Iron and molybdenum containing pellets
A technology of pellets and molybdenum oxide, which is applied in the field of preparing pellets containing iron and molybdenum, which can solve the problems of prolonging the dissolution time of ferromolybdenum, loss of molybdenum, and high raw material prices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
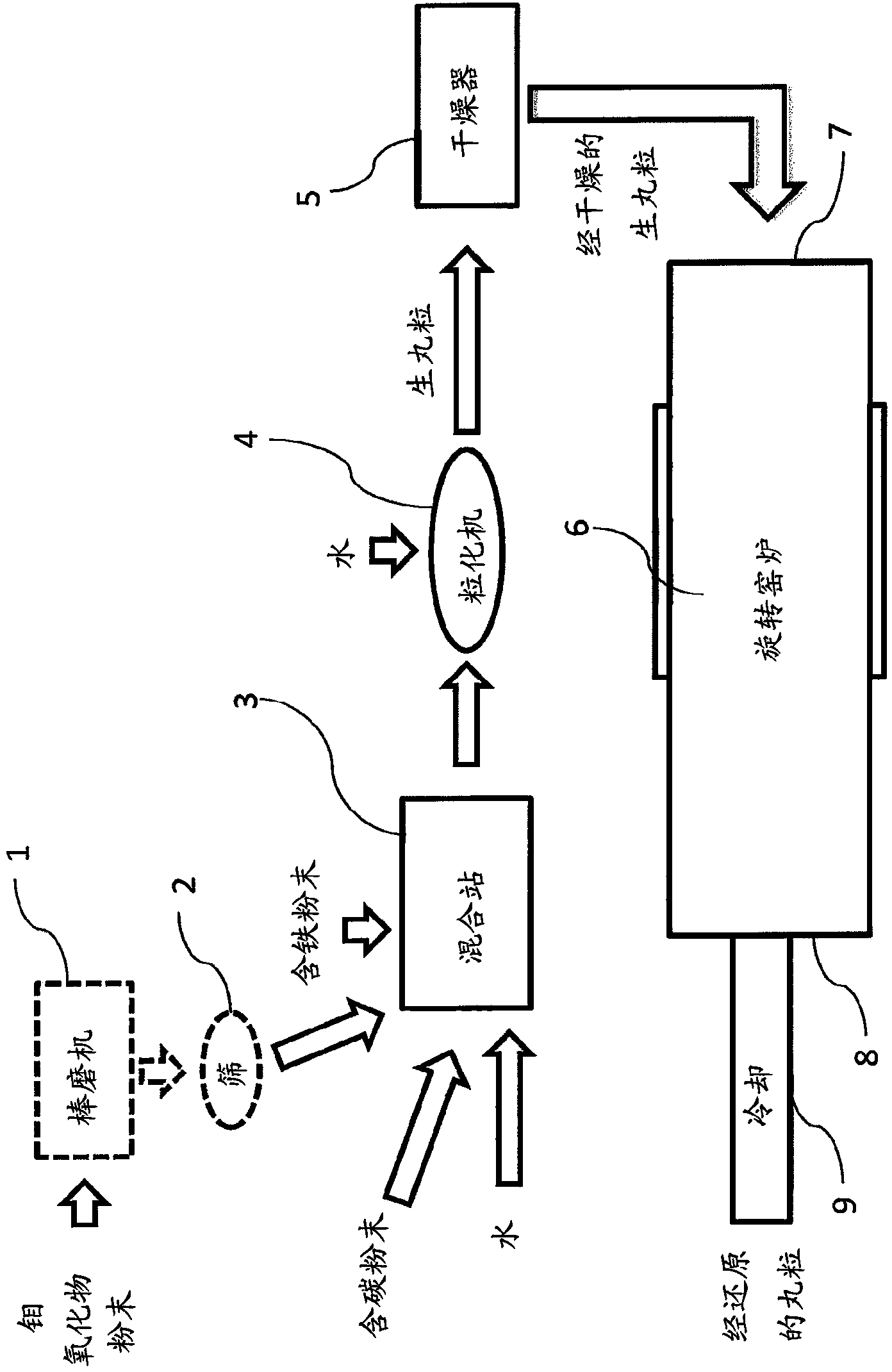
[0153] A mixture was prepared by adding 3% by weight of fine-grained iron powder (99% by weight Fe from AB's X-RSF40) was mixed with 84% by weight of technical grade molybdenum oxide (Mo>57% by weight, <40 μm) and 13% by weight of carbon powder (<20 μm, Carbon Black). Water was added to the mixture and green pellets were prepared in a disc granulator. According to ASTM D2216-10, the moisture content of the pellets measured by LOD is about 10% by weight. Then, the pellets were dried at room temperature to a moisture content of 2 wt%.
[0154] The green pellets were reduced in a batch furnace at a temperature of 1100° C. in an atmosphere of 95 vol-% N2 and 5 vol-% H2 for a period of 2 hours. The pellets were then allowed to cool to a temperature of about 100°C before the atmosphere was evacuated and removed from the batch furnace. The result was pellets with a weight of about 0.4 grams and a diameter of about 6-7 mm. The average geometric density of the pellets measured acc...
