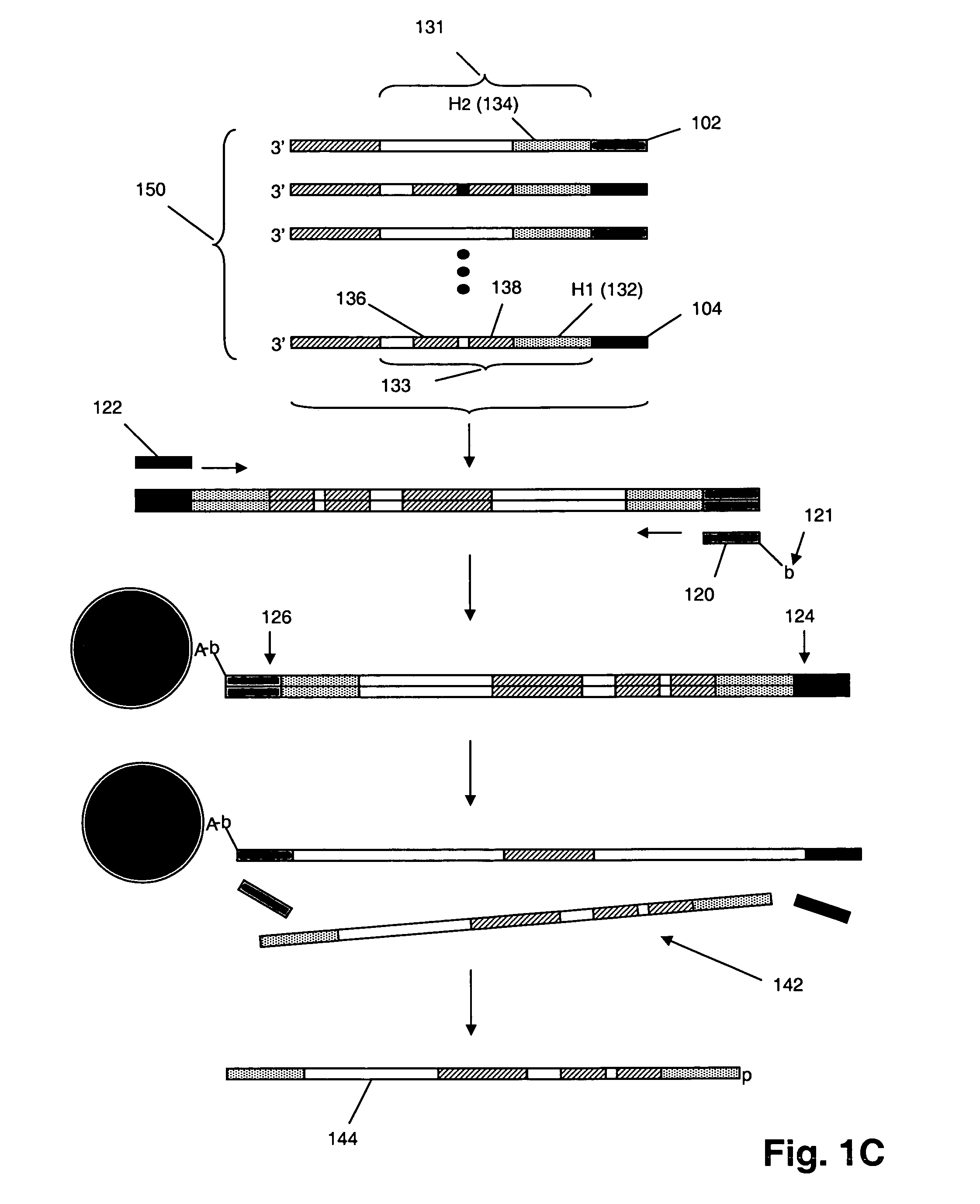
