Detection analysis method for asphalt volatile organic compound
A volatile organic compound and analysis method technology, which is applied in the field of thermal analysis and detection, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of detection and analysis of asphalt volatiles due to variability and detection technology, the complex composition of asphalt smoke, and the evaluation of asphalt volatilization ability and degree of volatilization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Select PJ90 base asphalt and 5-10 mg of PJ90 modified asphalt with 3% activated carbon, control the heating rate at 10°C / min, heat from room temperature to 250°C for thermogravimetric mass spectrometry analysis. Mass spectrometry analysis was performed directly on the volatile gas during the heating process, and the volatilization of asphalt VOC was evaluated by the amount of mass loss.
[0029] Refer to attached figure 1 , the results show that under the same conditions, the mass loss rate of base asphalt is 3.54%, while after adding 3% activated carbon, the mass loss rate is only 2.45%. By comparison, it can be found that the inhibitory effect of activated carbon on asphalt is obvious. Through the thermogravimetric method, the volatilization of asphalt during use can be quantitatively analyzed, and the inhibitor's inhibitory effect on asphalt can also be evaluated by comparative analysis.
Embodiment 2
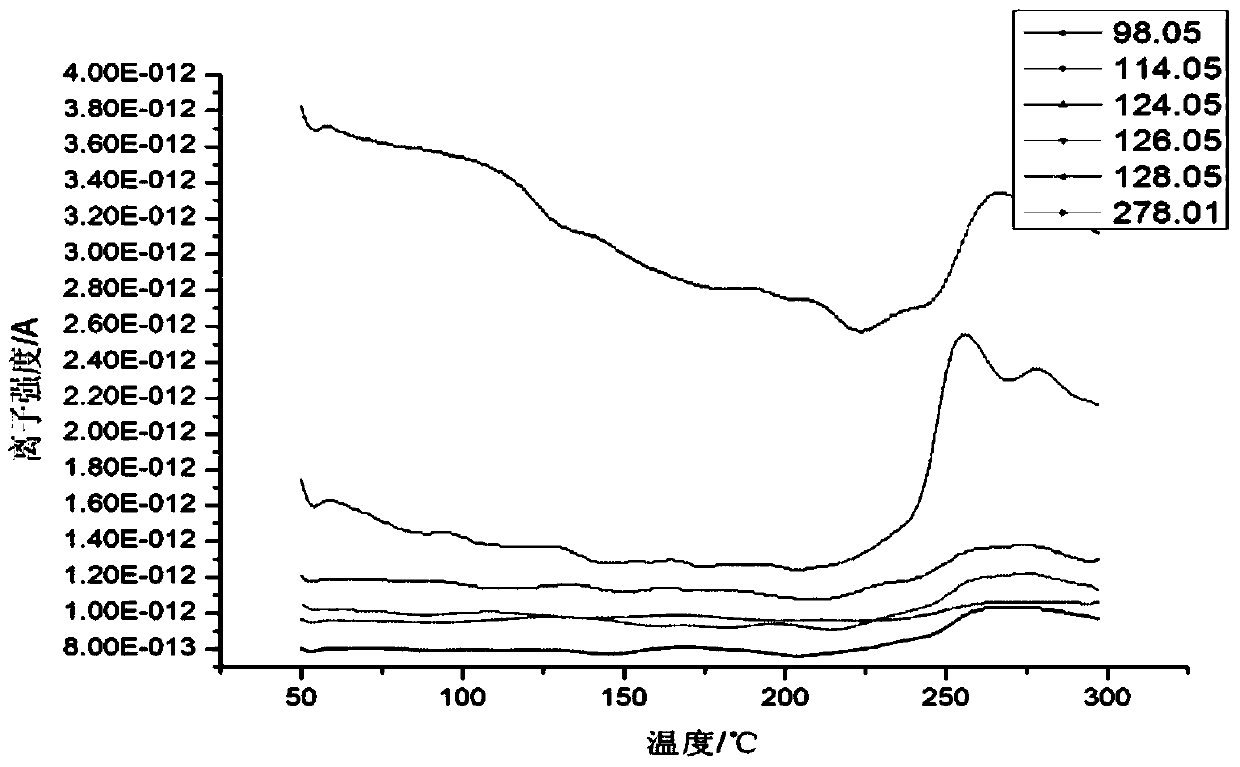
[0031] The base asphalt PJ90 is tested by thermogravimetric-mass spectrometry instrument. The test condition is to conduct thermogravimetric mass spectrometry analysis from room temperature to 250 °C at a speed of 10°C / min, and to perform mass spectrometry analysis by setting ion channels of various molecular weights.
