MLPA-enhanced specific method for detecting SNP sites
A specific, 216G-CSNP technology, applied in the field of genetic testing, can solve the problems of not being able to meet high throughput, high accuracy and low price at the same time, affect the interpretation of results, and have not been resolved, so as to eliminate false positive product peaks, Effect of reducing base mismatch rate and improving specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0012] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, but not as any limitation to the present invention.
[0013] Embodiments of the invention:
[0014] 1 Materials and methods
[0015] 1.1 Main reagents and instruments
[0016] Locked nucleic acid (LNA) primers and probes were synthesized by Shanghai Huirui Biotechnology Co., Ltd., plasmids pcDNA3-Kras216G and pcDNA3-Kras216C were preserved in our laboratory, Taq enzyme (Dalian Bao Biological Company), T4-DNA ligase (Beijing NEB company), SYBRGREEN quantitative PCR Mastermix (Shanghai Roche Company), sequencer (US ABI3730), quantitative PCR instrument (US ABI7500).
[0017] 1.2 Method
[0018] 1.2.1 Primers
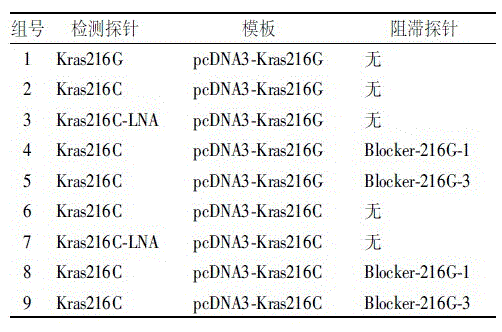
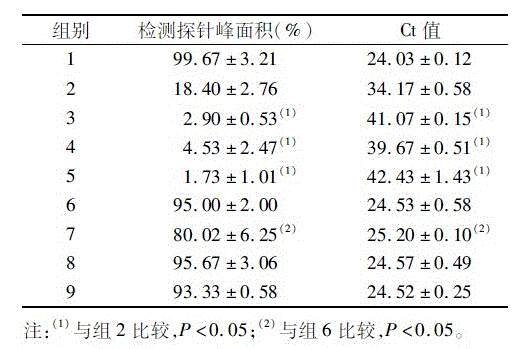
[0019] Using the pcDNA3-Kras216G plasmid containing the wild-type human Kras gene (ref|NM_004985.3|) and the pcDNA3-Kras216C plasmid containing the Kras gene at the 216-position G-CSNP site as templates, the corresponding MLPA probe sequences were desig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com