Embodiment 2
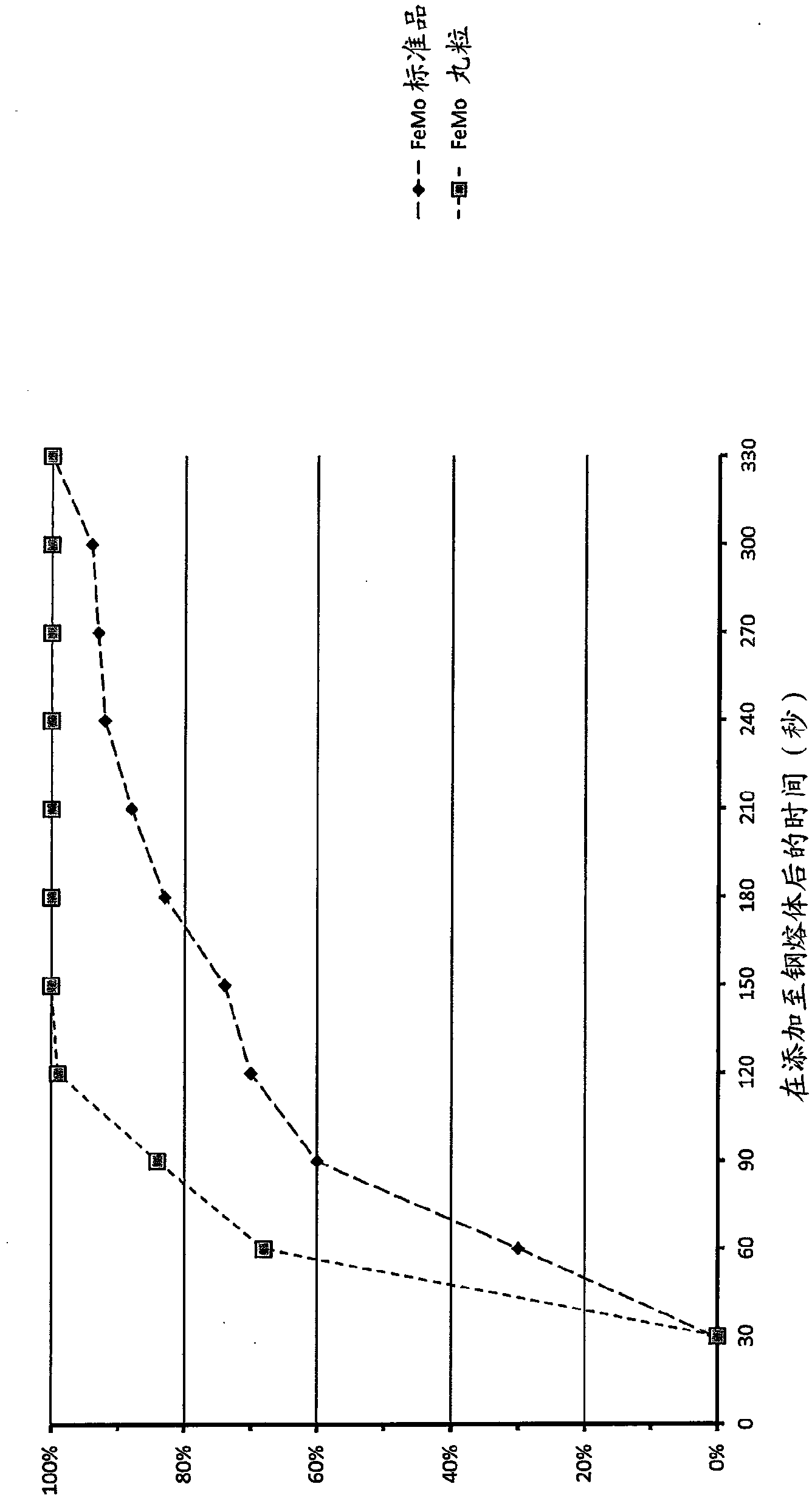
[0160] figure 1 Shown is a comparison of the dissolution rate of a standard reference grade of solid ferromolybdenum to the iron and molybdenum containing pellets described in the present invention, ie the novel ferromolybdenum grade. The same batch of pellets as in Example 1 was provided and therefore these pellets had the same composition as in Table 1. The average geometric density of the pellets was determined to be 2.6 g / cm as described in Example 1 3 .
[0161] The reference material was 10 standard pieces of ferromolybdenum containing 70% molybdenum by weight, no more than 2% impurities by weight and the balance being iron. Each piece measures approximately 10x50mm.
[0162] The purpose of the experiment was to evaluate whether pellets containing iron and molybdenum had a faster dissolution time than standard ferromolybdenum.
