Two-Shaft Gas Turbine
A gas turbine, dual-shaft technology, used in gas turbine installations, mechanical equipment, engine control, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0033] 1. Twin-shaft gas turbine
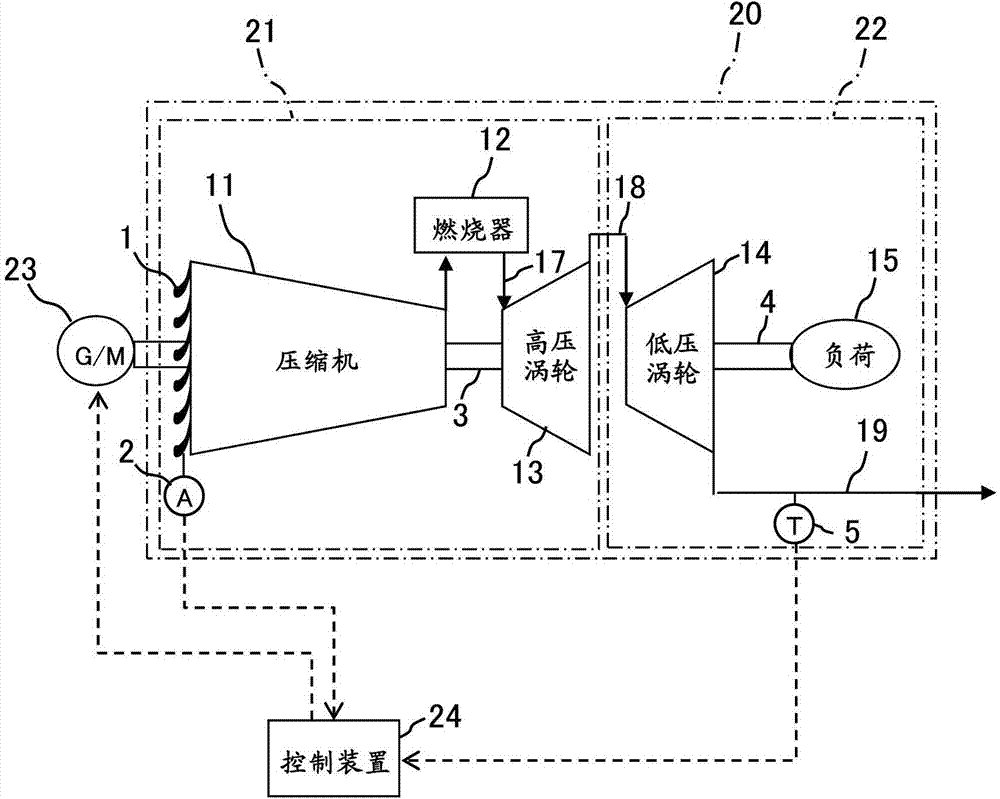
[0034] figure 1 It is a configuration diagram of the twin-shaft gas turbine according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0035] A twin-shaft gas turbine 20 shown in the figure includes a gas generator 21 , an output turbine 22 , a generator motor 23 , and a control device 24 .
[0036] (1) Gas generator
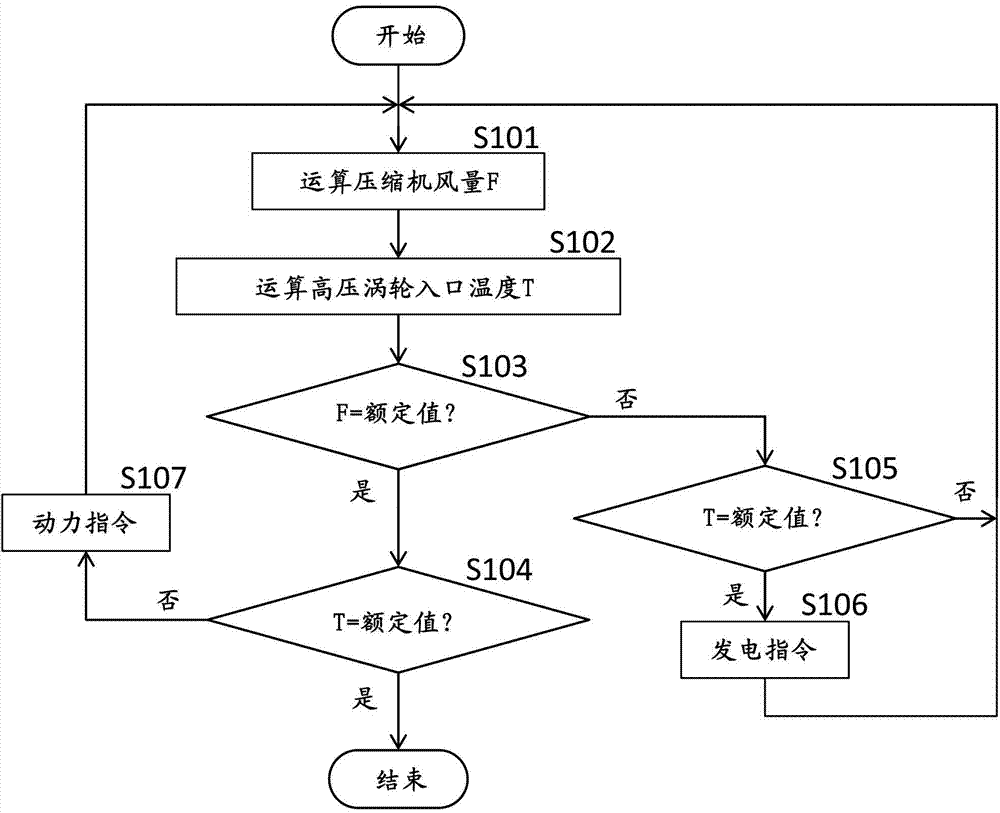
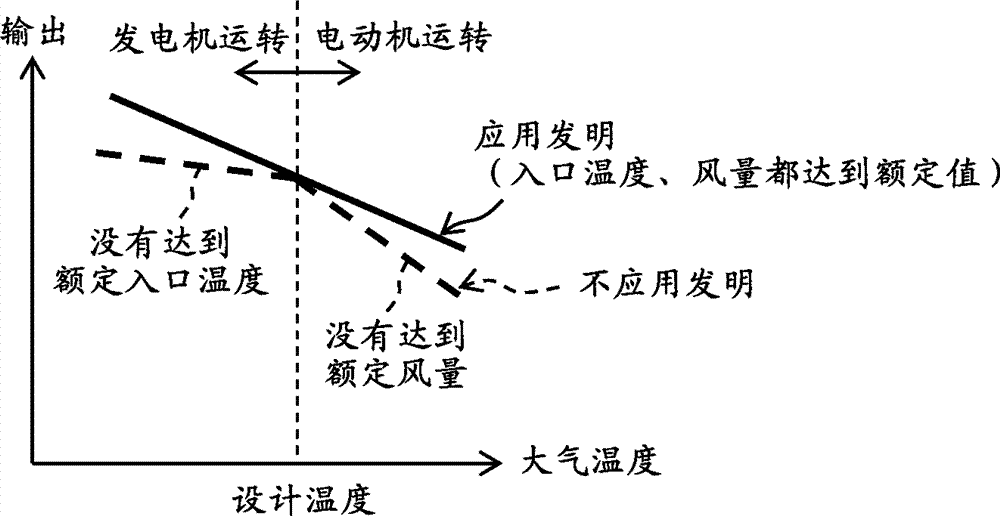
[0037] The gas generator 21 includes a compressor 11 , a combustor 12 , and a high-pressure turbine 13 as main elements. The compressor 11 compresses air taken in from the atmosphere to generate compressed air. An IGV (Inlet Guide Vane) 1 is provided at an inlet (air inlet) of the compressor 11 . The IGV1 is driven by an IGV driving device (not shown), and the air intake amount of the compressor 11 is changed by adjusting the opening degree of the IGV1. The angle detector 2 which detects the angle of the vane (opening degree of IGV1) is provided in IGV1. The combustor 12 mixes and combusts the compressed air from the c...
no. 2 approach
[0066] Figure 5 is a structural diagram of a twin-shaft gas turbine according to a second embodiment of the present invention, and is the same as figure 1 corresponding figure. In this figure, the same reference numerals as those in the preceding figures are assigned to the contents already explained, and description thereof will be omitted.
