Photovoltaic module adjusting circuit and remote monitoring system
A remote monitoring system and photovoltaic module technology, applied in the field of solar photovoltaic power generation, can solve the problems of inconsistent parameters of photovoltaic cells in the manufacturing process, unable to completely save power loss, difficult to find the maximum power point, etc., to facilitate performance analysis and fault diagnosis, The effect of low loss and low power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
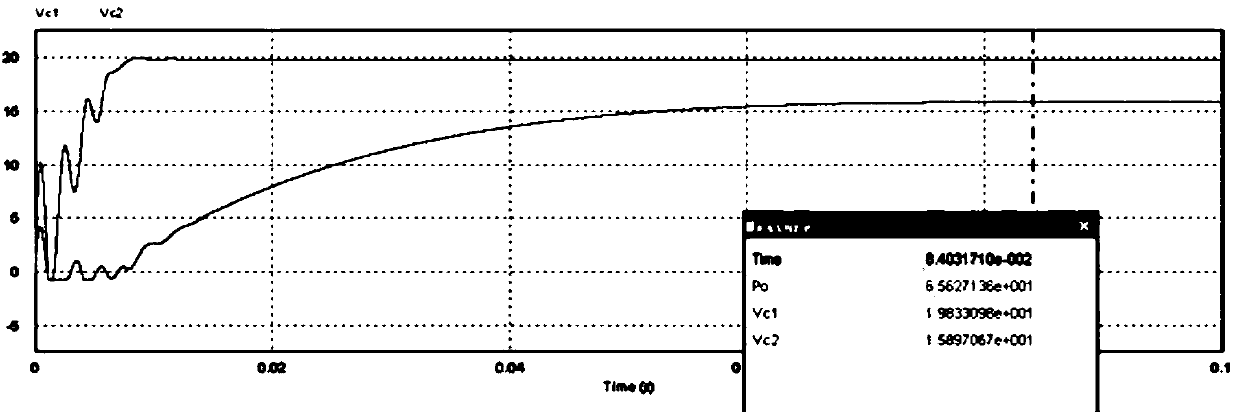
Examples
Embodiment 1
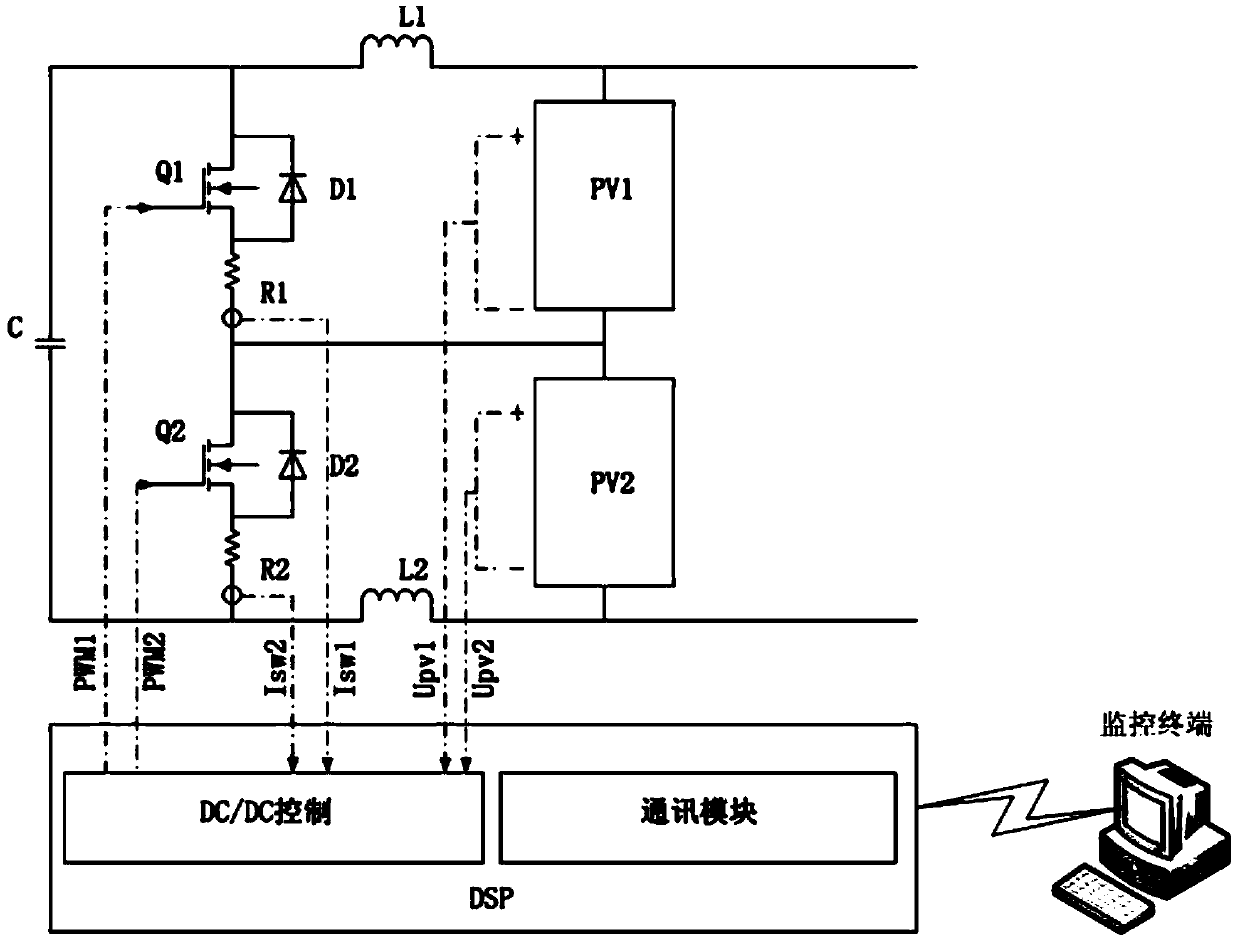
[0042] Such as figure 1 As shown, the electronic components of the regulating circuit include the first photovoltaic component PV1, the second photovoltaic component PV2, the first inductor L1, the second inductor L2, the capacitor C, the first N-MOS field effect transistor Q1, the second N-MOS type field effect transistor Q2, the first resistor R1, the second resistor R2, the first diode D1 and the second diode D2.
[0043] The first photovoltaic component PV1 is connected in series with the second photovoltaic component PV2, and the negative pole of the first photovoltaic component PV1 is connected with the positive pole of the second photovoltaic component PV2.
[0044] The anode of the first photovoltaic module PV1 is connected to one end of the first inductance L1, the other end of the first inductance L1 is connected to the drain of the first N-MOS field effect transistor Q1, and the source of the first N-MOS field effect transistor Q1 One end of the first resistor R1 i...
