Loran-C passive radar TOA estimating method based on total variation and compressed sensing
A passive radar, compressed sensing technology, applied in measurement devices, instruments, radio wave measurement systems, etc., can solve problems such as main lobe width, false target arrival time, inaccurate number of Roland C source estimates, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0062] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
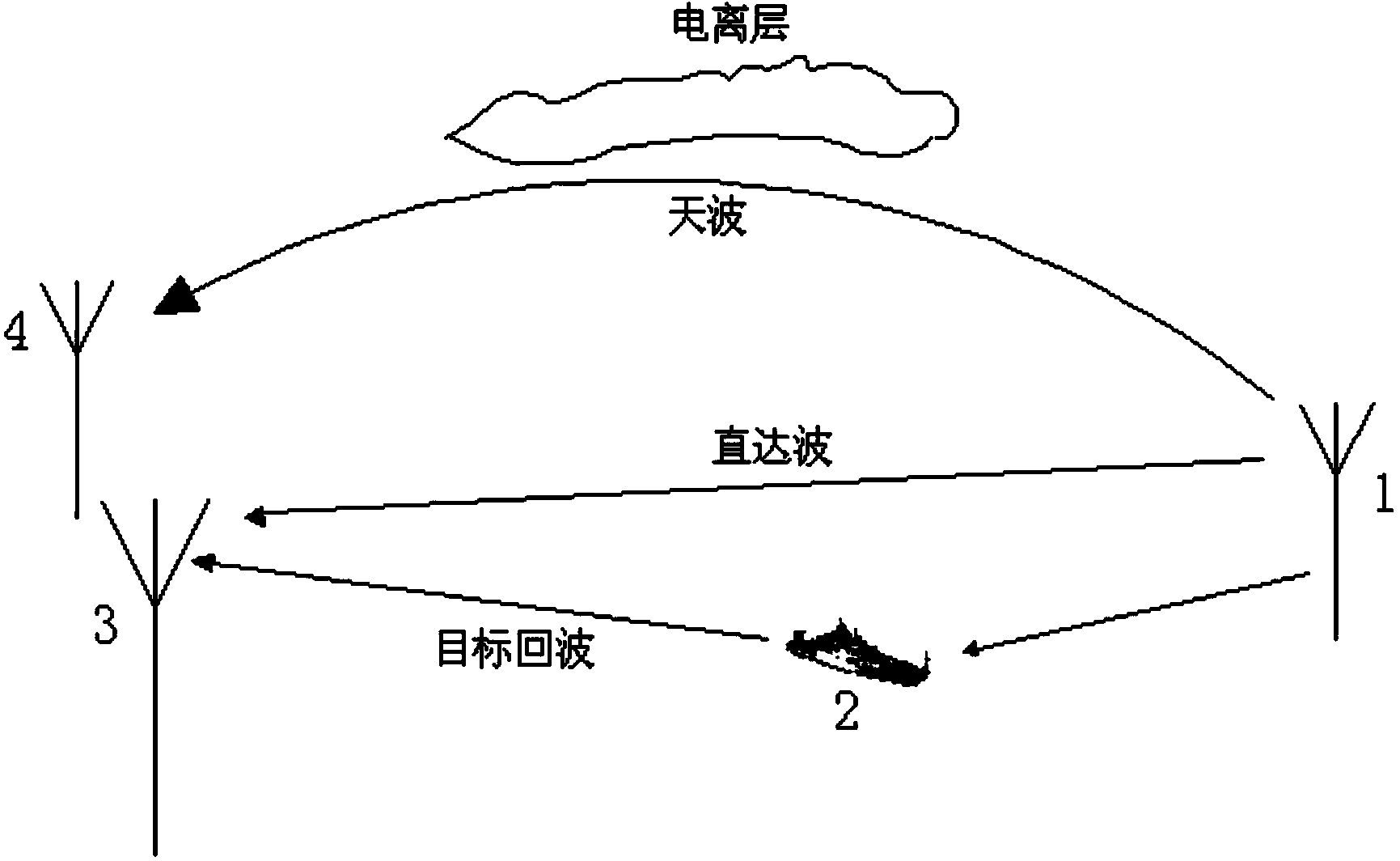
[0063] refer to figure 1 , is a schematic diagram of an application scenario of the present invention. In this application scenario, it includes the Loran C launch pad, the target to be detected, the ionosphere, and passive radar. The signals received by the passive radar include the Loran-C direct wave signal, the Loran-C sky-wave signal (signal emitted through the ionosphere), and the Loran-C target echo signal. The Roland C transmitter station 1 transmits signals outward, uses the main antenna 3 of the passive radar to receive the Roland C direct wave signal, the Roland C sky wave signal, and the Loran C target echo signal, and uses the passive radar's auxiliary antenna 4 to receive the Roland C direct wave signal , and Roland C sky-wave signals, in figure 1 Among them, 2 represents the target.
