Ultra-rapid diagnostic tissue preparation as an alternative to frozen section
A solid tissue, mixture technology, applied in the preparation of test samples, the determination/inspection of microorganisms, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as inconsistency and delay
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
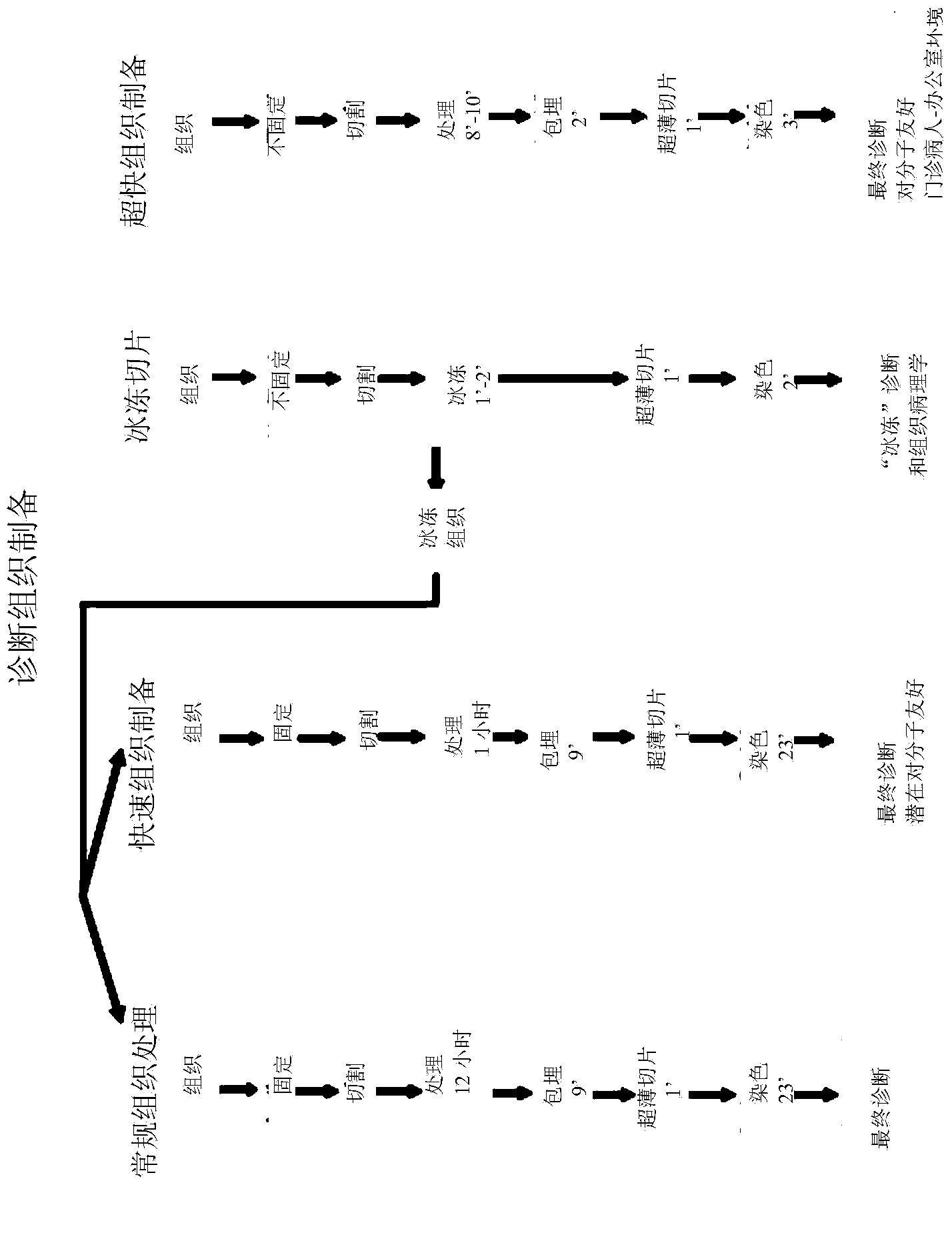
[0074] Fresh (i.e., not frozen and not pre-fixed) tissue is cut to a generally uniform thickness of about 0.6 mm (e.g., from about 0.4 mm to about 0.8 mm) to provide one or more tissue samples for processing . Hardening preferably begins when solid tissue is sectioned by contacting fresh tissue with a chemical mixture, which may or may not be the same as that used for processing (see below) during cutting. According to the new method, residual tissues from multiple different and diseased skin, lung, spleen, liver, uterus, placenta, intestine, ovary, carcinoma (e.g. breast, kidney, testis), sarcoma and leiomyoma were prepared Slice forever.
