Hatching fluid enzymes and uses thereof
A technology of sequences and amino acids, applied in the field of hatching liquid enzymes and their uses, can solve the problem of high price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0183] Example 1: Identification and Characterization of VAPs
[0184] protein separation
[0185] During the analysis of the hatching fluid composition of Atlantic salmon, new proteins were identified that were present in the hatching fluid.
[0186] A method for preparing a portion of the hatching fluid from which zonase can be prepared which can be used as starting material for isolating the VAPs (or their precursor sequences) of the invention is provided in WO99 / 29836, incorporated herein For reference (in particular Example 1 of the process, but optionally without the urea step).
[0187] Therefore, the following method was used for separation. VAPs were isolated from hatching fluid (crude or filtered through a 0.45 μm filter). VAPs were then precipitated by adding 4x volumes of acetone at room temperature or 4°C. After 20-30 minutes, the precipitated VAPs were collected as a pellet after centrifugation at low speed (about 5000 xg) and resuspended in a suitable buff...
Embodiment 2
[0196] Example 2: In vitro medical / cosmetic applications of VAPs
[0197] Materials and methods
[0198] The following studies were performed with Atlantic salmon VAPs prepared as described in Example 1.
[0199] Differentiated human skin epithelial cultures were obtained from SkinEthics (Nice, France) 16 days after seeding onto plastic growth substrates with micropores allowing nutrients to reach the epithelial tissue from below. Such cultures exhibit normal skin morphology after differentiation during incubation at 37°C. These cultures were maintained in vitro for an additional 2 days, exposing the upper stratum corneum to air and the basal layer to the growth medium.
[0200] Parallel cultures were moved to media provided with a phosphate-buffered saline matrix containing Ca, Mg in the presence or absence of 0.5 mg / ml VAPs (measured at OD280) in a humidified atmosphere at 30°C for 6 hours. Cultures were formalin fixed and paraffin embedded and stained with hematoxylin / ...
Embodiment 3
[0205] Example 3: Medical / cosmetic application of choriolysin L in vivo
[0206] Materials and methods
[0207] The following studies were performed using choriolysin L of Atlantic salmon prepared from salmon hatching fluid as described by Yasumasu et al. 1989, supra.
[0208] Human skin epithelial cultures were prepared as described in Example 2, and 0.15 mU / ml oocysin L from salmon hatchery fluid was applied for 6 hours at 30°C.
[0209] result
[0210] A. Exfoliation
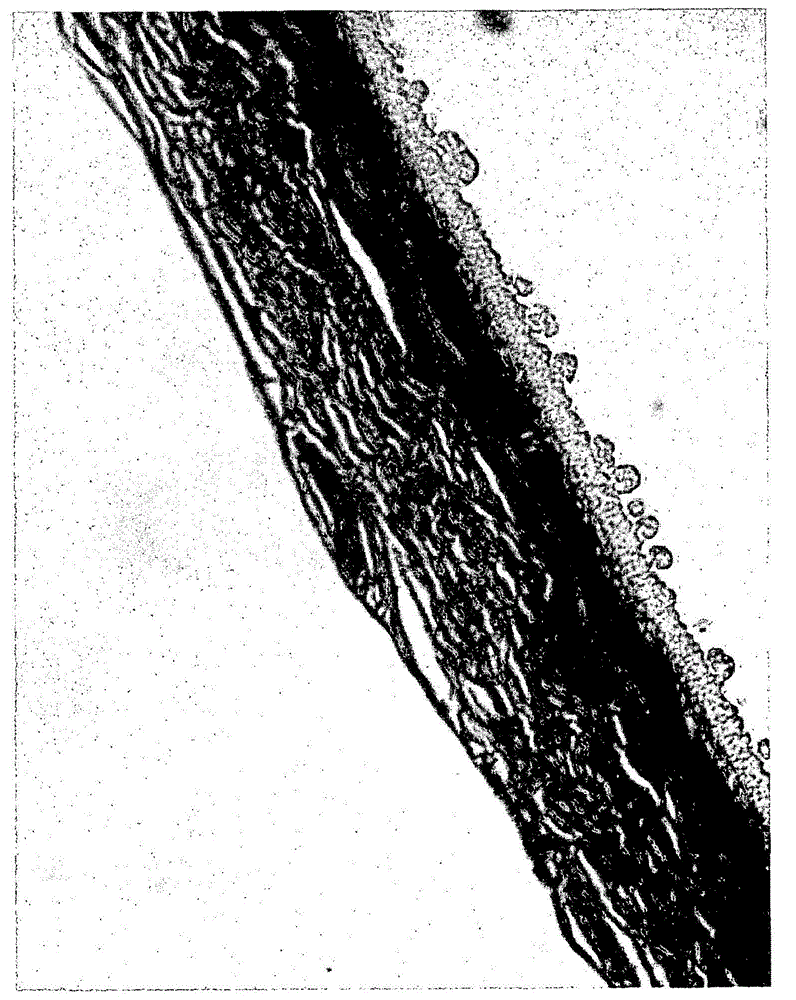
[0211] Figure 3A Results are shown in and B, where A shows skin cultures exposed to salmon ooshell lysin L and B shows control skin cultures. The results showed that choriolysin L caused the skin layers to delaminate and crack.
[0212] Exfoliation can also be analyzed by assessing the supernatant of the skin culture to assess the amount of epithelial cells removed from the skin culture during treatment. Since chotolysin L is inhibited by 1 mM EDTA, its effect can be easily inhibited to demonstrate i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com