Multifunctional ecological purification system for large-scale circulation breeding water
A technology of ecological purification and recirculation breeding, which is applied in the field of aquaculture technology and water treatment, can solve the problems of less attention and waste of nutrients, and achieve the effects of strong purification stability, water conservation and water conservation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
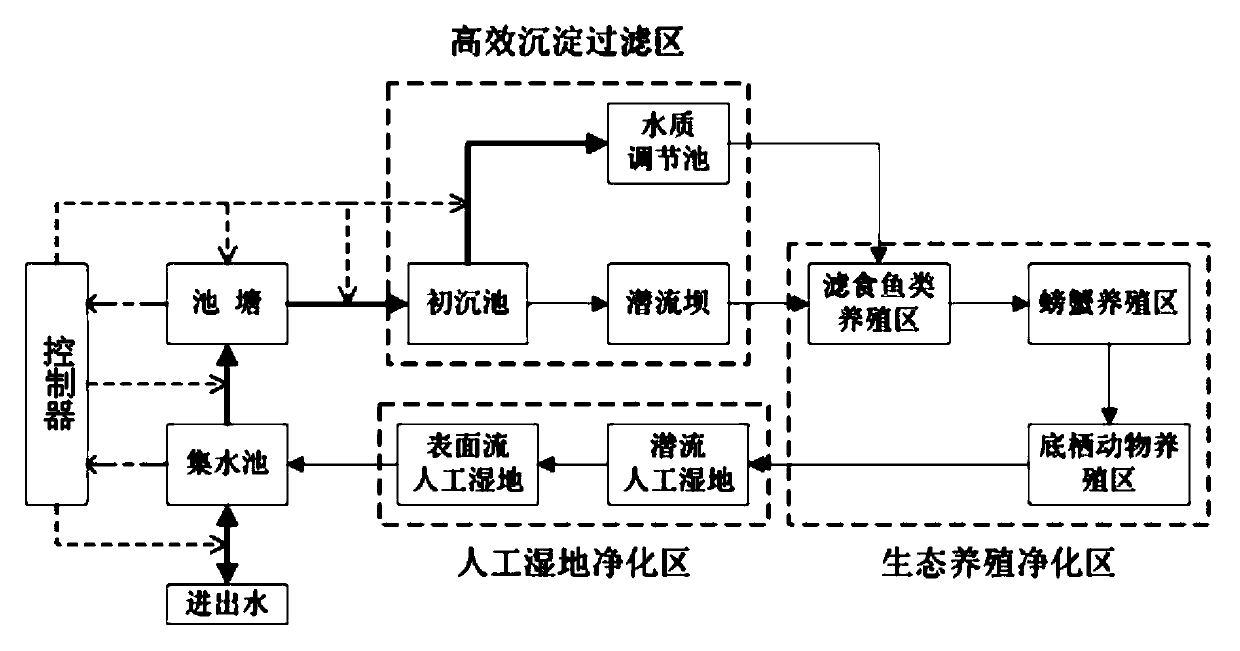
[0039] A multifunctional ecological purification system for large-scale circulating aquaculture water, such as figure 1 , figure 2As shown, the system includes a high-efficiency sedimentation filtration area, an ecological breeding purification area, and a constructed wetland purification area. It is also equipped with an automatic water quality monitoring and control device. At the same time, the aquatic animals, plants and sediment produced in the purification system can realize resource recycling.