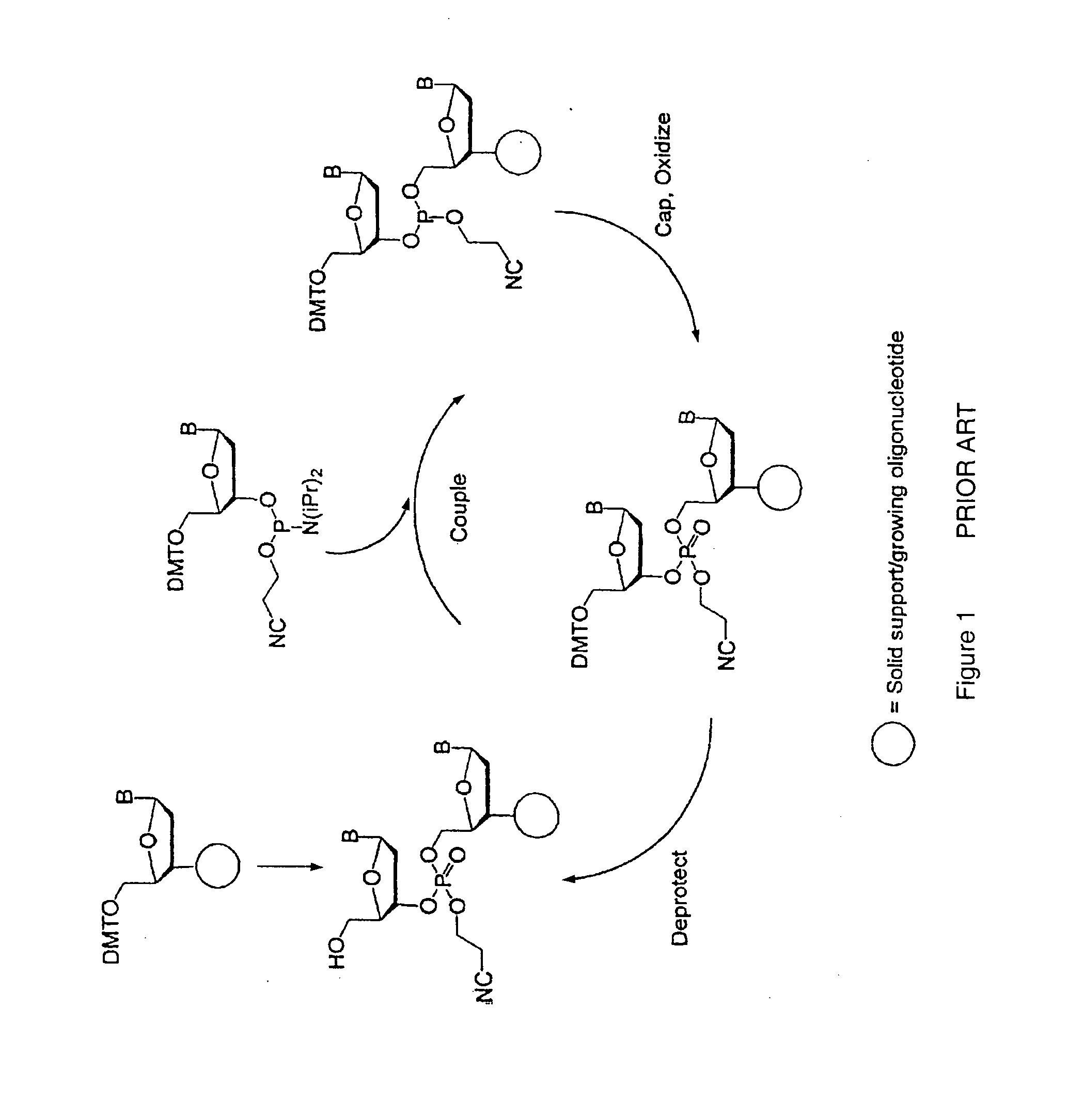