Embodiment 2
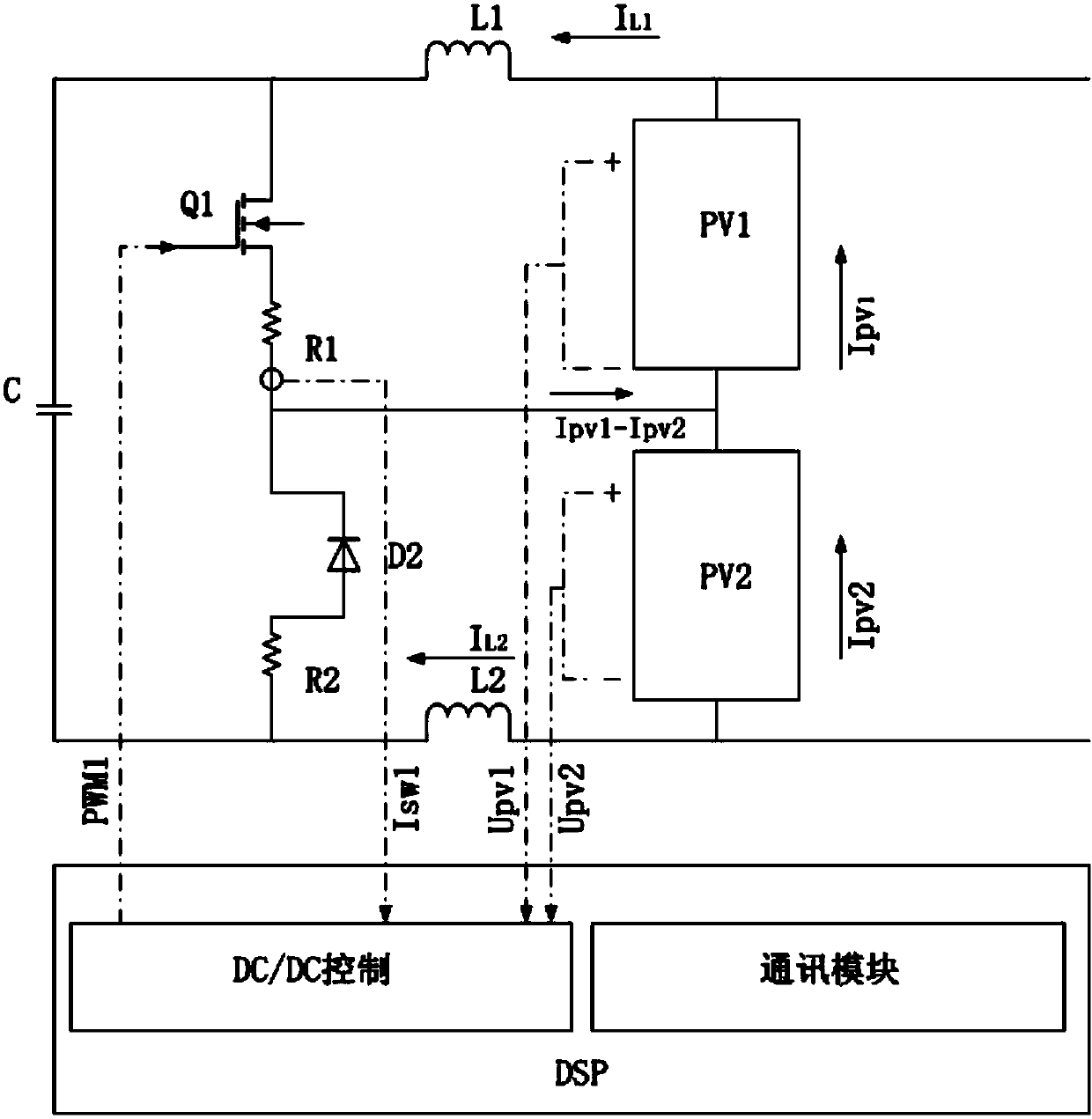
[0059] Such as Figure 11 As shown, the regulator circuit can also apply the topological structure of a buck-boost DC / DC circuit, including an inductor L, a third N-MOS field effect transistor Q3, a fourth N-MOS field effect transistor Q4, and a third diode tube D3, fourth diode D4 and first capacitor C1,
[0060] The positive pole of the first photovoltaic component PV1 is connected to one side of the third N-MOS field effect transistor Q3, and the other side of the third N-MOS field effect transistor Q3 is connected to the negative pole of the first photovoltaic component PV1;
[0061] The positive pole of the second photovoltaic module PV2 is connected to one side of the fourth N-MOS field effect transistor Q4, and the other side of the fourth N-MOS field effect transistor Q4 is connected to the negative pole of the second photovoltaic module PV2;
[0062] One side of the inductor L is connected to the connection point between the third N-MOS field effect transistor Q3 and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com