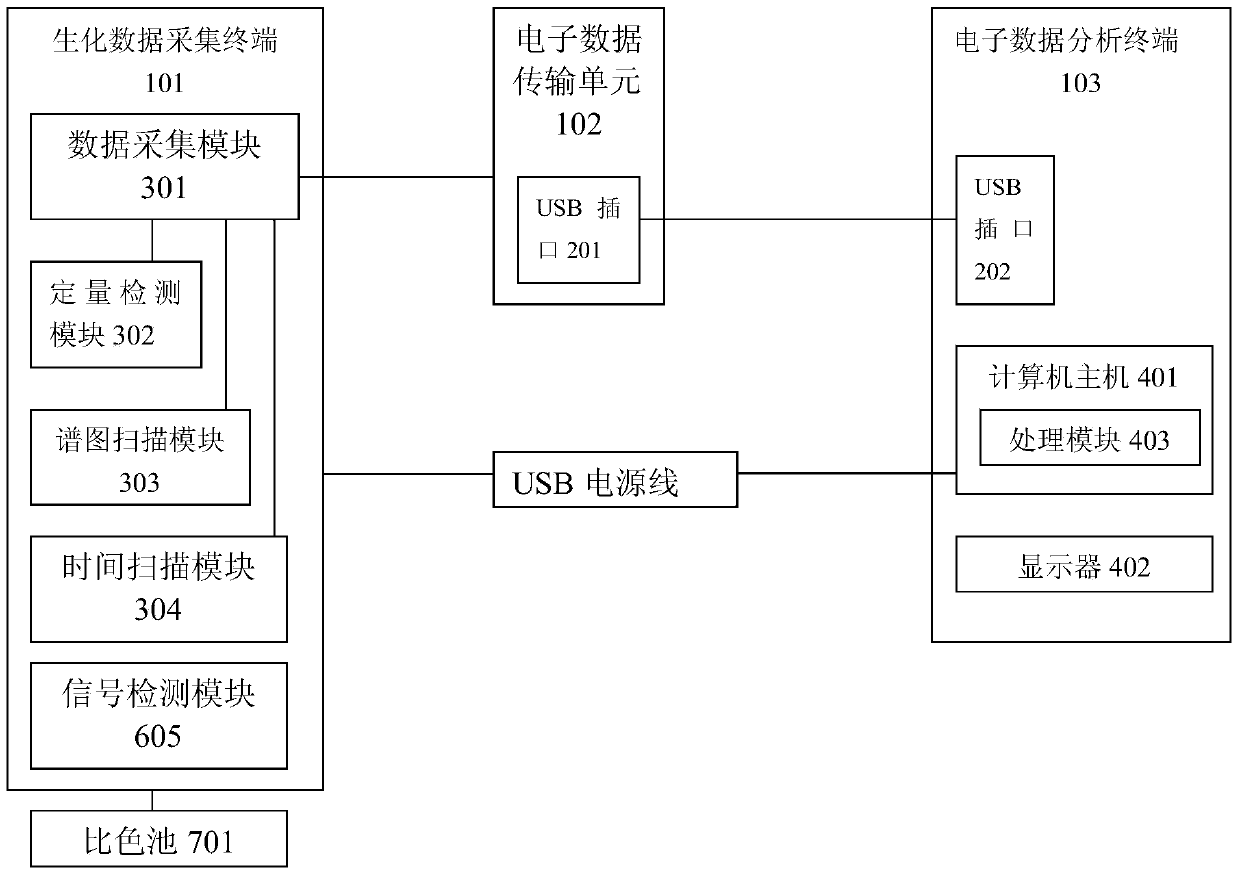
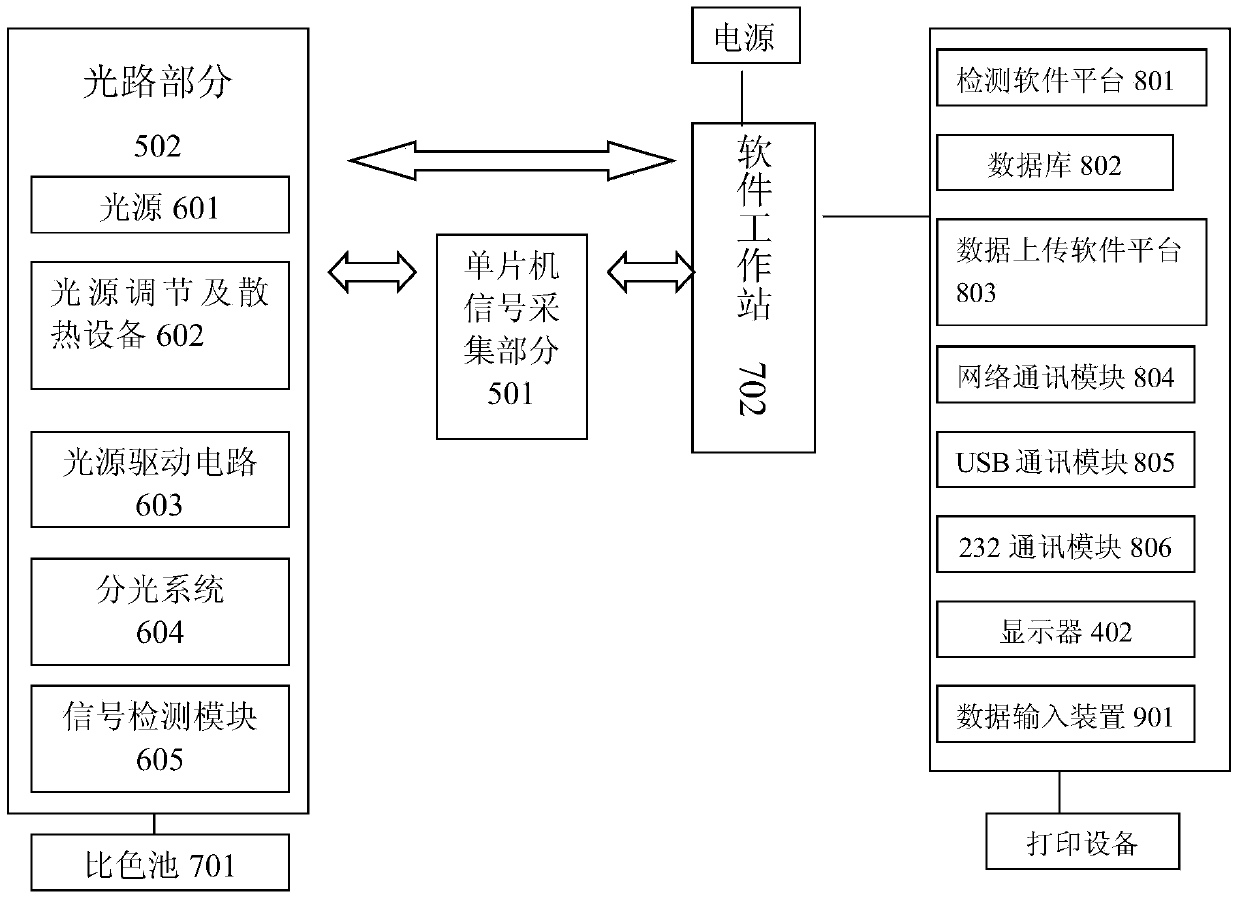
Method for detecting artificially synthesized edible pigments
A technology for artificially synthesizing pigments and synthetic pigments, which is applied in the measurement of color/spectral characteristics, etc., which can solve the problems of high cost, testing in a laboratory, and long testing time, and achieves low cost, improved supervision efficiency, and easy operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1 detects the step of the synthetic pigment in wolfberry
[0045] (1) Extraction of synthetic pigments: Take 6 grams of a commercially available wolfberry sample, wash the sample repeatedly with 60ml of distilled water until the extract is colorless, combine the washing solution into a 100ml beaker; centrifuge at 8000r / min for 10 minutes, and take the supernatant The pH of the solution was adjusted to 4 with tartaric acid;
[0046] (2) Separation of synthetic pigments:
[0047] a. Activation of the macroporous adsorption resin: put an appropriate amount of macroporous adsorption resin into a conical flask, add absolute ethanol and fully soak it. Then wash it with distilled water several times until there is no ethanol smell, and drain the water for later use;
[0048] b. Pigment adsorption: Weigh an appropriate amount of pretreated NKA-9 macroporous resin 1.5g and add it to a 100ml conical flask, add the treated pigment extract, add 1g of ammonium chloride ...