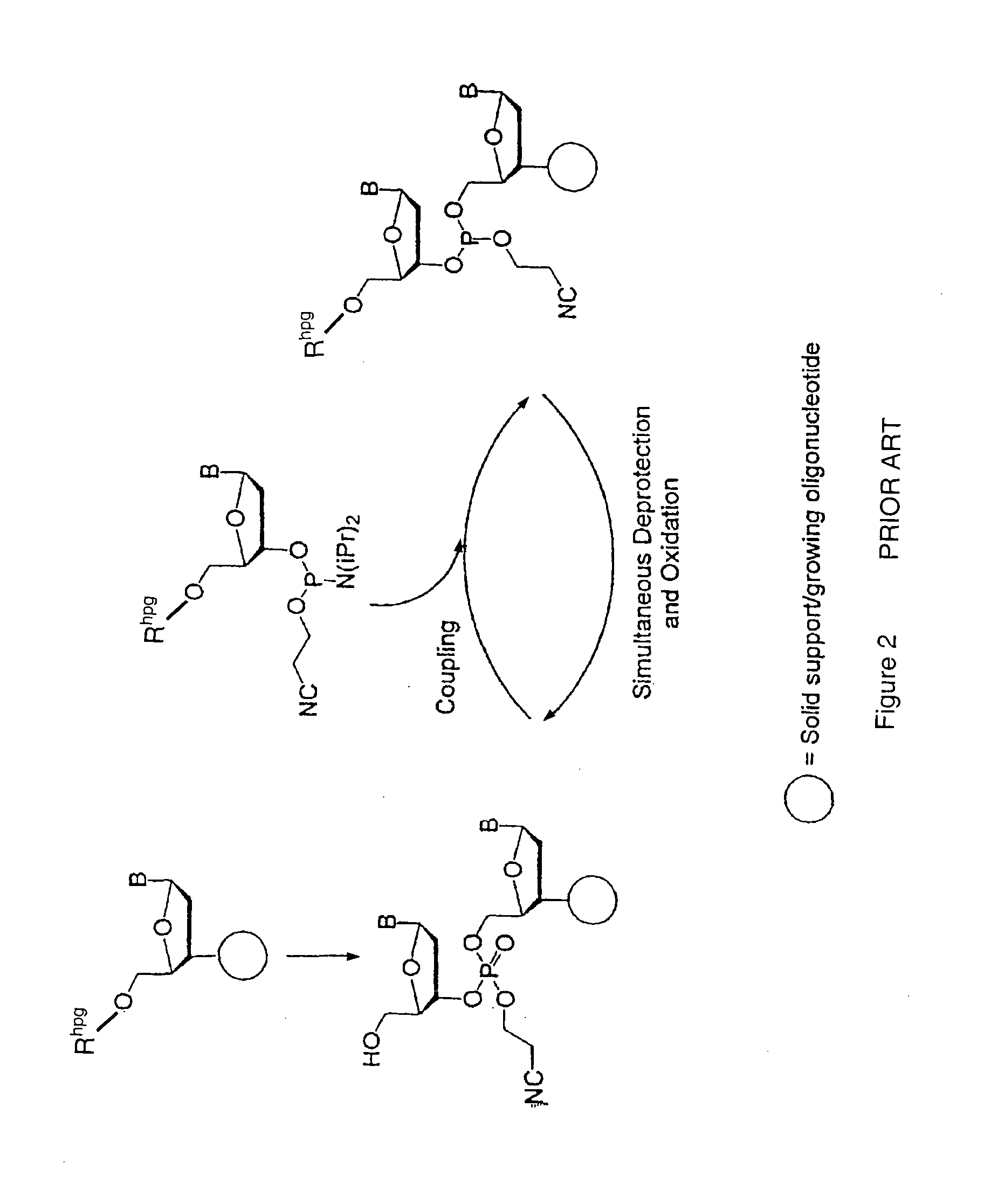