[0032] Refer to attached figure 2 , the TG-MS diagram of No. PJ90 asphalt, the ordinate is the ionic strength, under the premise of the same test quality, the size of the ionic strength is a direct proportional relationship with the mass of volatilized substances, the results show that these 6 different molecular weight volatilized The mass change trend is basically the same, there is release in the range of 0-300, and the mass change is great after 250 degrees. Compared with the other four releases, the asphalt smoke with molecular weight of 98.05 and 128.05 releases A little more.
Embodiment 3
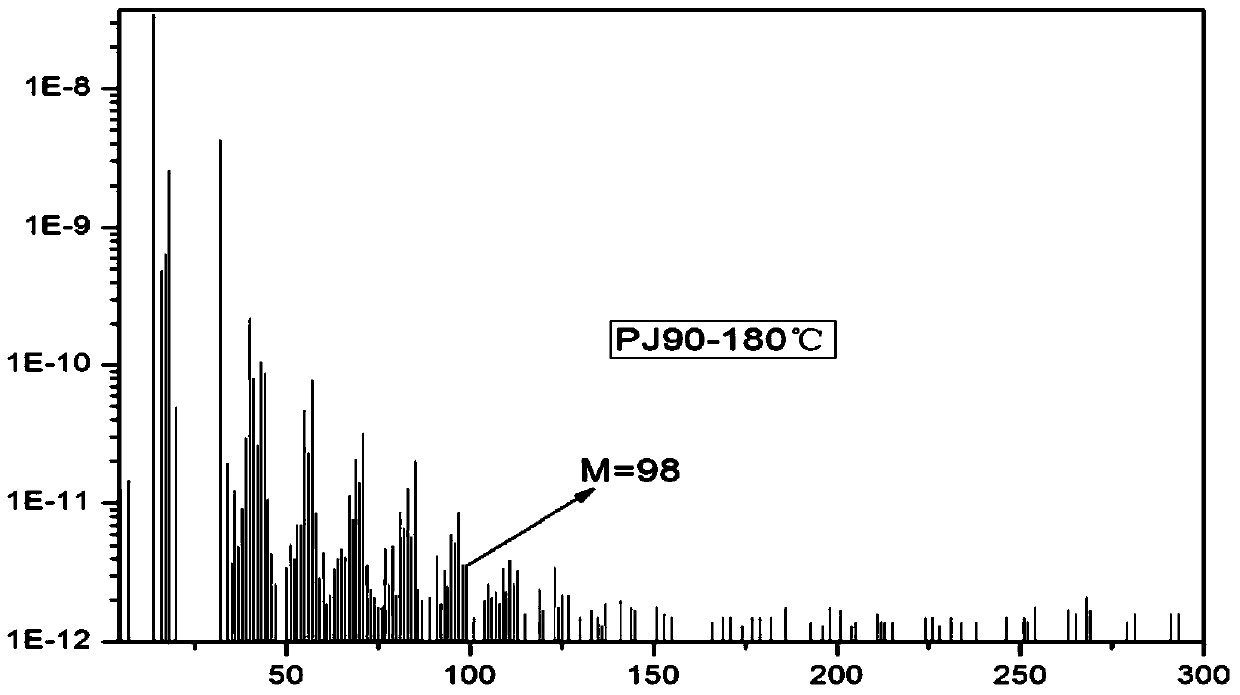
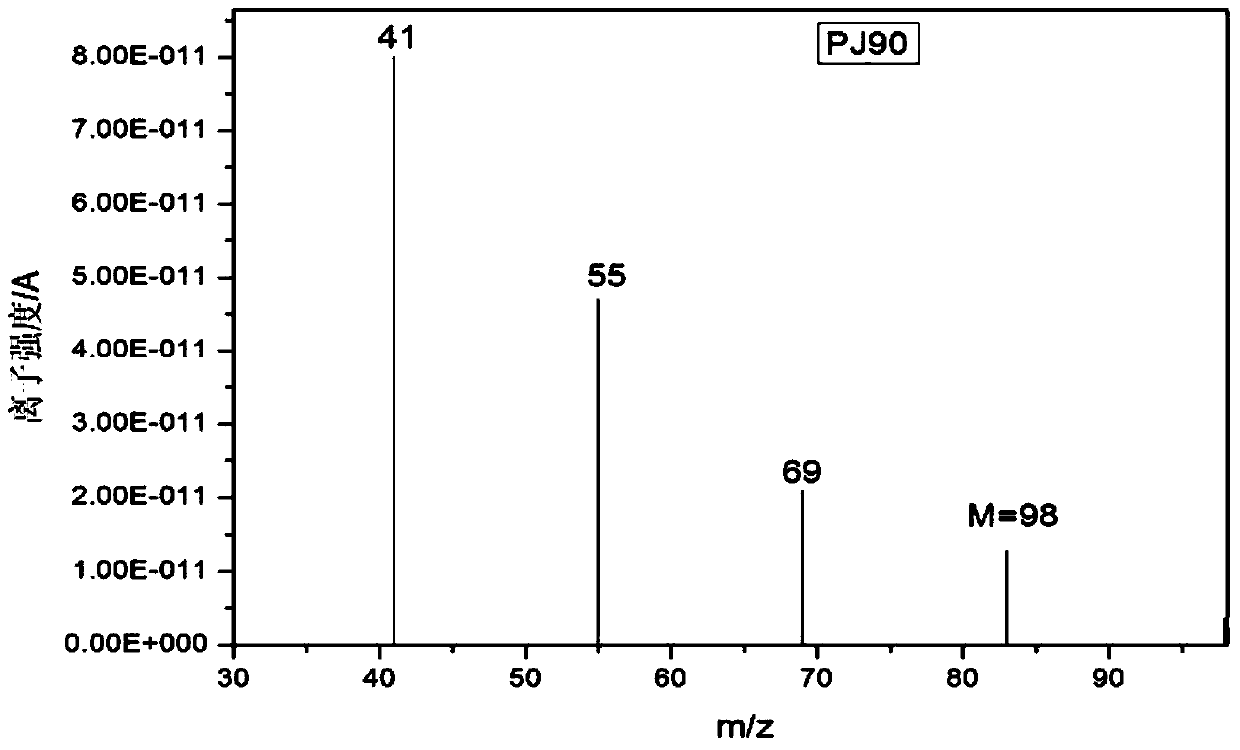
[0034] For the full mass spectrum ion histogram of PJ90 at 180°C, refer to the attached image 3 , 4 , image 3 Marked is the mass spectrum with a molecular weight of 98, the abscissa is the molecular weight, and the ordinate is the ionic strength. Figure 4 is the distribution diagram of the molecular weight 98 material cracking molecular weight 41, 55 and 69
[0035] image 3 The ion intensity of relatively small molecular weight is obviously greater than that of ions with large molecular weight. This is because in the mass spectrometer, various ions volatilized from the thermogravimetric instrument may undergo fragmentation and rearrangement under the action of an electric field. Figure 4 It is a distribution diagram of a selected molecular weight of 98 with a cracked molecular weight of 41, 55 and 69. A substance with a molecular weight of 83 was obtained by cleavage of a methyl group, and the final molecular weight of the substance was 41, 55, and 69 after rearrangem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com