Methods for the phenotypic detection of HCV inhibitor resistant subpopulations
An inhibitor and resistance technology, applied in the field of phenotype detection of HCV inhibitor resistant subgroups, can solve the problem of reduced susceptibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0152] [Example 1: Preparation of samples for phenotypic analysis]
[0153] 【Sample preparation and amplification】
[0154] Most samples were received as frozen plasma with information including HCV subtype (ie, 1a or 1b) and viral load. Thaw samples, store in frozen aliquots if necessary, and process 200 μL aliquots. Viral particles are disrupted by adding a lysis buffer containing a chaotropic agent. Genomic viral RNA (vRNA) was extracted from viral lysates using oligonucleotide-linked magnetic beads. Purified vRNA was used as a template for first-strand cDNA synthesis in a reverse transcriptase (RT) reaction. The resulting cDNA was used as template for the first round of nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR), resulting in amplification of the entire NS5B region. Due to the sequence variation between subtypes 1a and 1b, specific 1a and 1b RTs and round 1 and 2 PCR primers were used. If no isoform information is available, the two primer sets can be used sequentially or...
Embodiment 2
[0159] [Example 2: Phenotypic assay to determine susceptibility to HCV inhibitors]
[0160] RTV RNA was electroporated into the Huh7 cell line and electroporated cells were incubated in the absence and presence of serially diluted inhibitors. RNA input was monitored by measuring the amount of luciferase activity produced in electroporated cells 4 hours after electroporation. Luciferase activity is expressed as relative light units (RLU). Replication competence (RC) was determined by evaluating luciferase activity in the absence of inhibitor relative to RNA input and a control reference replicon RTV (Con1) 72-96 hours after electroporation. Assay background was determined using a replication defective Con1 replicon (Con1 polymerase deficient) (data not shown). Inhibitor susceptibility was determined by evaluating the ability of RTV to replicate in the absence and presence of inhibitors 72-96 hours after electroporation. The % inhibition at each serially diluted inhibitor con...
Embodiment 3
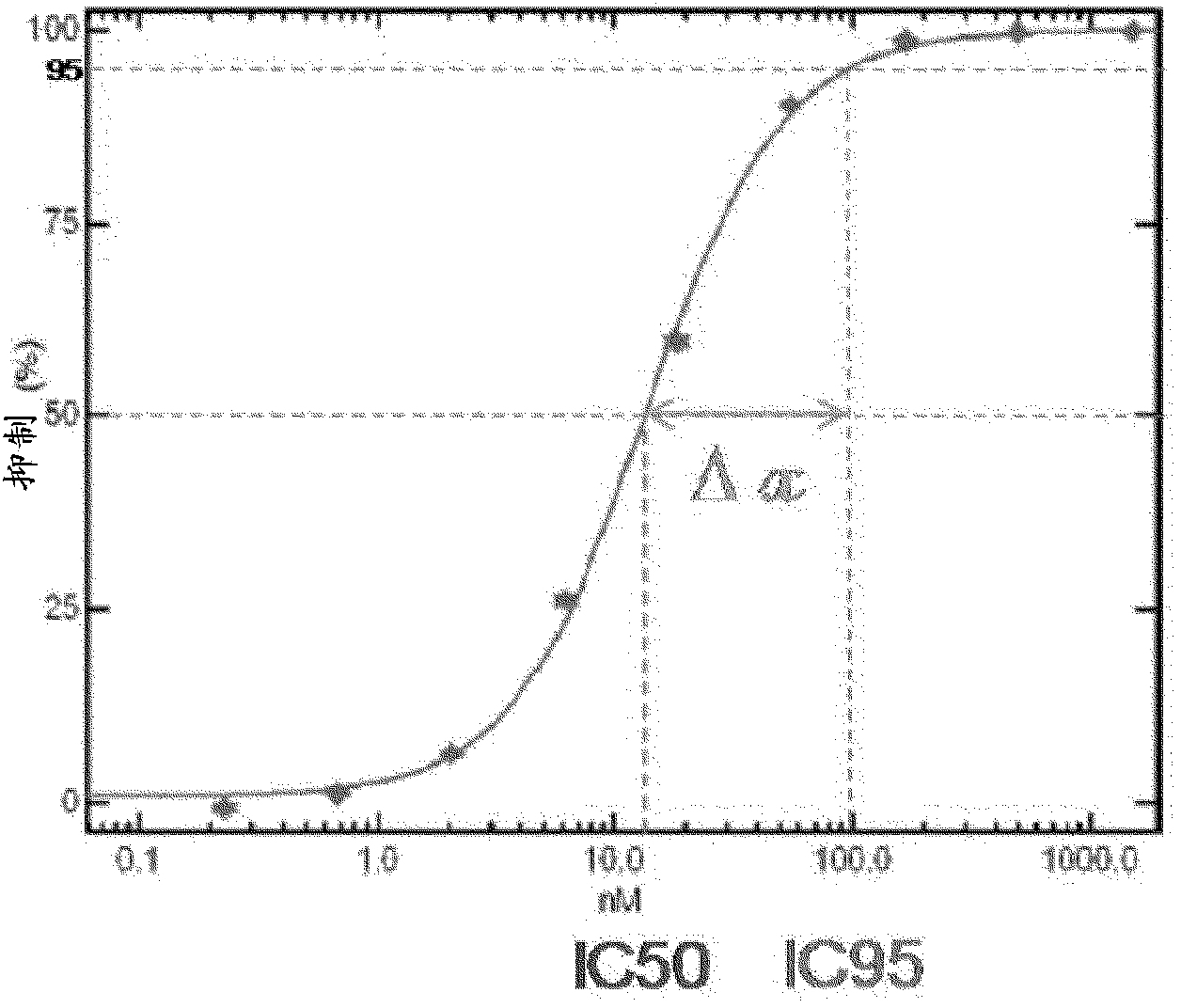
[0165] [Example 3: For IC 95 Measurement of FC improves sensitivity for detection of inhibitor susceptibility]
[0166] for evaluation Sensitivity of HCV NS5B assays to detect subpopulations of drug-resistant variants using data from reference viruses (wild-type, WT) containing Con1 or H77 and containing specific SDMs conferring reduced susceptibility to one or more NS5B inhibitors C o RNA of RTV from the NS5B region of n1 or H77 (mutant, MT). WT and MT RTV (100% WT or 100% MT) were evaluated independently or as defined MT:WT mixtures (20:80, 40:60, 60:40 and 80:20%). Samples were assessed for susceptibility to specific NS5B inhibitors, as well as INF as a control (SDM is not expected to affect INF susceptibility). Inhibitor susceptibility data were obtained for all samples tested. Evaluation on IC 50 -FC and IC 95 - Observed differences in FC values to define the relationship between the percentage of each MT RTV in the mixture and the IC-FC susceptibility parameter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com