Novel self-heat-preserving system of cast-in-place combined type wall body
A self-insulation system, combined wall technology, applied in the direction of insulation, walls, building components, etc., can solve the problems of poor durability, easy cracking of walls, and poor fire safety.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0085] (1) Construction and practice of self-insulating columns, self-insulating shear walls, self-insulating beams and self-insulating floors:
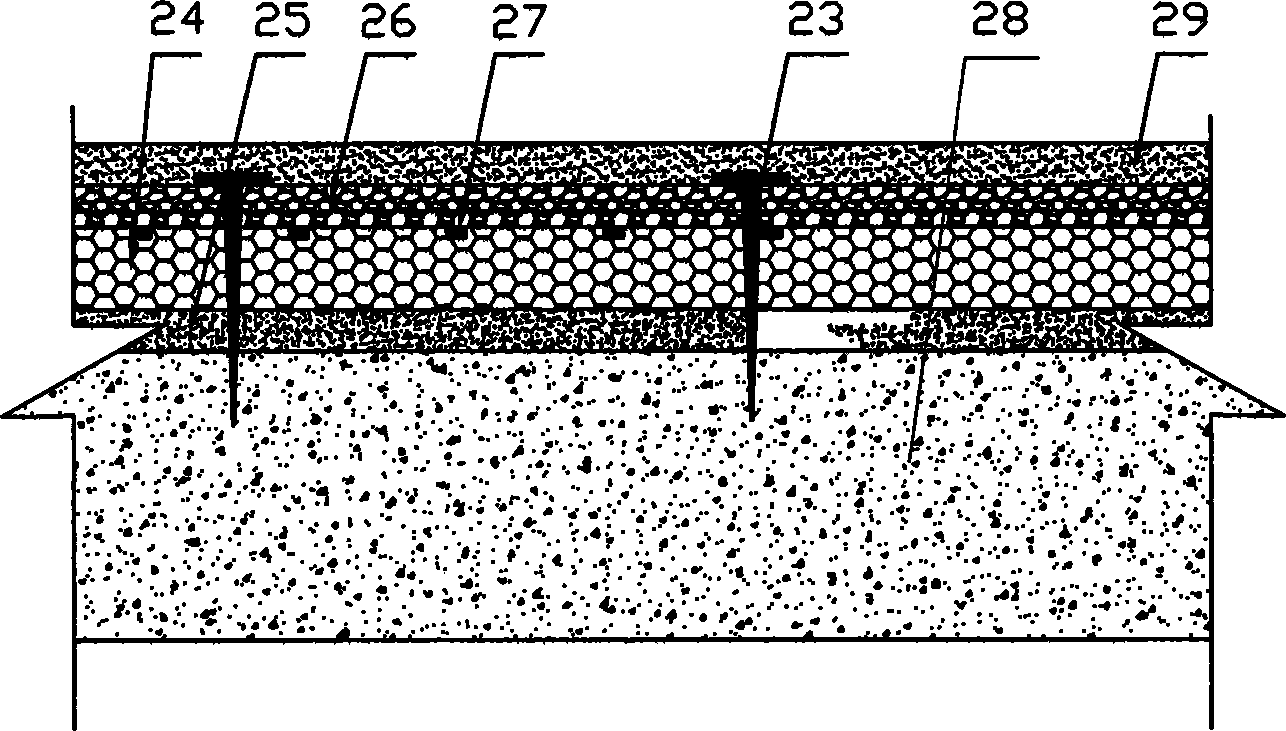
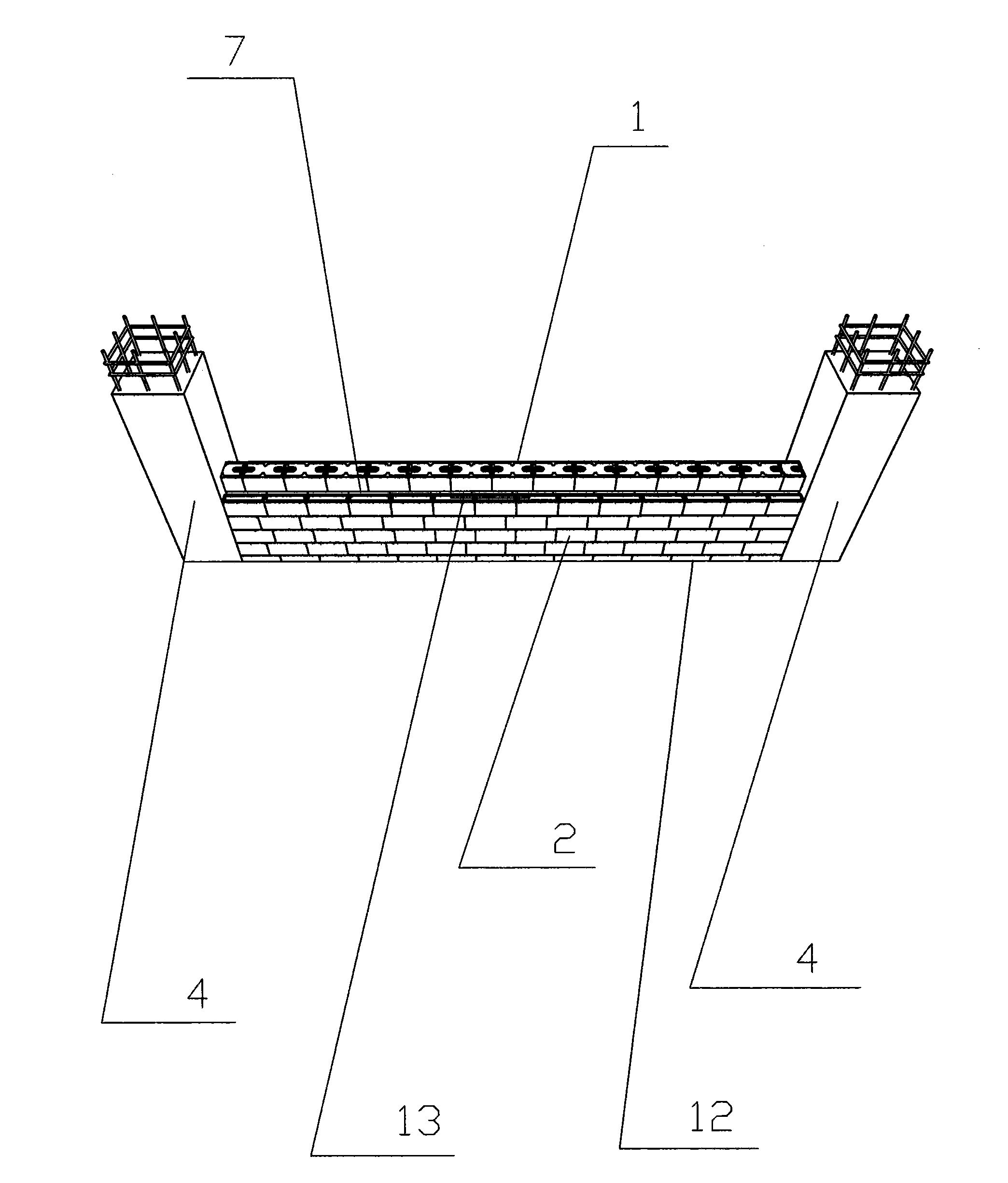
[0086] The cast-in-place self-insulating wall structure includes self-insulating columns, self-insulating shear walls, self-insulating beams and self-insulating floors. like figure 1 , figure 2As shown, the high-strength composite thermal insulation board is composed of a polystyrene board 24, an inner reinforcement layer 25, an outer reinforcement layer 26 and a reinforcement rib 27. The inner reinforcement layer 25 is arranged on the inside of the polystyrene board 24, and the reinforcement rib 27 is arranged on the outer side of the polystyrene board 24. , the outer reinforcing layer 26 is arranged outside the reinforcing rib 27 . During construction, the high-strength composite thermal insulation board is placed on the outer side of the steel bars of the bound columns, walls, beams and floors, and a plurality of connecting fix...
Embodiment approach 2
[0094] (1) Construction and practice of self-insulating columns, self-insulating shear walls, self-insulating beams and self-insulating floors:
