Preparation method of non-noble metal catalyst used for oxygen reduction reaction
A non-precious metal catalyst technology, applied in the field of non-precious metal catalysts, can solve the problems of different, expensive, and restricting the industrialization and commercialization of fuel cells and metal-air batteries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
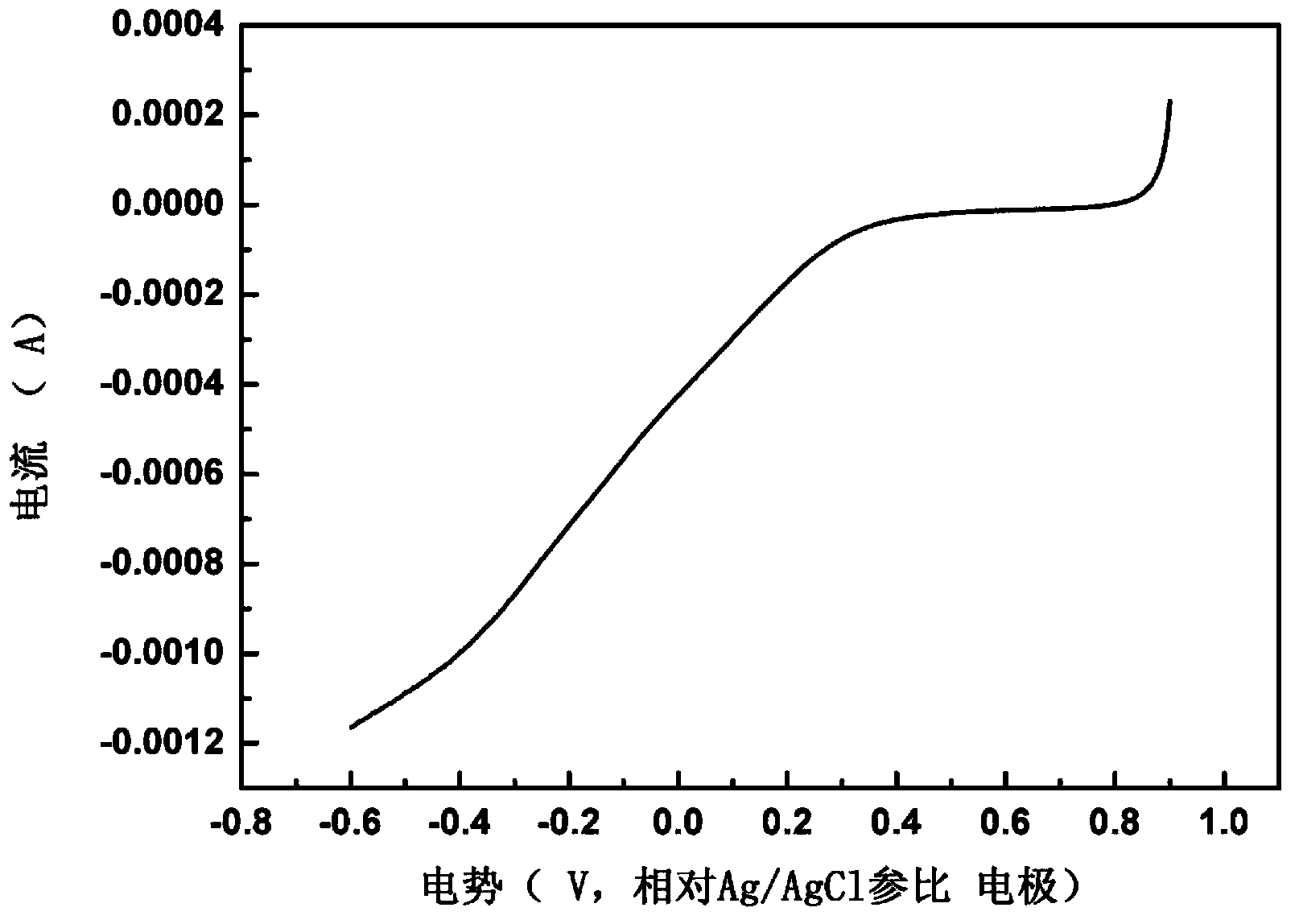
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
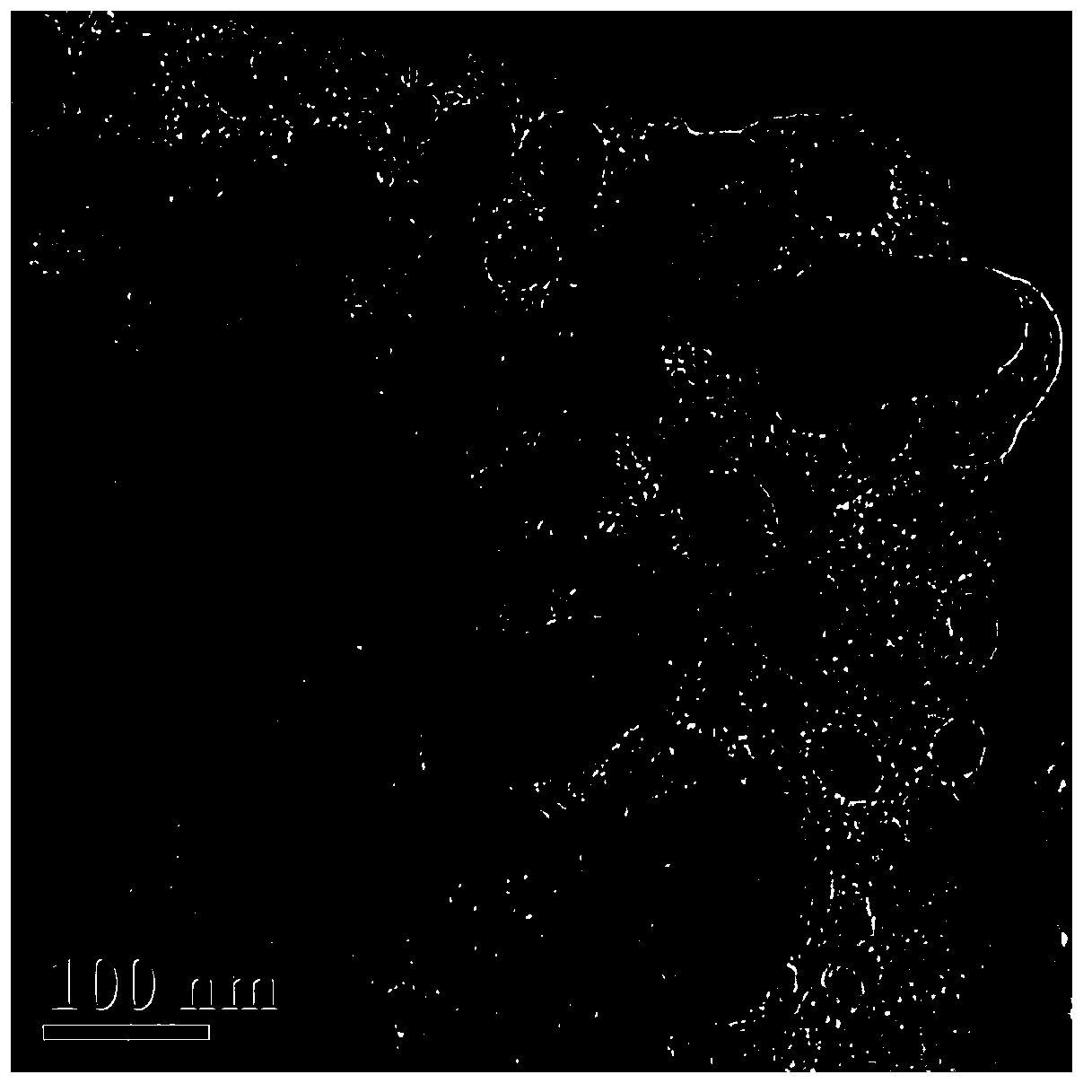
[0029] Weigh 8g of ferric ammonium citrate, dissolve it in 15mL of aqueous solution containing 0.15g of graphene oxide, mix well and remove the solvent at 80°C; put the solid mixture in a quartz boat, and then put it into a tube equipped with a quartz tube In a furnace, under a nitrogen atmosphere, at 10°C min -1 Raise the temperature to 600°C, and keep it for 5 hours, take it out after cooling to room temperature. The obtained solid was dissolved in 0.1mol L -1 HClO 4 The solution was neutralized at 80° C. for 24 hours, filtered, washed and dried to obtain a graphene-carbon nanocage composite.
Embodiment 2
[0031] Weigh 8g of ferric ammonium citrate, dissolve it in 50mL of aqueous solution containing 0.3g of graphene oxide, mix well and remove the solvent by freeze-drying; put the solid mixture in a quartz boat, and then put it into a tube furnace equipped with a quartz tube in a nitrogen atmosphere at 15°C min -1 Raise the temperature to 1000°C, and keep it for 1 hour, take it out after cooling to room temperature. Dilute the obtained solid in 1mol L -1 h 2 SO 4 The solution was neutralized at 90° C. and treated for 12 hours, filtered, washed and dried to obtain a graphene-carbon nanocage composite material.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Weigh 8g of ferric ammonium citrate, dissolve it in 60mL of aqueous solution containing 0.6g of graphene oxide, mix well and remove the solvent at 80°C; put the solid mixture in a quartz boat, and then put it into a tube equipped with a quartz tube In a furnace, under a nitrogen atmosphere, at 5°C min -1 Raise the temperature to 800°C, and keep it for 2 hours, take it out after cooling to room temperature. Dilute the obtained solid in 2mol L -1 The HCl solution was neutralized at 70°C for 36 hours, filtered, washed and dried to obtain a graphene-carbon nanocage composite.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com