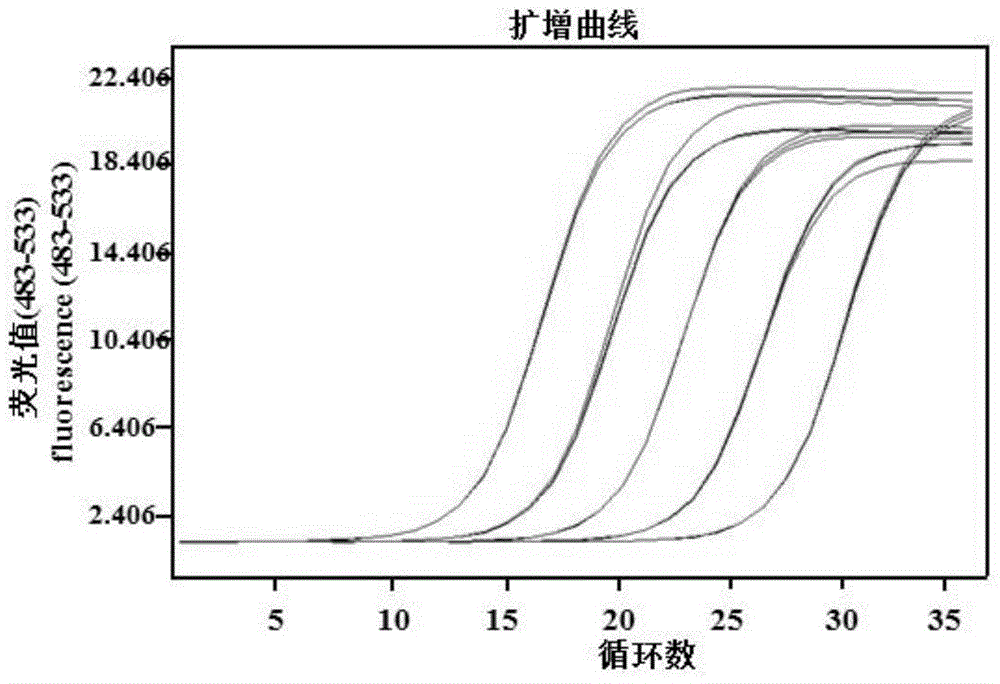
[0069] Embodiment 2, fluorescent quantitative PCR method detects Verticillium dahliae pathogenic bacteria in the sample
[0070] 1. Sample preparation
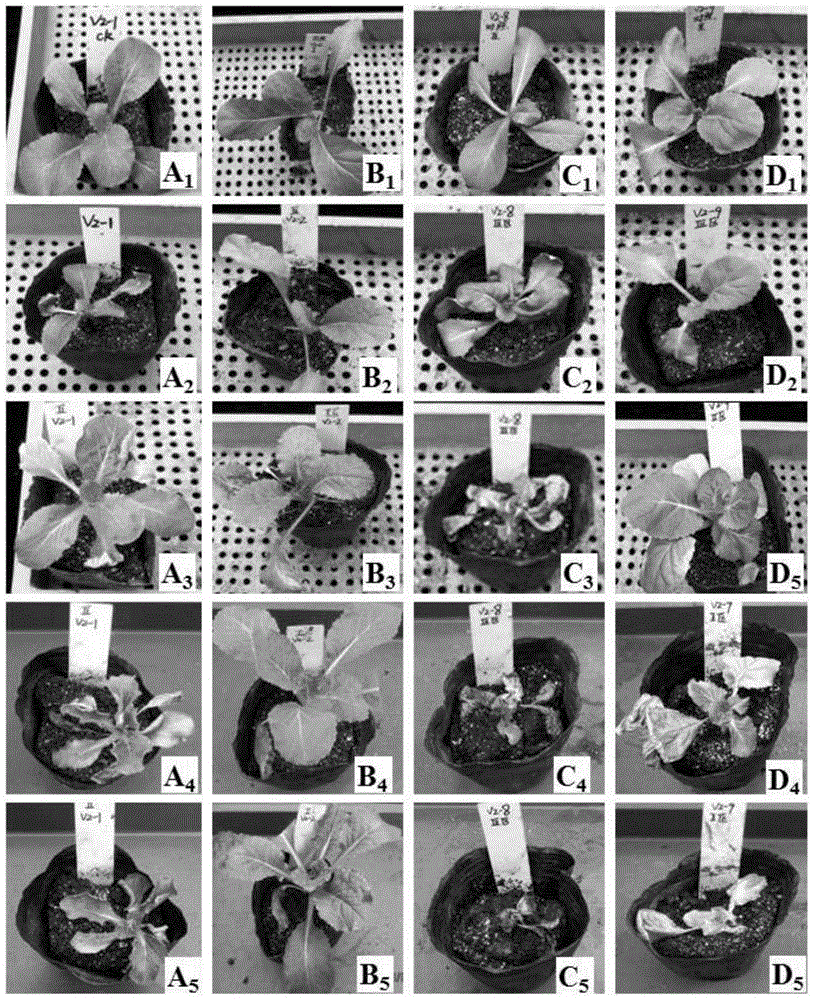
[0071] Greenhouse sample: The seedlings of various varieties of Chinese cabbage that have grown to three leaves and one heart are pulled out from the nutrient pot (natural root injury), and the spore suspension of Chinese cabbage verticillium wilt pathogen BCHW10-2 (concentration is 1 × 10 7 seedlings / mL) soaked the roots of seedlings for 15 minutes, and then replanted the seedlings in a 6×6cm nutrient pot, and inoculated sterile water as a control; The plants inoculated with pathogenic bacteria were sampled, and the plants inoculated with sterile water were used as the control group. Five plants were taken from each group of materials, and the roots, stems and leaves were stored separately, and freeze-dried in an ultra-low temperature vacuum freezer for later use.
[0072] Field samples: the leaves of each variety of cabbag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com