[0067] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the twin-shaft gas turbine 20A of this embodiment differs from the twin-shaft gas turbine 20 of the first embodiment in that a fuel compressor 25 is connected to the gas generator 21 as a load conditioner instead of the generator motor 23 . The fuel compressor 25 is a device that compresses fuel gas and supplies the compressed fuel gas 26 to the combustor 12 , and is connected to the compressor 11 via the gas generator shaft 3 . When the operating fluid of the compressor 11 reaches the rated flow rate (for example, when the IGV1 is fully opened or exceeds the set opening degree), the control device ...
no. 3 approach
[0070] Figure 6 is a structural diagram of a twin-shaft gas turbine according to a third embodiment of the present invention, and is the same as figure 1 corresponding figure. In this figure, the same reference numerals as those in the preceding figures are assigned to the contents already explained, and description thereof will be omitted.
[0071] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the difference between the twin-shaft gas turbine 20B of the present embodiment and the twin-shaft gas turbine 20 of the first embodiment is that, instead of the generator motor 23 , an extraction air flow control valve 27 is provided as a load regulator. The air extraction flow adjustment valve 27 is provided on the air extraction line 28 for extracting compressed air from the compressor 11 . The suction line 28 connects, for example, the intermediate section of the compressor 11 and the inlet of the low-pressure turbine 14 . In the present embodiment, when the air volume of the compressor 11 reach...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com