Signal decoding circuit applied to wireless charging or radio frequency identification system
A technology of radio frequency identification system and decoding circuit, which is applied in the field of signal decoding circuit applied to wireless charging or radio frequency identification system, and can solve problems such as screen lighting, screen extinguishing, and coil failing to pass inspection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
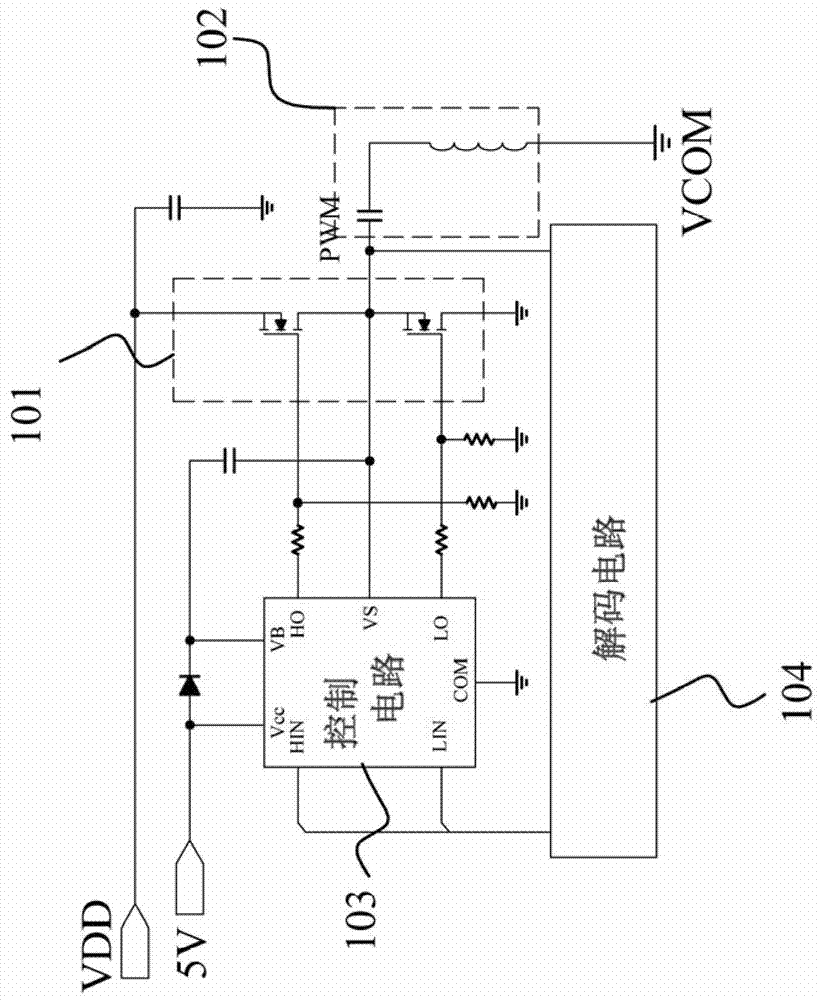
[0068] figure 2 Shown is a circuit block diagram of a signal decoding circuit applied to a wireless charging or radio frequency identification system according to an embodiment of the present invention. Please refer to figure 2 , the signal decoding circuit applied to wireless charging or radio frequency identification system includes an upper bridge switch 201 , a lower bridge switch 202 , an LC resonant circuit 203 , a voltage decoding circuit 204 , a current decoding circuit 205 , and a control circuit 206 .
[0069] The high-bridge switch 201 includes a first terminal, a second terminal and a control terminal, wherein the first terminal of the high-bridge switch 201 is coupled to a power supply voltage VDD. The lower bridge switch 202 includes a first end, a second end and a control end, wherein the first end of the lower bridge switch 202 is coupled to the second end of the upper bridge switch, and the second end of the lower bridge switch 202 is coupled to a total Co...
