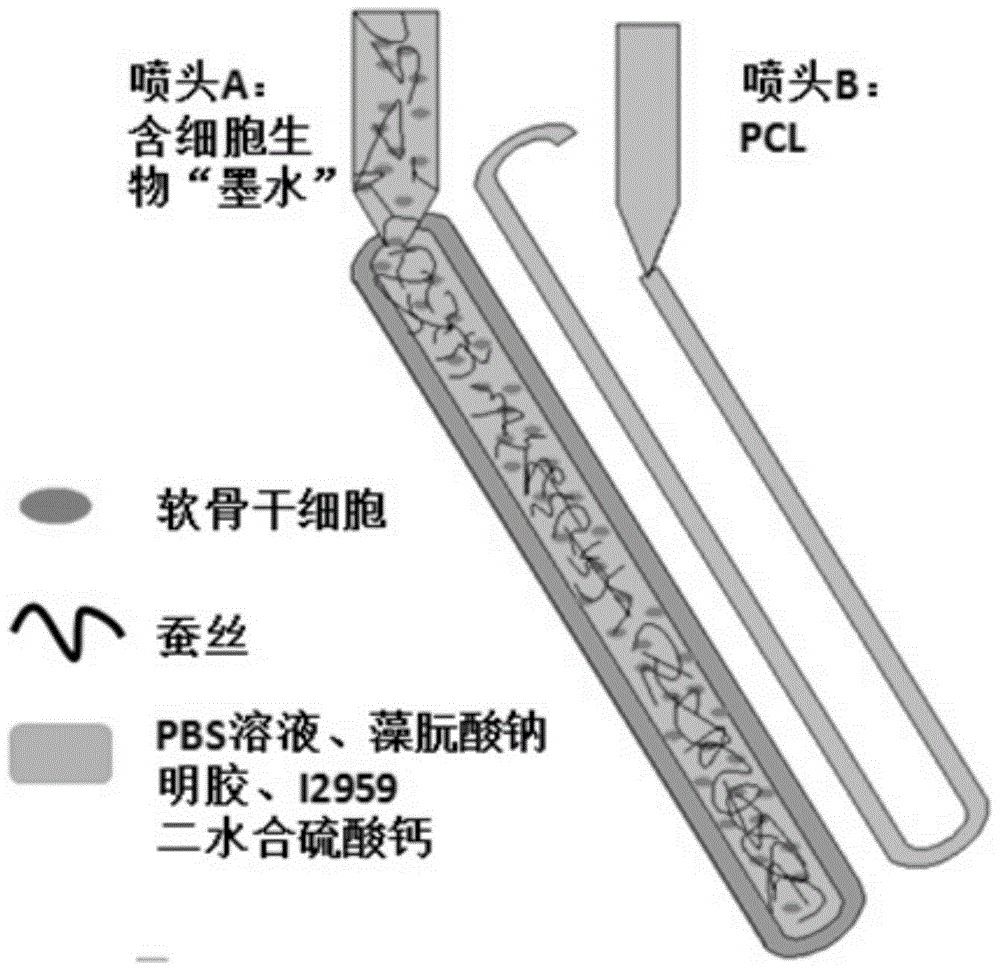
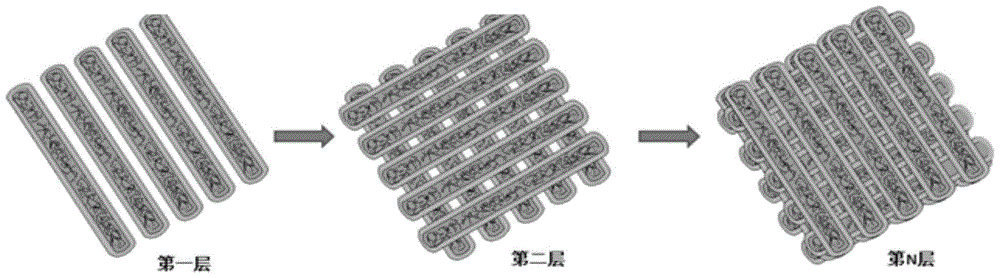
Method for preparing cartilage with high mechanical properties based on 3D bioprinting
A technology of bioprinting and cartilage, applied in the field of 3D bioprinting, can solve the problems of low cell survival rate and poor mechanical properties, and achieve the effect of improving mechanical properties, excellent mechanical properties, and not easy to break
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] (1) Silk fiber preparation: cut silkworm cocoons into pieces with a side length of 0.5 cm, put the pieces into a sodium carbonate solution with a volume molar concentration of 0.02M, stir and boil for 40 minutes, rinse the silk three times for 20 minutes, take it out with tweezers and dry it overnight. Drop a lithium bromide solution with a volume molar concentration of 10.0M on the silk and incubate at 70°C for 3 hours, put the cultured silk into a dialysis box and dialyze in ultrapure water for 24 hours, take out the silk solution in the dialysis box, centrifuge twice, and incubate at 4°C Save it.
[0023] (2) Preparation of gelatin solution: Add 7.0% wt gelatin in phosphate buffer solution to the phosphate buffer solution, stir continuously at 45°C until the gelatin is completely dissolved, and add 1.5 mL to the solution while stirring at a speed of 0.5 mL / min. A methacrylic anhydride solution with a mass concentration of 94% was reacted at 50°C for 1 hour, then dilu...
Embodiment 2
[0029] (1) Silk fiber preparation: cut the silkworm cocoons into pieces with a side length of 1.0 cm, put the pieces into a sodium carbonate solution with a volume molar concentration of 0.02M, stir and boil for 50 minutes, rinse the silk three times for 20 minutes, take it out with tweezers and dry it overnight. Drop a lithium bromide solution with a volume molar concentration of 7.0M on the silk and incubate at 50°C for 5 hours, put the cultured silk into a dialysis box and dialyze in ultrapure water for 48 hours, take out the silk solution in the dialysis box, centrifuge twice, and incubate at 4°C Save it.
[0030](2) Preparation of gelatin solution: Add 10.0% wt gelatin in phosphate buffer to phosphate buffer, stir continuously at 60°C until the gelatin is completely dissolved, and add 0.5 mL to the solution while stirring at a speed of 1.0 mL / min. A methacrylic anhydride solution with a mass concentration of 94% was reacted at 50°C for 1 hour, then diluted with 40 mL of p...
Embodiment 3
[0036] (1) Silk fiber preparation: cut the silkworm cocoon into 0.8cm pieces with a side length, put the pieces into a sodium carbonate solution with a volume molar concentration of 0.02M, stir and boil for 30min, rinse the silk three times for 20min, take it out with tweezers and dry it overnight. Drop a lithium bromide solution with a volume molar concentration of 12.0M on the silk and incubate at 30°C for 2 hours, put the cultured silk into a dialysis box and dialyze in ultrapure water for 60 hours, take out the silk solution in the dialysis box, centrifuge twice, and incubate at 4°C Save it.
[0037] (2) Preparation of gelatin solution: Add 12% wt of gelatin in phosphate buffer to phosphate buffer, stir continuously at 30°C until the gelatin is completely dissolved, add 1mL of mass to the solution while stirring at a speed of 0.1mL / min The methacrylic anhydride solution with a concentration of 94% was reacted at 50°C for 1h, then diluted with 40mL phosphate buffer at 40°C,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com