[0095] The cast-in-place self-insulating wall structure includes self-insulating columns, self-insulating shear walls, self-insulating beams and self-insulating floors. like figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, the high-strength composite thermal insulation board is composed of a polystyrene board 24, an inner reinforcement layer 25, an outer reinforcement layer 26 and a reinforcement rib 27. The inner reinforcement layer 25 is arranged on the inside of the polystyrene board 24, and the reinforcement rib 27 is arranged on the outer side of the polystyrene board 24. , the outer reinforcing layer 26 is arranged outside the reinforcing rib 27 . During construction, the high-strength composite thermal insulation board is placed on the outer side of the steel bars of the bound columns, walls, beams and floors, and a plurality of connecting fi...
Embodiment approach 3
[0103] (1) Construction and practice of self-insulating columns, self-insulating shear walls, self-insulating beams and self-insulating floors:
[0104] The cast-in-place self-insulating wall structure includes self-insulating columns, self-insulating shear walls, self-insulating beams and self-insulating floors. like figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, the high-strength composite thermal insulation board is composed of a polystyrene board 24, an inner reinforcement layer 25, an outer reinforcement layer 26 and a reinforcement rib 27. The inner reinforcement layer 25 is arranged on the inside of the polystyrene board 24, and the reinforcement rib 27 is arranged on the outer side of the polystyrene board 24. , the outer reinforcing layer 26 is arranged outside the reinforcing rib 27 . During construction, the high-strength composite thermal insulation board is placed on the outer side of the steel bars of the bound columns, walls, beams and floors, and a plurality of connecting fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com