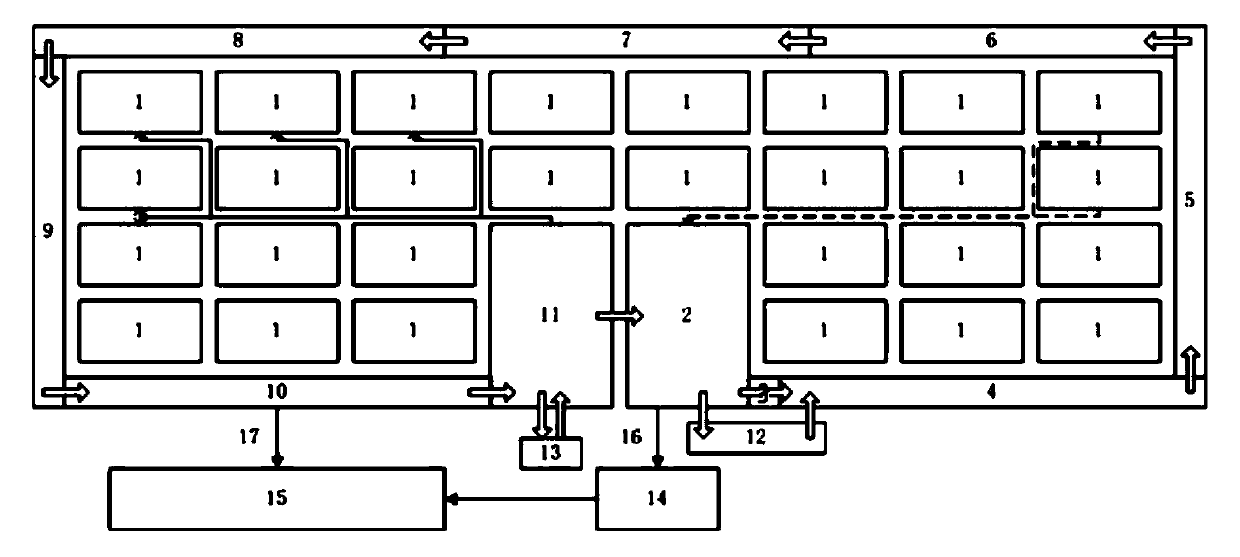
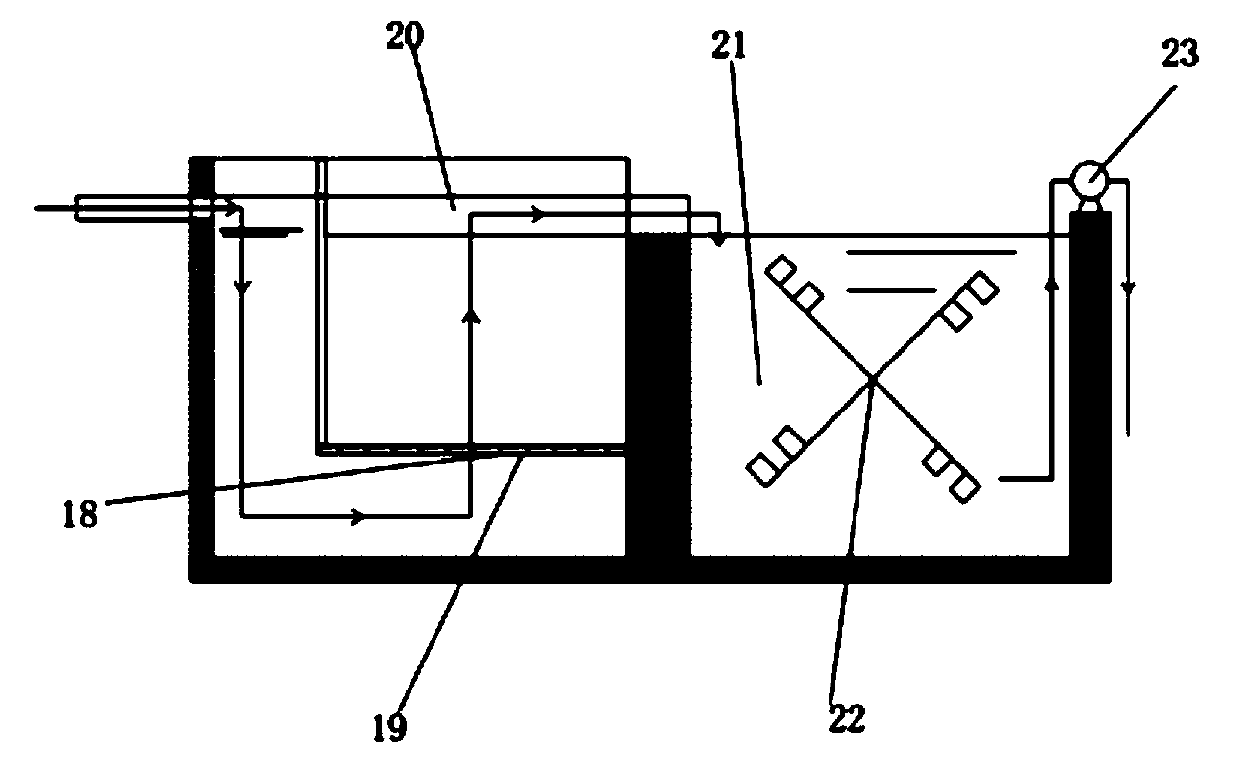
[0040] Such as figure 2 As shown, pond 1 is connected to primary sedimentation tank 2 through PVC pipes. When the purification starts, the tail water discharged from the pond 1 containing the excrement and bait from the culture enters the primary sedimentation tank 2 through the action of the pump for pretreatment. During conventional purification, the pretreated tail water enters the subsurface dam 3, the filter-feeding fish breeding area 4, the crab breeding area 5, the be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com