Micro-fluidic spectral waveguide structure for regulating light sensing gene
A technology of waveguide structure and light-sensing genes, which is applied in specific-purpose bioreactors/fermenters, enzymology/microbiology devices, tissue cell/virus culture devices, etc., can solve the problem of being unable to achieve multi-point tiny light source stimulation Nerve cells, inability to achieve fixed-point culture, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The technical solutions of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and through specific implementation methods.
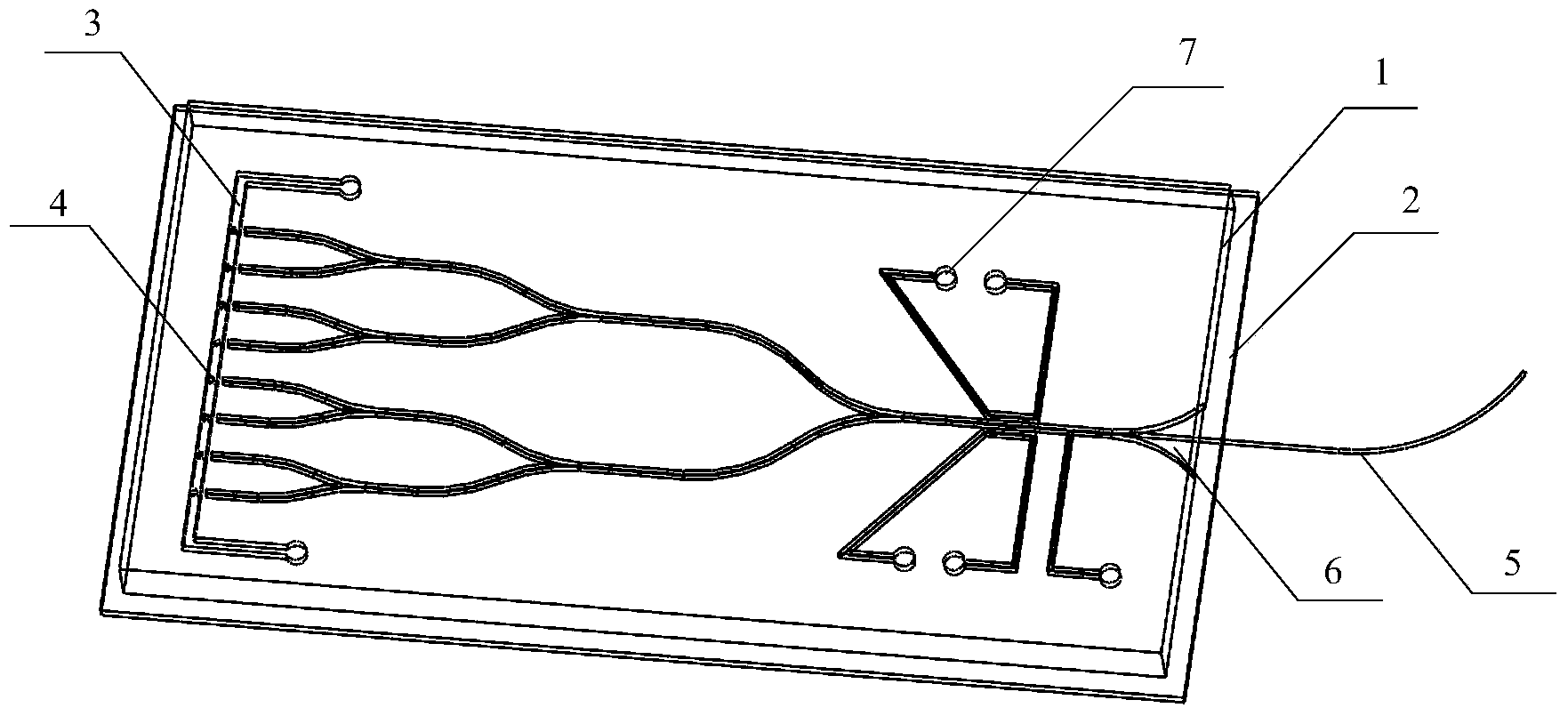
[0021] figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of a microfluidic light-splitting waveguide structure for light-sensing gene regulation provided by a specific embodiment of the present invention. like figure 1 As shown, a microfluidic light-splitting waveguide structure for light-sensing gene regulation according to the present invention includes: a light-splitting waveguide chip 1, an electrode detection recording sheet 2 and a cell culture channel 3, and the cell culture channel 3 It is arranged at the light outlet of the light-splitting waveguide chip 1; the light-splitting waveguide chip 1 adopts a multi-splitting light-splitting structure, which is used to divide the stimulating light into multiples, and the stimulating light is used to control the light in the cell culture channel 3. Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com