High-temperature superconducting magnet online monitoring system
A high-temperature superconducting and monitoring system technology, applied in thermometers, measuring devices, measuring heat, etc., can solve the problems of temperature, current and voltage monitoring difficulties, small heat capacity, and aggravating the danger of hot spots.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0048] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
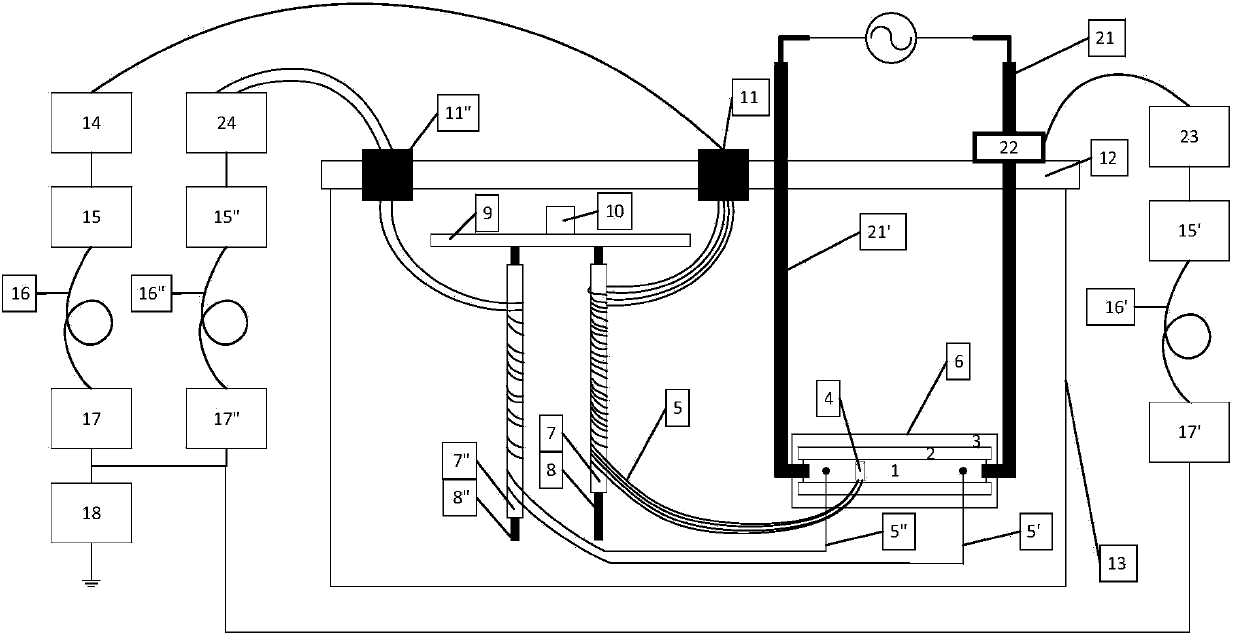
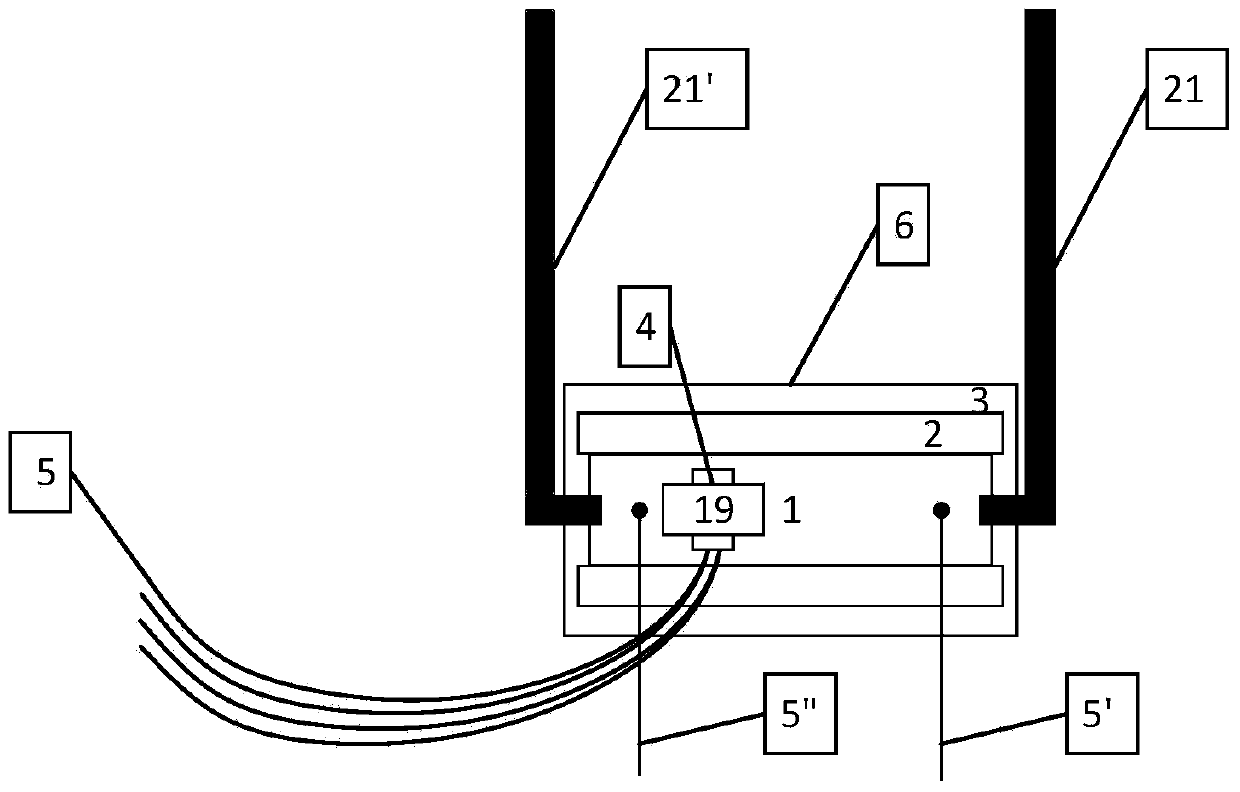
[0049] Figure 1 ~ Figure 3 Shown is the online monitoring system of the high temperature superconducting magnet of the present invention.