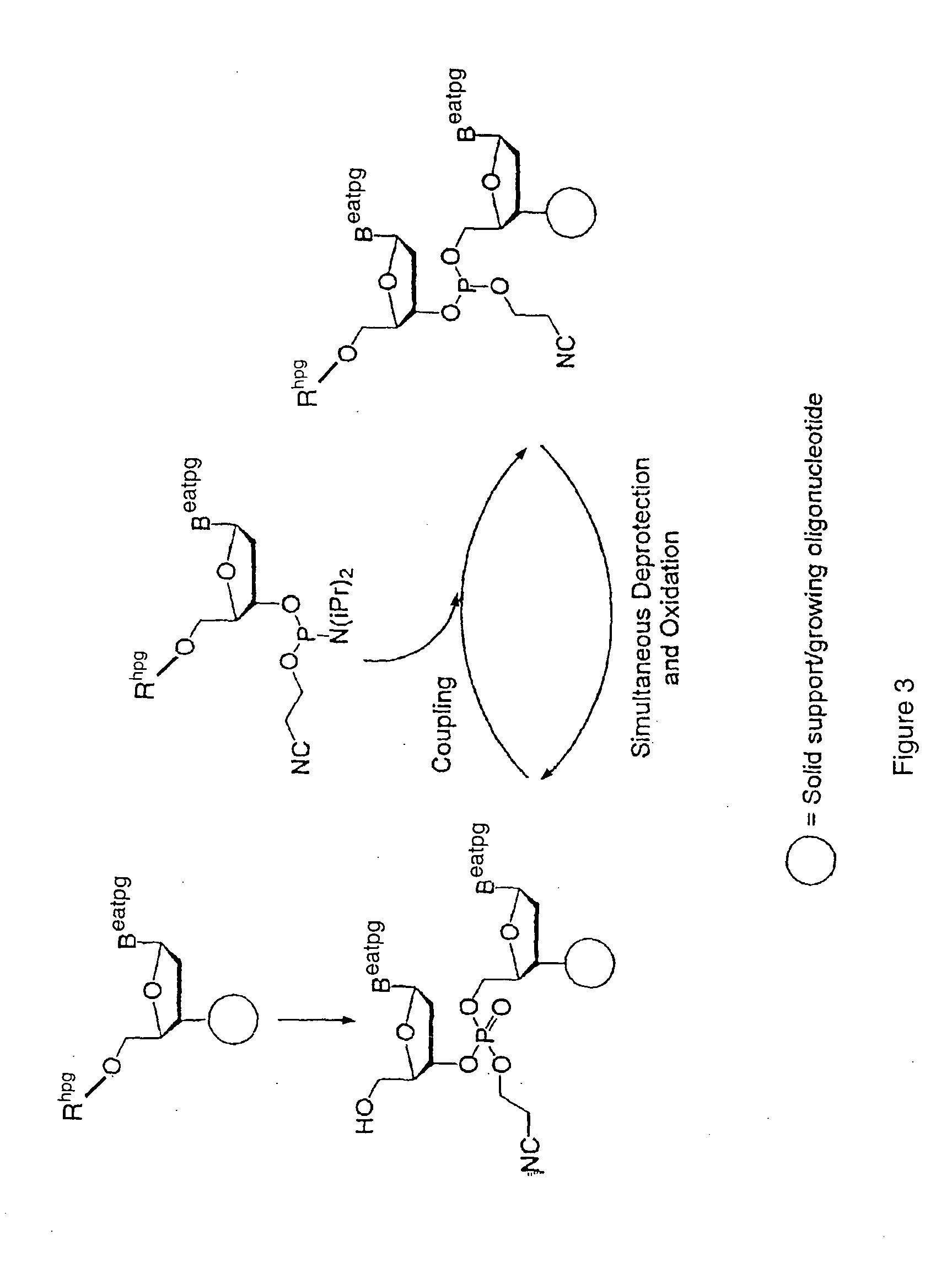