[0075] Tissue specimens were processed in a chemical mixture containing about 90% (v / v) acetone, about 10% (v / v) mineral oil, and about 0.1% (v / v) dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). The two main components were mixed in a volume of 3.8 L, to which 5 ml of DMSO was added. The tissue specimen is incubated in the chemical mixture at about 50° C. fo...
Embodiment 2
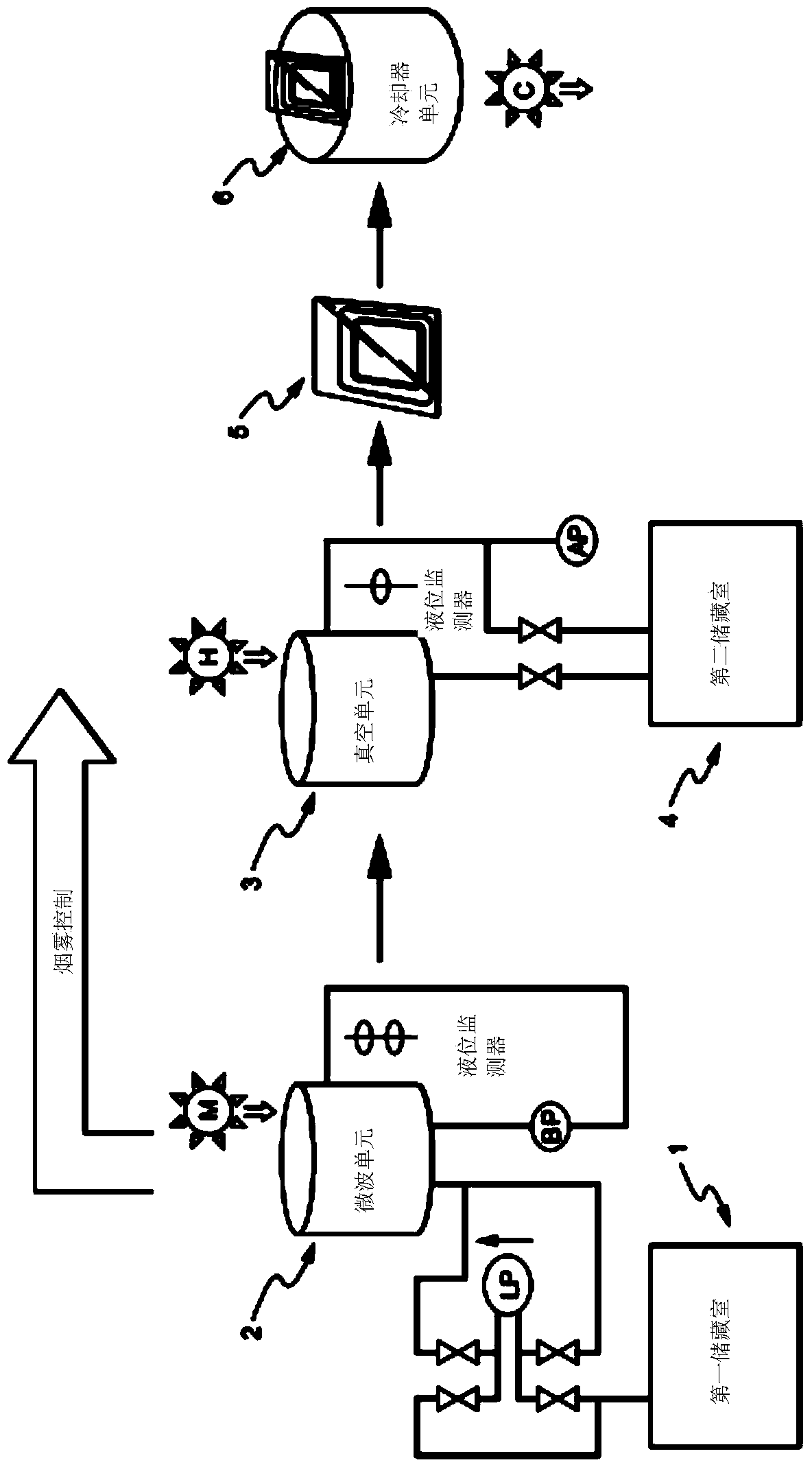
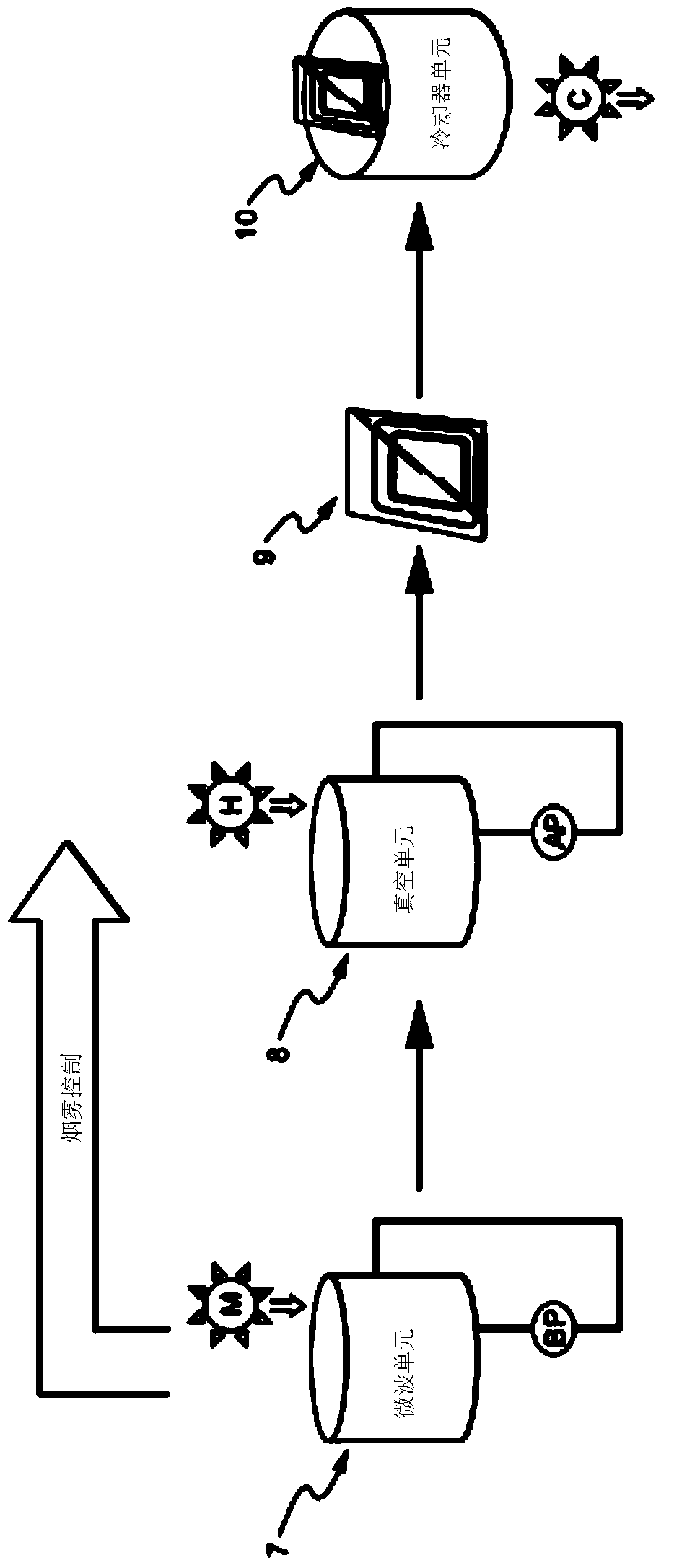
[0078] One embodiment of the invention can be used (in figure 2 shown in ) was tissue processed in the following manner. In the microwave unit, a chemical mixture and microwave energy are brought into contact with the tissue specimen to harden the tissue specimen in a chamber whose interior is shaped like a whispering gallery. A radiation source M provides microwave energy in the hardening module. Stirring in the microwave unit can be provided by aeration (pump BP). The chemical mixture can be transferred between its storage and its chambers using lines regulated by valves, level monitors and pump LP. Then, in a vacuum unit, the hardened cast specimen is brought into contact with the molten matrix and thermal energy under vacuum (pump AP) in a chamber for infiltration. The Joule heat source H provides the heat source in the infiltration module. Agitation in the vacuum unit can be provided by P / V circulation using the same pump AP which also transfers the molten substrate ...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Example 3: Cutting of Solid Tissue
[0089] Another embodiment of the present invention can be used in the following manner (in Figure 4 to Figure 9 shown in ) to perform tissue dissection. The cutting system includes a sterilizable base 20 , a tissue support 30 and a tissue retainer 40 . Tissue support 30 and tissue anchor 40 may be fabricated from a resilient plastic material such as acrylic. Each has a generally planar roughened surface (eg, a plurality of barbs, spikes or serrations having an area similar to that of fresh tissue); during cutting, both roughened surfaces come into contact with the tissue. The retainer has a handle on the top and a rough surface on the bottom. Alternatively, fingers can be used in place of the anchors to apply light pressure to the solid tissue and push it against the support (not shown).
[0090] The tissue holder 30 can be snugly engaged with the receiving hole 24 by being pushed in with the fingers, so that the upper surface o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com