Parallel computing method for distributed hydrodynamic model of large-scale watershed system
A parallel computing and large-scale technology, applied in computing, concurrent instruction execution, machine execution devices, etc., can solve the problem that the hydrodynamic model cannot simulate the hydrodynamic conditions of large-scale water systems with fine grids, and achieve high efficiency and high efficiency. Precision computing, accuracy assurance, and the effect of using computer hardware and software resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
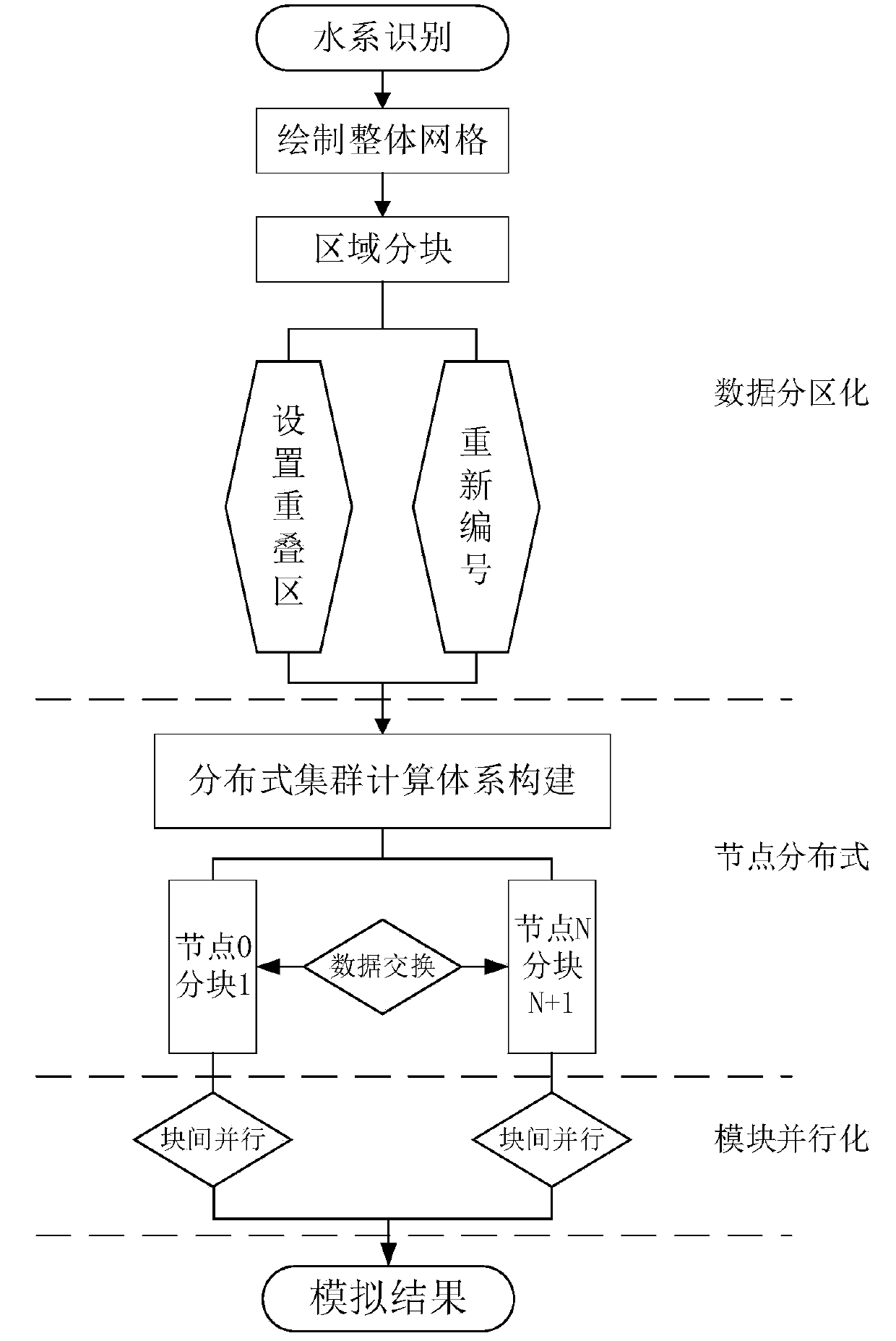
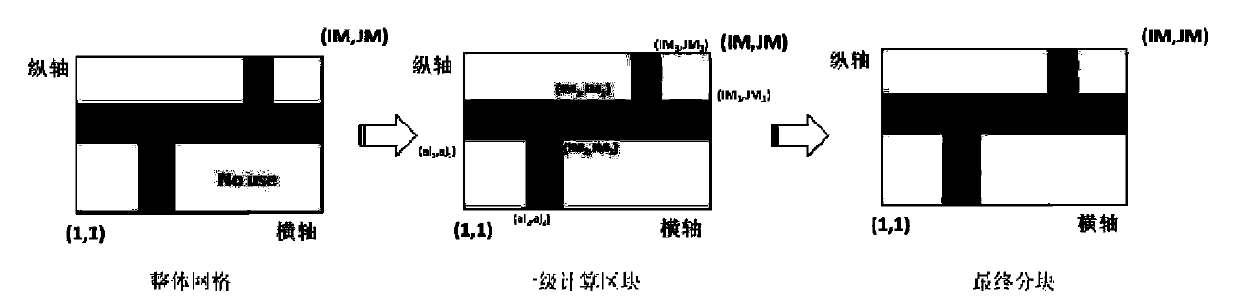
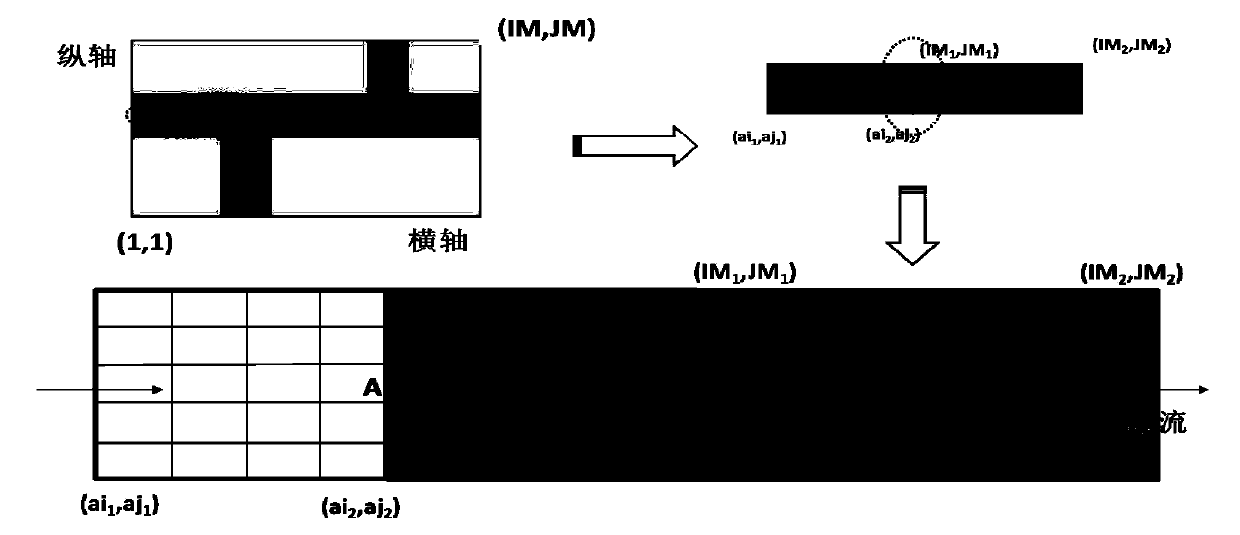
[0041] In order to facilitate those of ordinary skill in the art to understand and implement the present invention, the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the implementation examples described here are only used to illustrate and explain the present invention, and are not intended to limit this invention.
[0042] The theory of watershed hydrodynamic model is mature, the mechanism is rich, and it has a history of decades of development. Now it has been widely used in various fields of fluid calculation. Large-scale fluid dynamic calculation has attracted more and more attention from all walks of life. One of the main factors in the development and application of the model is still the speed and effect of its calculation. The limitation of the inherent 2G array memory of the win32 operating system and the incompatibility between the fineness of the model grid and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com