[0163] Two steel melts (a first steel melt and a second steel melt) were prepared and analyzed for their composition. The target compositio...
Embodiment 3
[0165] Mixture A was prepared by adding 2.5 wt% fine-grained iron powder (99 wt% Fe from AB's X-RSF40) was mixed with 84% by weight of technical grade molybdenum oxide (Mo>57wt.%, <40μm) and 13.5% by weight of carbon powder (<20μm, carbon black (Carbon Black)). Water was added to the mixture and green pellets were prepared in a disc granulator. After granulation, the green pellets were dried at a temperature of 90° C. for 2 hours to reduce the moisture content to below 2 wt%.
[0166] The dried green pellets were reduced for 0.5 hours at a temperature of 1120° C. in a rotary oven. Provide countercurrent weak reducing atmosphere 95vol-%N during reduction 2 and 5vol-%H 2 . The pellets were then allowed to cool to a temperature of approximately 100°C under a protective atmosphere. The result was a pellet having a weight of about 1.9 grams and a diameter of about 12 mm.
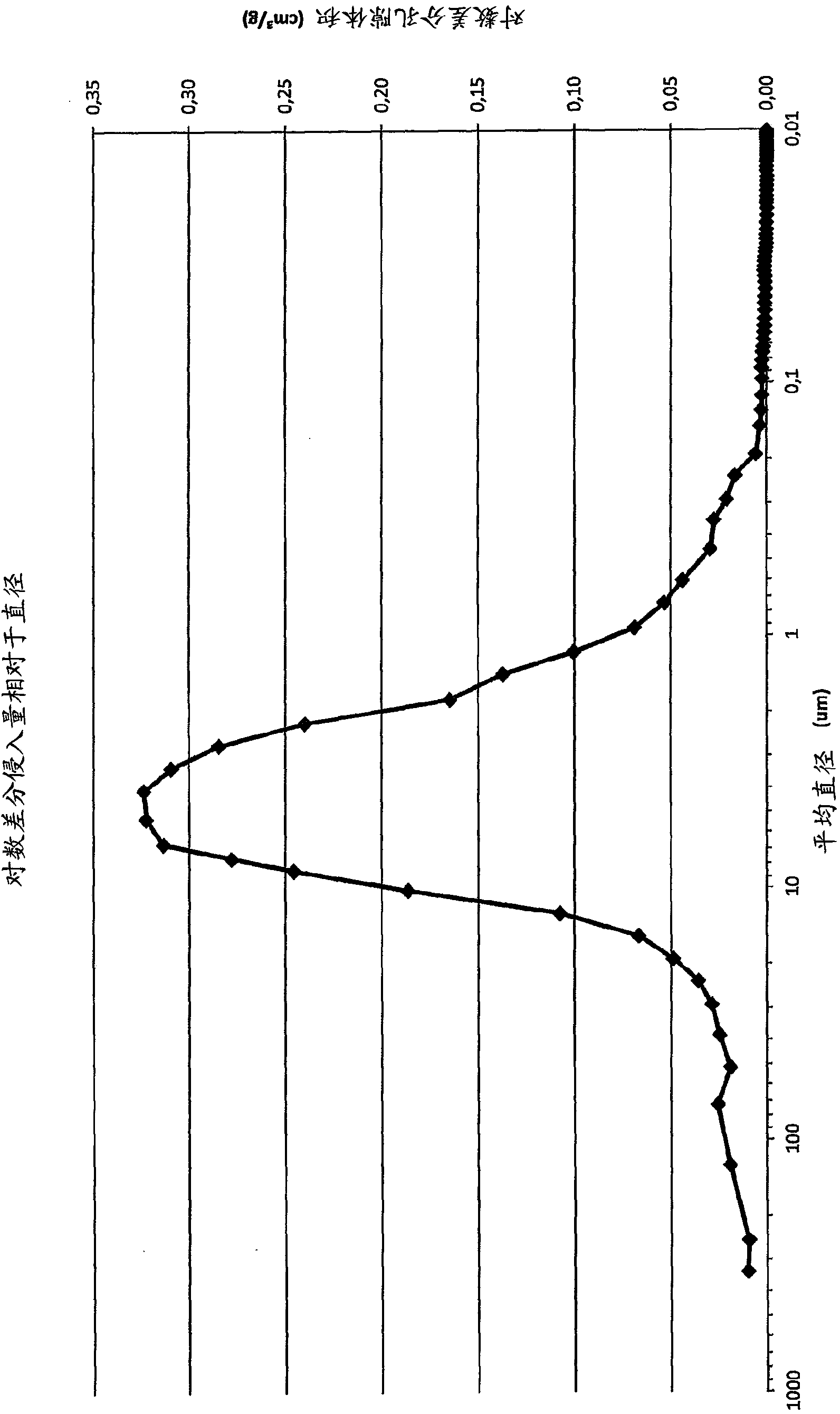
[0167] Two pellets were analyzed in a mercury porosimeter at a pressure of 4.45 psia (instrument: Micro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com