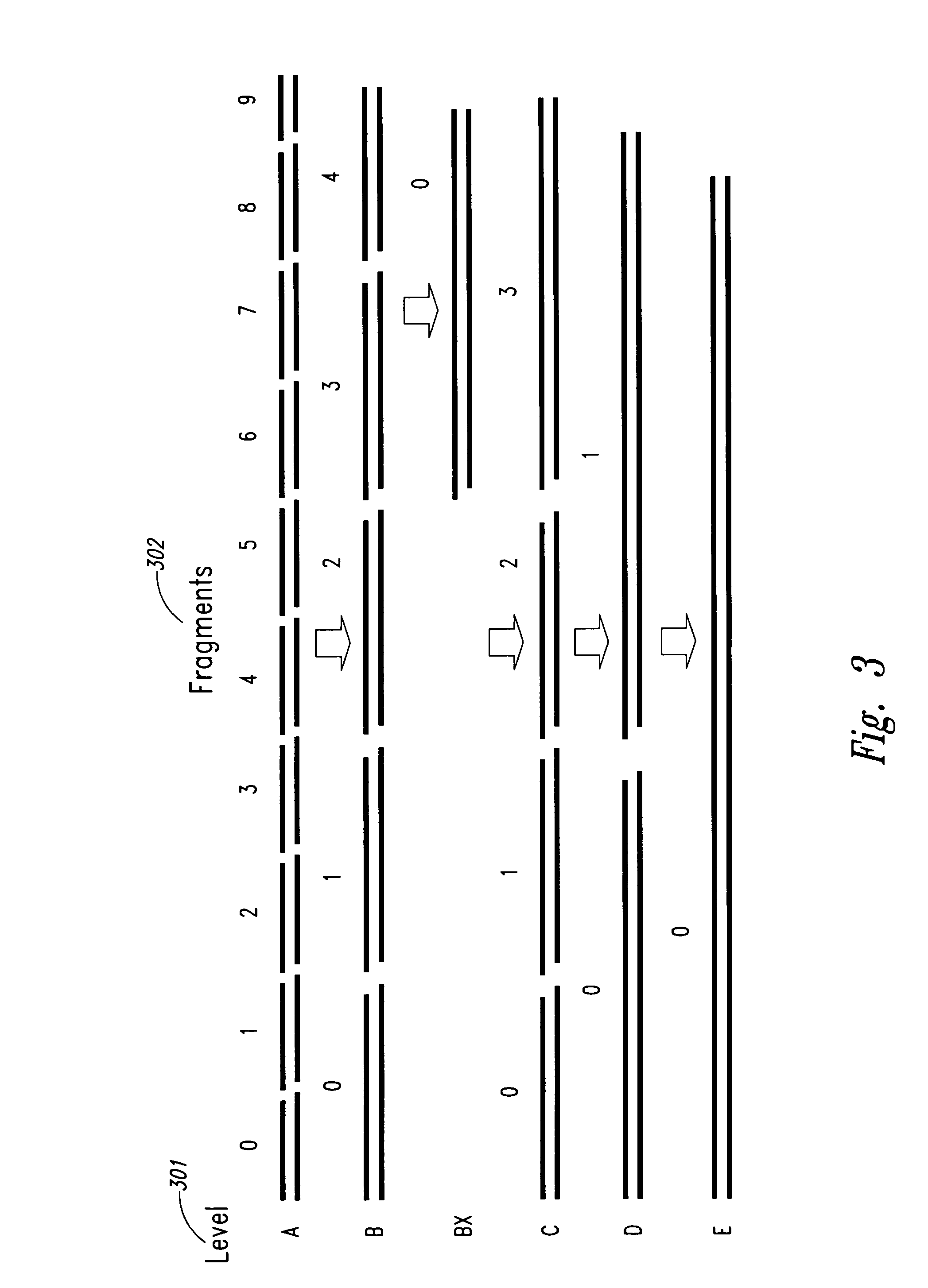
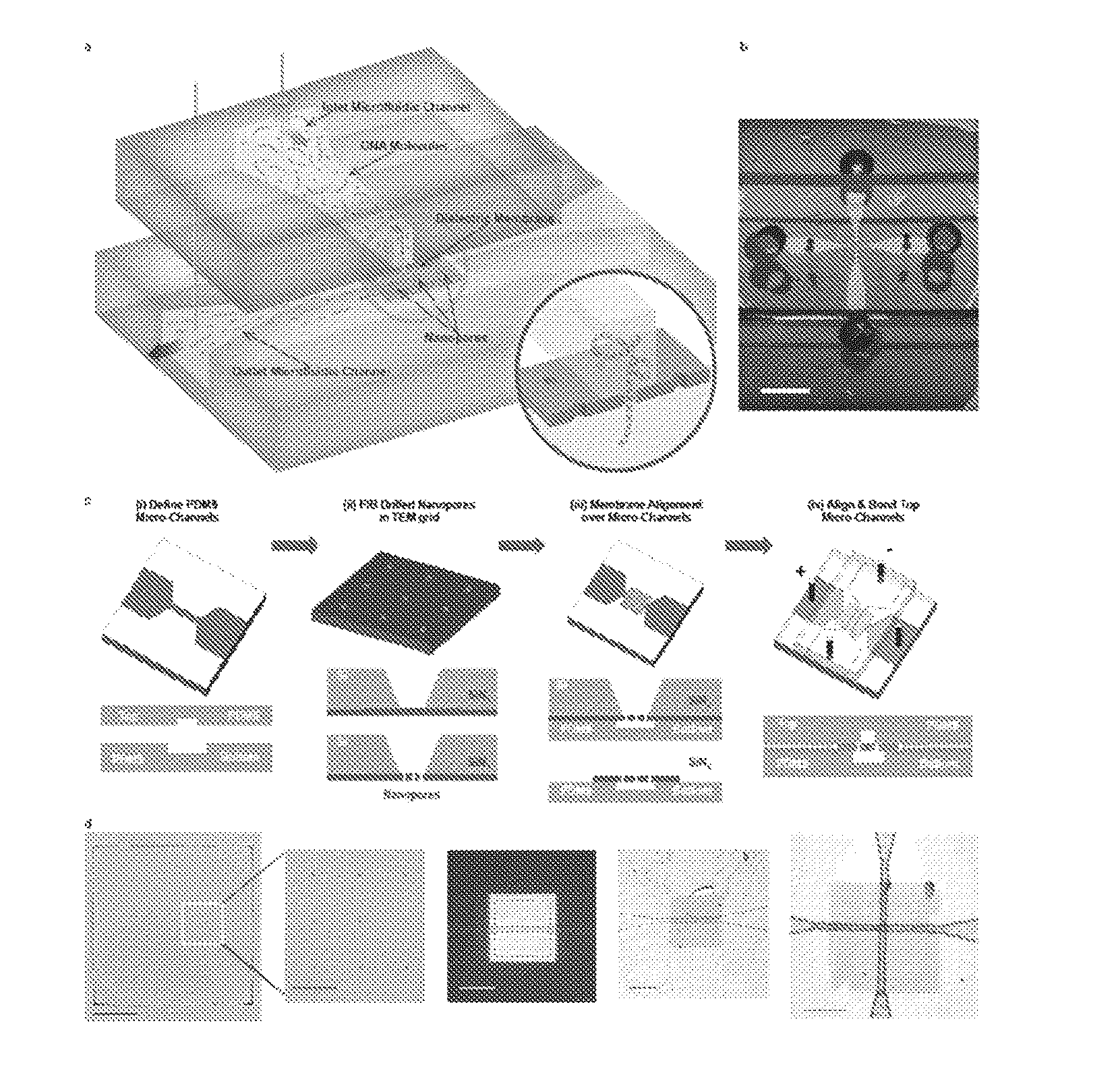