no. 2 example
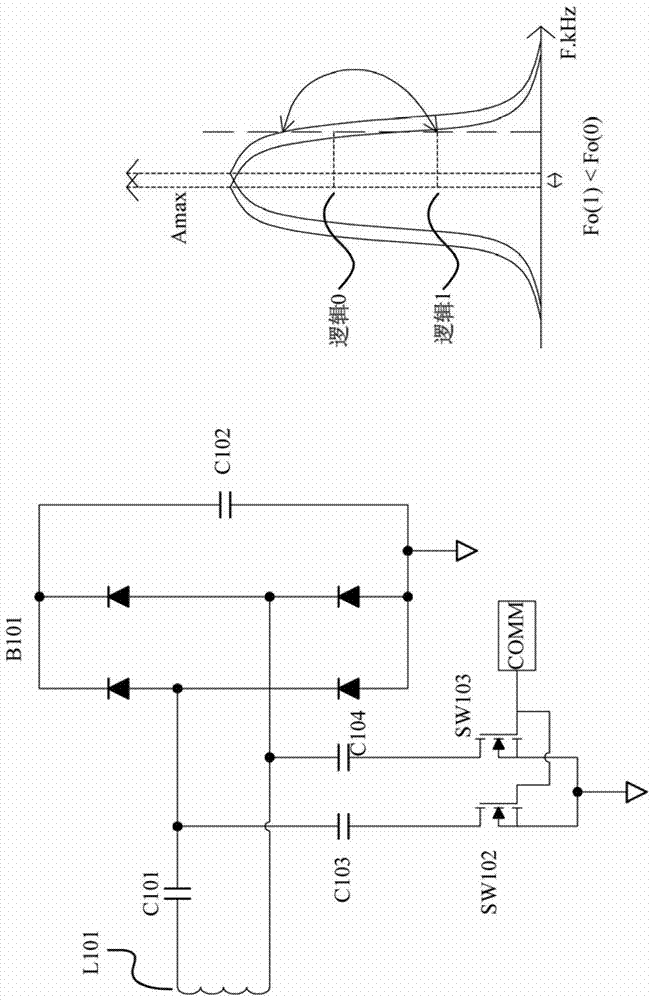
[0083] Figure 4 Shown is a circuit diagram of a voltage decoding circuit applied to a wireless charging or RFID system according to an embodiment of the present invention. Please refer to Figure 4 , the voltage decoding circuit includes a peak detection circuit composed of a diode D6, a resistor R31 and a capacitor C39, an isolation capacitor C33, a DC bias circuit composed of a voltage divider composed of a resistor R43 and R42, and a buffer circuit composed of an amplifier U7A, a signal amplifier made up of resistors R44, R45, R46, capacitors C36, C37 and amplifier U7B, a first filter circuit made up of resistor R48 and capacitor C42, a second filter circuit made up of resistor R19 and capacitor C27, and A Schmitt trigger (comparator) composed of resistors R18, R29 and amplifier U7C.
[0084] Firstly, the voltage at the node V back will pass through the peak detection circuit composed of the diode D6, the resistor R31 and the capacitor C39 to obtain a peak signal. Since...
no. 3 example
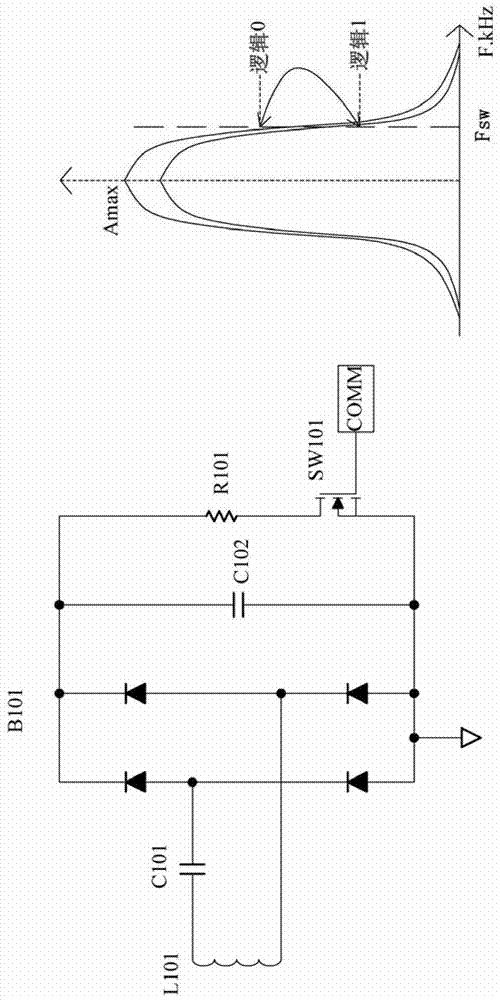
[0087] Figure 5 Shown is a circuit diagram of a current decoding circuit applied to a wireless charging or RFID system according to an embodiment of the present invention. Please refer to Figure 5 , the current decoding circuit includes a current sensing resistor R32 coupled to the lower bridge switch 202 , a primary amplifier 501 composed of resistors R54 , R66 , R68 , capacitor C28 and amplifier U7D, and a high current decoding circuit 502 . Wherein, the high current decoding circuit 502 includes a high cut-off frequency filter (resistor R22 and capacitor C40 ), a low cut-off frequency filter (resistor R23 and capacitor C43 ), and a comparator U9A.
[0088] This circuit converts the current originally flowing through the lower bridge switch 202 into a current sensing voltage IDC through the current sensing resistor R32, and then initially amplifies the current sensing voltage IDC through the primary amplifier. Next, the amplified After filtering out noise (resistor R22 a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com