Method for in-situ remediation of heavy metal hexavalent chromium-contaminated soil
A technology for in-situ remediation and contaminated soil, applied in the field of soil pollution remediation, can solve problems such as immature operation methods, and achieve the effects of low cost, high removal efficiency and good safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
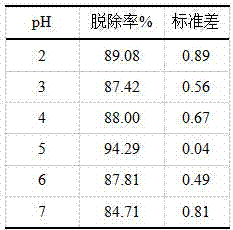
[0032] Example 1 Determination of the optimum reaction pH value
[0033] The following experiments were designed to study the optimal pH conditions for the in-situ removal of hexavalent chromium in polluted soil by MFC: Mix the polluted soil and add it to a reactor with a length, width and height of 0.5m*0.5m*0.5m as a contaminated soil treatment unit According to the series connection, the anode group and the cathode group are respectively buried in the polluted soil and connected by wires. Adjust the pH range of the polluted soil to 2-7. The reaction was run at a constant temperature of 25±1°C for 6 days. During the measurement, randomly take soil samples from 3 parallel groups, mix them evenly, accurately weigh 5 g of the mixed soil samples, put them into a 100 ml beaker, add 50 ml of 0.4 mol / L KCl solution, stir electromagnetically for 5 min, and centrifuge (6500 rpm, 10 ~ 20 min) for separation, the supernatant was taken, and the concentration of hexavalent chromium re...
Embodiment 2
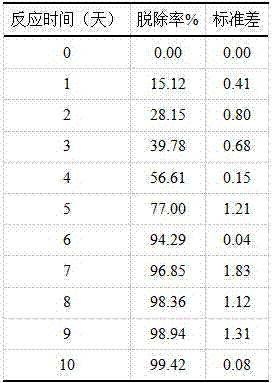
[0037] Embodiment 2 Determination of optimal reaction time
[0038] The following experiment was designed to study the optimal reaction time of MFC for in-situ removal of hexavalent chromium in polluted soil: mix the polluted soil and add it to a reactor with a length, width and height of 0.5m*0.5m*0.5m as contaminated soil treatment In the unit, the anode group and the cathode group are respectively buried in the polluted soil in series and connected by wires. Adjust the pH of the contaminated soil to 5. The reaction was run at a constant temperature of 25±1°C for 0–10 days. During the measurement, randomly take 3 soil samples and mix them evenly. Accurately weigh 5g of the mixed soil samples. As for the 100ml beaker, add 50ml of 0.4 mol / L KCl solution, electromagnetically stir for 5min, and centrifuge (6500 rpm, 10-20 min) Separate, take the supernatant, analyze the concentration of hexavalent chromium remaining in the aqueous solution by diphenylcarbazide spectrophotome...
Embodiment 3
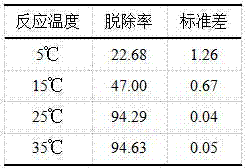
[0042] Embodiment 3 Determination of optimum reaction temperature
[0043] The following experiments were designed to study the optimum reaction temperature for in-situ removal of hexavalent chromium in contaminated soil by MFC: the contaminated soil was mixed and added to a reactor whose length, width and height were 0.5m*0.5m*0.5m respectively as the contaminated soil In the processing unit, the anode group and the cathode group are respectively buried in the polluted soil in series and connected by wires. Adjust the pH of the contaminated soil to 5. The reaction was run at a constant temperature of 5-35°C for 6 days. During the measurement, randomly take 3 soil samples and mix them evenly. Accurately weigh 5g of the mixed soil samples. As for the 100ml beaker, add 50ml of 0.4mol / L KCl solution, electromagnetically stir for 5min, and centrifuge (6500rpm, 10-20min) Separate, take the supernatant, analyze the concentration of hexavalent chromium remaining in the aqueous so...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com