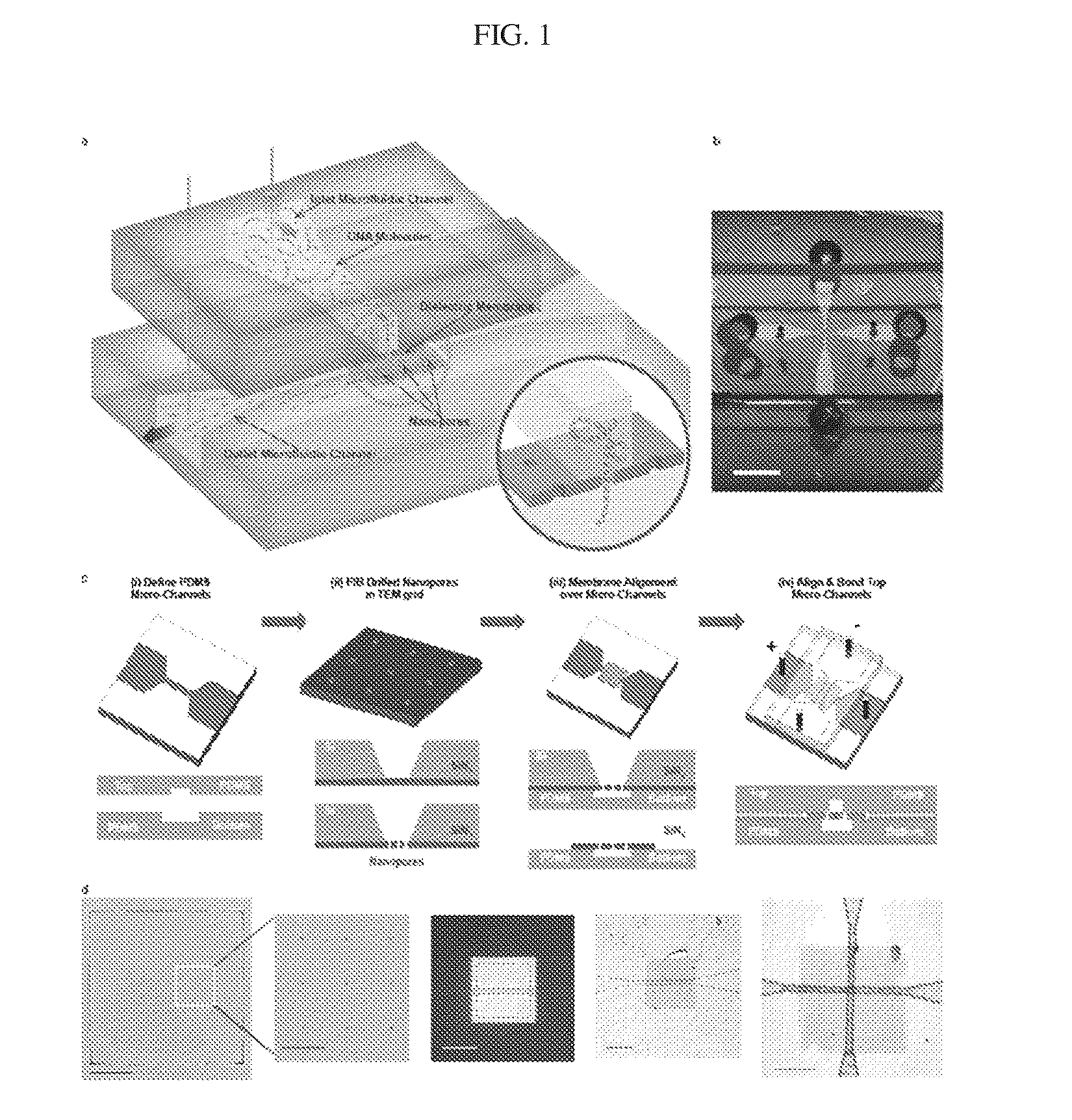
