Method for determining COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) value by laboratory microwave digestion method
A microwave digestion method and laboratory technology, applied in the field of COD determination, can solve the problems of long time-consuming, low efficiency and inapplicability of boiling reflux
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific embodiments.
[0022] Experiment overview:
[0023] This method is applicable to various types of water samples containing COD (chemical oxygen demand) value greater than 50mg / L; the upper limit of determination for undiluted water samples is 1000mg / L. This method is not suitable for chlorine-containing water samples with a chloride ion concentration greater than 1000mg / L (after dilution).
[0024] Experimental principle:
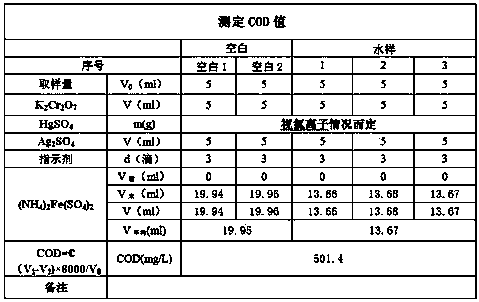
[0025] In a strong acidic solution, potassium dichromate is used to oxidize the reducing substances in the water sample, and microwave digestion is carried out in a closed (sealed) state. Excessive potassium dichromate uses ferrous iron as an indicator, and ferrous sulfate Ammonium drips back. Calculate the COD value of the water sample according to the amount of ammonium ferrous sulfate.
[0026] Instruments and medicines required for the experiment
[0027] (1) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com