Low Dropout Linear Regulators
A low-dropout linear and voltage regulator technology, which is applied in the direction of instruments, electrical variable adjustment, control/regulation systems, etc., can solve the problems of high overall power consumption and high circuit power consumption, and achieve low noise, high PSRR, and low power consumption Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
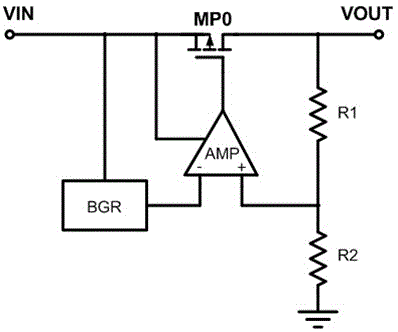
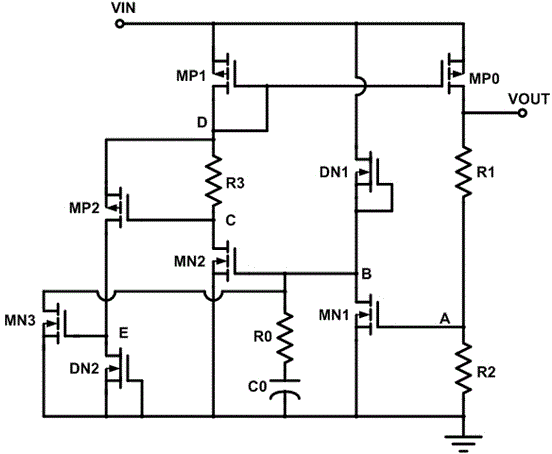
[0021] Such as figure 2 The low-dropout linear regulator shown includes: an enhanced PMOS transistor MP0 (output MOS transistor), and a voltage sampling circuit connected in series to the current outflow terminal of the output MOS transistor (that is, the drain of the enhanced PMOS transistor MP0). The sampling signal and the reference voltage value obtain the voltage comparison circuit of the error signal, and the Buffer driving circuit that outputs the MOS tube is driven by the error signal. The voltage sampling circuit is composed of resistors R1 and R2 connected in series, and the connection point A of the resistors R1 and R2 outputs a sampling signal VA.
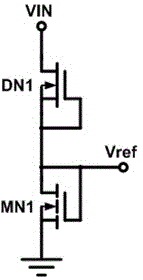
[0022] The voltage comparison circuit includes: depletion-type NMOS tube DN1, enhanced NMOS tube MN1, the drain of the depletion-type NMOS tube DN1 is connected to the input power supply VIN, the gate and source of the depletion-type NMOS tube DN1 are short-circuited and then connected to the enhanced NMOS The drain o...
specific Embodiment 2
[0026] On the basis of Embodiment 1, further optimize the design of the Buffer drive circuit. The Buffer drive circuit includes: enhanced PMOS transistor MP1, resistor R3, enhanced NMOS transistor MN2, the source of the enhanced PMOS transistor MP1 is connected to the input power supply, the gate and drain of the enhanced PMOS transistor MP1 are short-circuited and then connected to one end of the resistor R3 (point D), the other end of the resistor R3 is connected to the drain of the enhanced NMOS transistor MN2 (point C), the gate of the enhanced NMOS transistor MN2 is connected to the drain of the enhanced NMOS transistor MN1, and the source of the enhanced NMOS transistor MN2 is grounded.
[0027] figure 2 In the circuit shown, the gate of the enhanced NMOS transistor MN1 is separated from the drain, the gate of the enhanced NMOS transistor MN1 is connected between the resistor R1 and the resistor R2 as the input terminal of the voltage comparison circuit, and the enhance...
specific Embodiment 3
[0029] In order to limit the excessive output current of the enhanced PMOS transistor MP0, the present invention designs a current limiting protection circuit by utilizing the feature that the enhanced PMOS transistor MP1 in the Buffer drive circuit can copy the current of the enhanced PMOS transistor MP0. The current limiting protection circuit includes: enhanced PMOS transistor MP2, enhanced NMOS transistor MN3, depleted NMOS transistor DN2, the source of the enhanced PMOS transistor MP2 is connected to the drain of the enhanced PMOS transistor MP1, and the gate of the enhanced PMOS transistor MP2 is connected to the enhanced The drain of the enhanced NMOS transistor MN2, the drain of the enhanced PMOS transistor MP2 is connected to the drain of the depleted NMOS transistor DN2 (point E), the gate and source of the depleted NMOS transistor DN2 are shorted and grounded, and the drain of the enhanced NMOS transistor MN3 The pole is connected to the drain of the enhanced NMOS tr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com