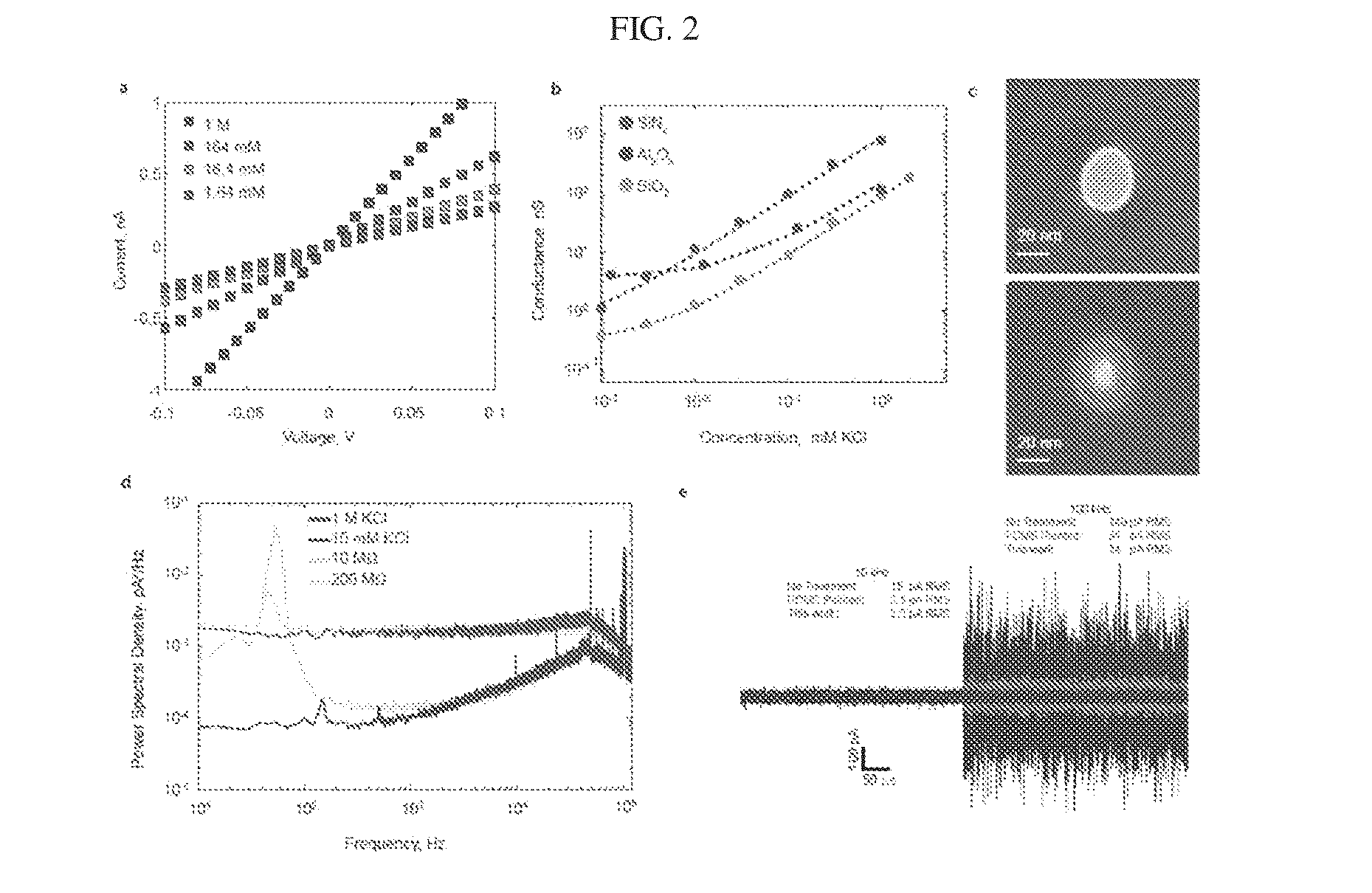