Embodiment 2
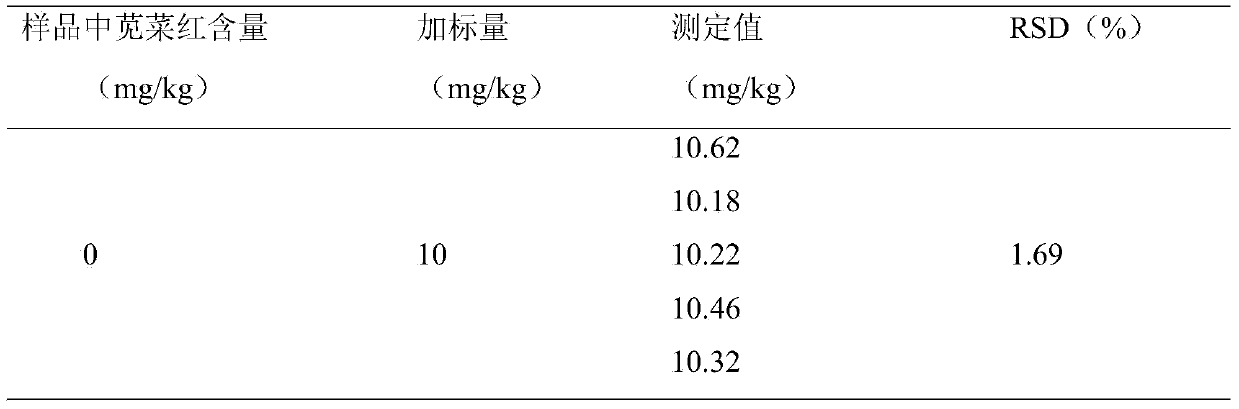
[0051] Example 2 Repeatability experiment of pigment detection method.
[0052] Weigh 0.1 g of amaranth standard substance and dissolve it in a 100ml volumetric flask to prepare a 1 μg / μl standard solution. Take 6 grams of a commercially available wolfberry sample, wash the sample repeatedly with 60ml of distilled water, combine the washing liquid into a 100ml beaker, add 60ul of a 1μg / μl standard solution, and stir evenly. Centrifuge at 8000r / min for 10 minutes, take the supernatant and adjust the pH to 4 with tartaric acid. Weigh the treated NKA-9 macroporous resin and carry out adsorption and desorption according to the steps in Example 1, and measure after making the sample liquid to be tested. Repeat the above steps 6 times, it can be seen from the obtained experimental data that RSD<5%, indicating that the method has good repeatability.
[0053] Table 1 The repeatability experimental data of amaranth detection
[0054]
[0055]
Embodiment 3
[0056] Example 3 Pigment detection method precision and accuracy experiments.
[0057] Weigh 0.1 g of amaranth and carmine standard substances and dissolve them in a 100ml volumetric flask to prepare a 1 μg / μl standard solution. The operation was carried out according to the steps of Example 2, and the volume of the standard solution added was changed to 300 μl, and the rest of the steps were the same as in Example 2, and repeated 6 times.
[0058] Table 2 The recovery data of amaranth and carmine
[0059]
[0060] It can be seen from Table 2 that the recovery error of amaranth and carmine is within 5%, indicating that this method has good accuracy and precision, and can fully meet the needs of quantitative analysis and determination of synthetic pigments.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com