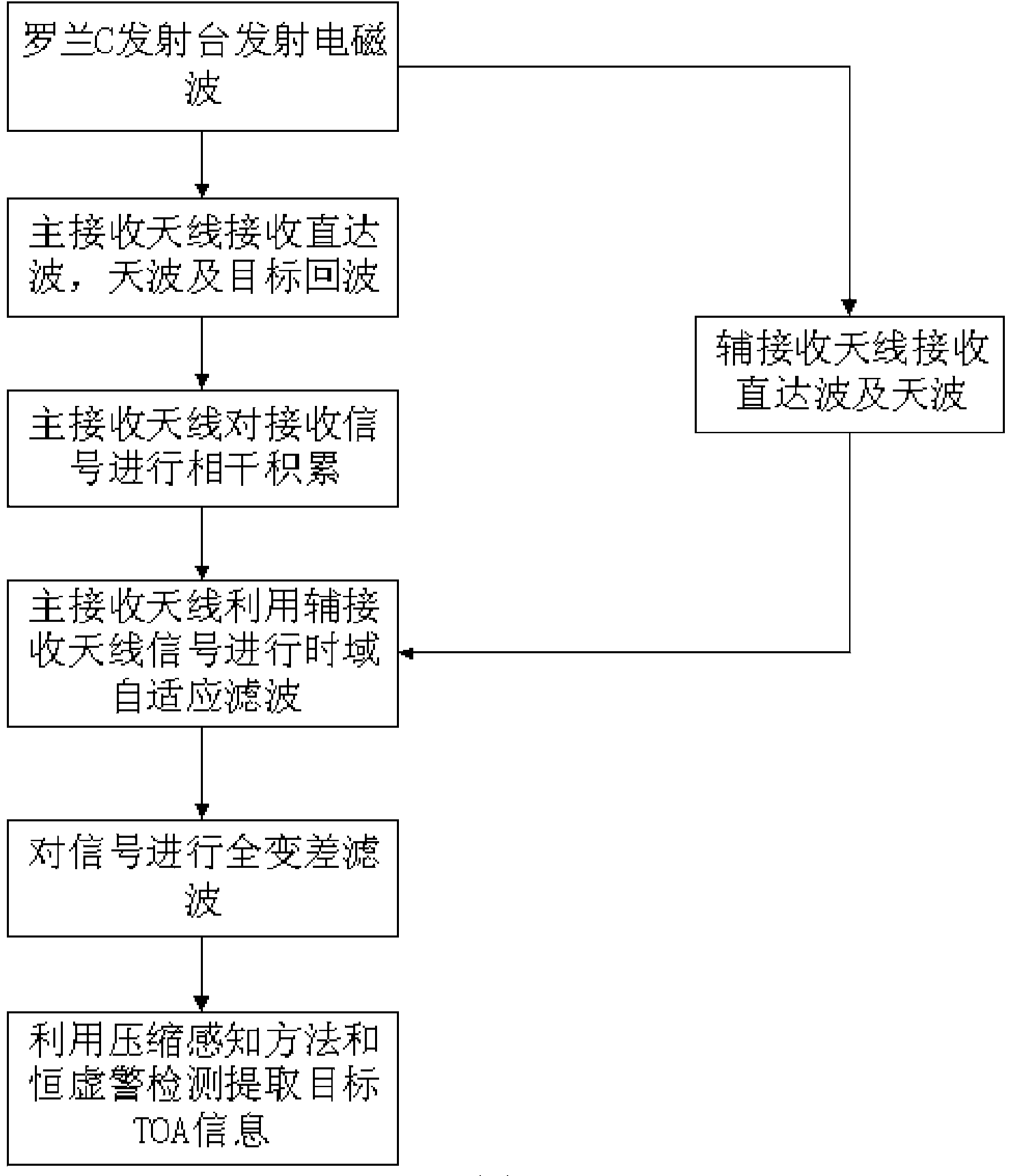
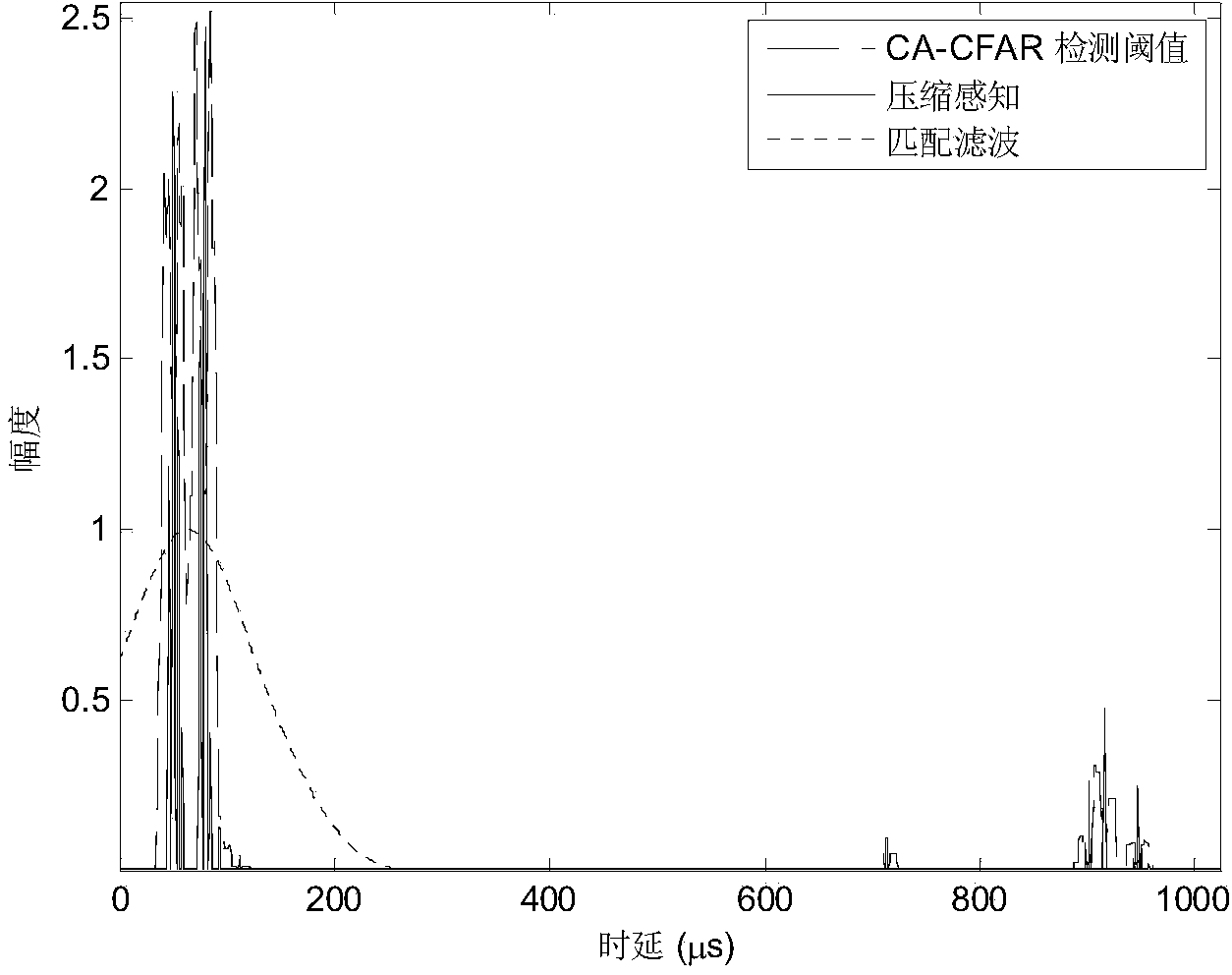
[0064] refer to figure 2 , is a flow chart of the Loran C passive rad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com