[0050] figure 1 Shown, the online monitoring system of the present invention comprises:
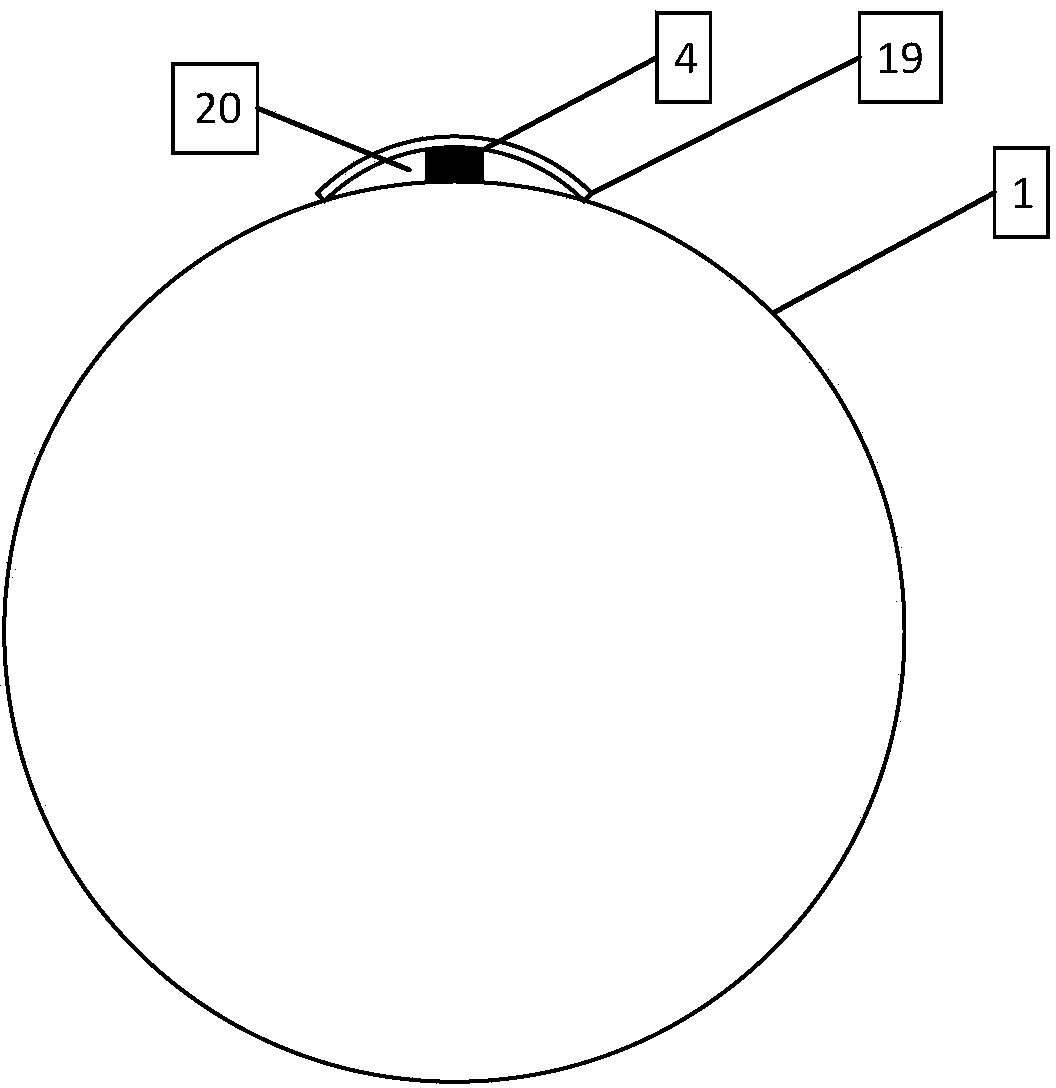
[0051] 1) A high-temperature superconducting magnet system 6, which includes: a high-temperature superconducting strip 1, a conduction-cooled superconducting magnet skeleton 2, a first current lead 21 and a second current lead 21'; The superconducting strip 1 is wound on the conduction cooling superconducting magnet skeleton 2; one end of the first current lead 21 and the first end of the high temperature superconducting strip 1 are connected to each other by welding, The other end of the first current lead 21 is connected to the first end of the external power supply; one end of the second current lead 21' is co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com