Molecular mark of rice brown planthopper inhibition major gene qBph29(t) and application of molecular mark
A technology of anti-BPH and main gene, applied in the field of plant molecular genetics, can solve problems such as difficult to effectively introduce and aggregate anti-insect genes, complex identification of insect resistance, etc., and achieve convenient identification, simple detection methods, and clear selection targets Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
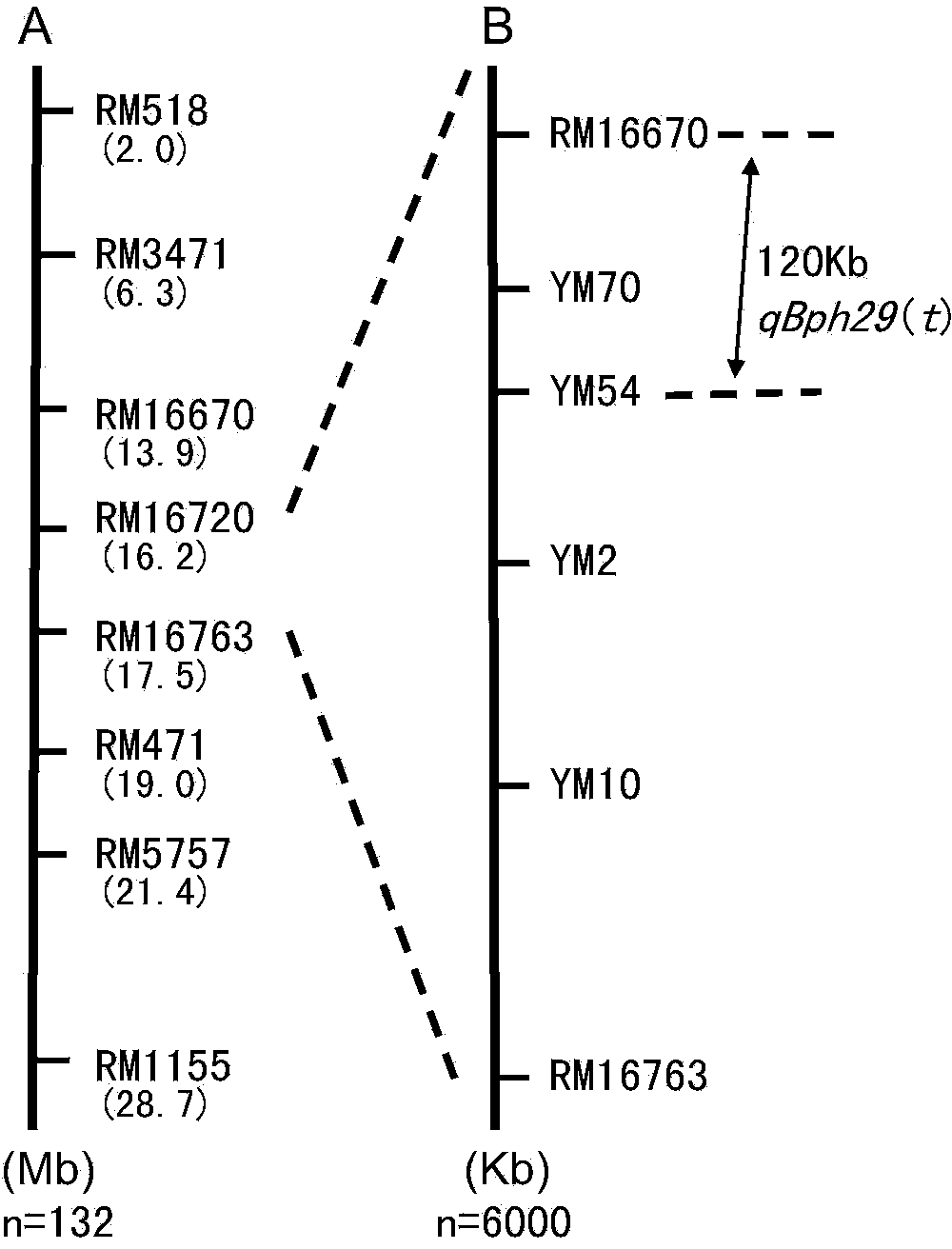
[0024] Example 1: Acquisition of Molecular Markers
[0025] (1) 186S / 08BPH327F 2 Population construction and phenotyping
[0026] (1) In the previous research, researcher Li Rongbai of Guangxi University screened a large number of wild rice materials with high resistance to brown planthopper from a large number of common wild rice materials in Guangxi. Through hybridization and backcrossing with cultivated rice varieties, combined with the identification of brown planthopper resistance, The resistance traits were transferred to cultivated rice materials, and after multi-generation self-crossing and insect resistance identification, rice lines with high resistance to brown planthopper and stable agronomic traits were screened. Among them, the new resistance source 08BPH327 is the progeny material of the hybridization and backcrossing of the common wild rice that is resistant to brown planthoppers and Xixiangnuo. The insect resistance identification experiment shows that 08BPH3...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2: Verification of Molecular Markers
[0053] 1. Materials and methods
[0054] 1.1 Materials
[0055] Negative varieties: 30 copies, susceptible lines (species) 186S, 9311, Nipponbare, Taichung Native No. 1, Baimao and Bai R54, all of which are conventional rice materials preserved in our laboratory, offspring of 186S×08BPH327 or 9311×08BPH327 hybrid combinations 24 susceptible families in the
[0056] Positive varieties: 29 insect-resistant lines in the progeny of high insect-resistant lines 08BPH327, 186S×08BPH327 or 9311×08BPH327 hybrids.
[0057] YM70 is a molecular marker designed and developed based on the corresponding sequences of 08BPH327 and 9311 genomes.
[0058] The upstream primer of the primer pair for amplifying the molecular marker is the sequence shown in Seq ID NO.1, and the downstream primer of the primer pair is the sequence shown in Seq ID NO.2;
[0059] Seq ID NO.1: 5'-CTCTCCCCTCCAATCCTTTT-3'
[0060] Seq ID NO.2: 5'-AGCACCCTGGAAAGCAG...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com