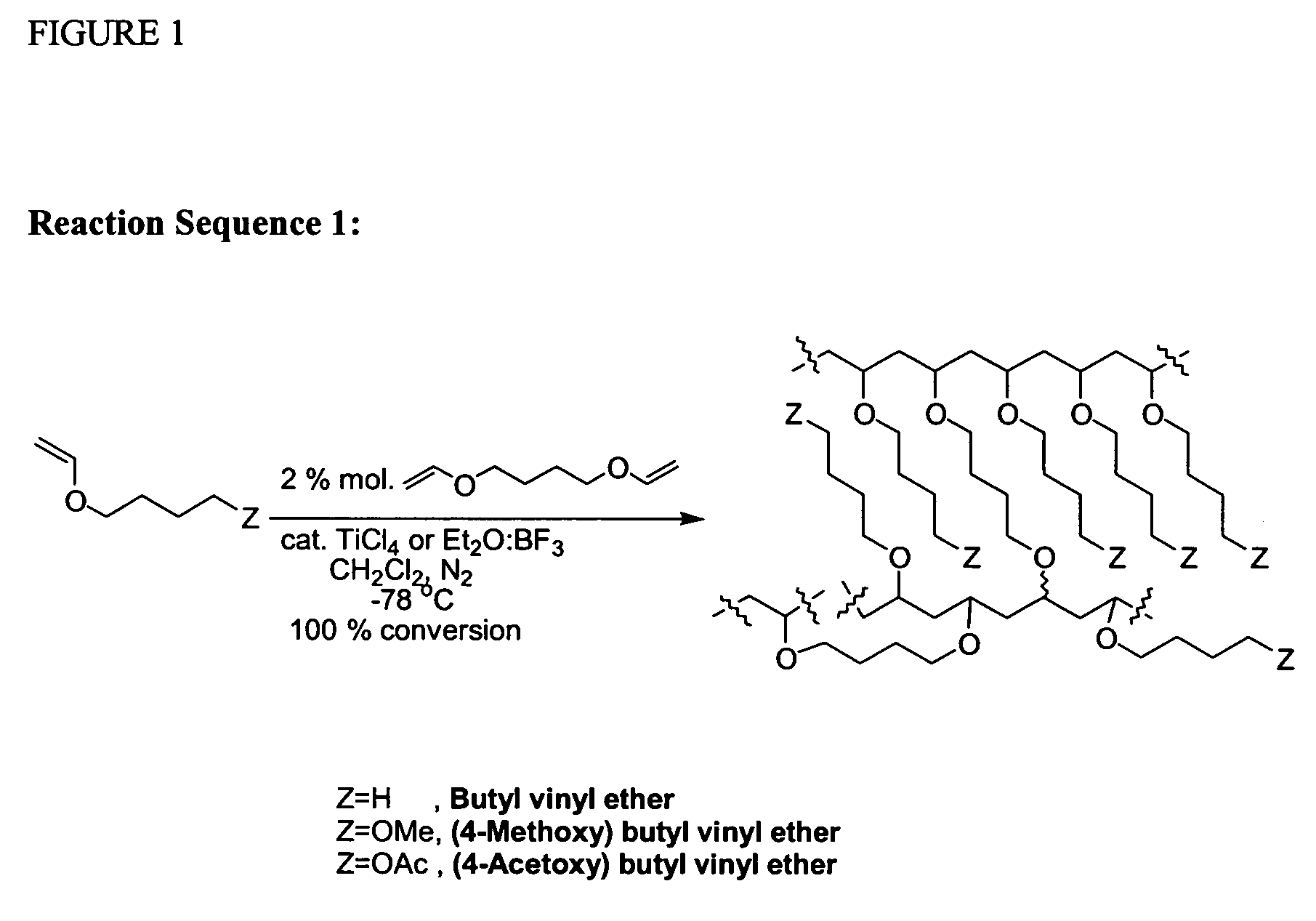
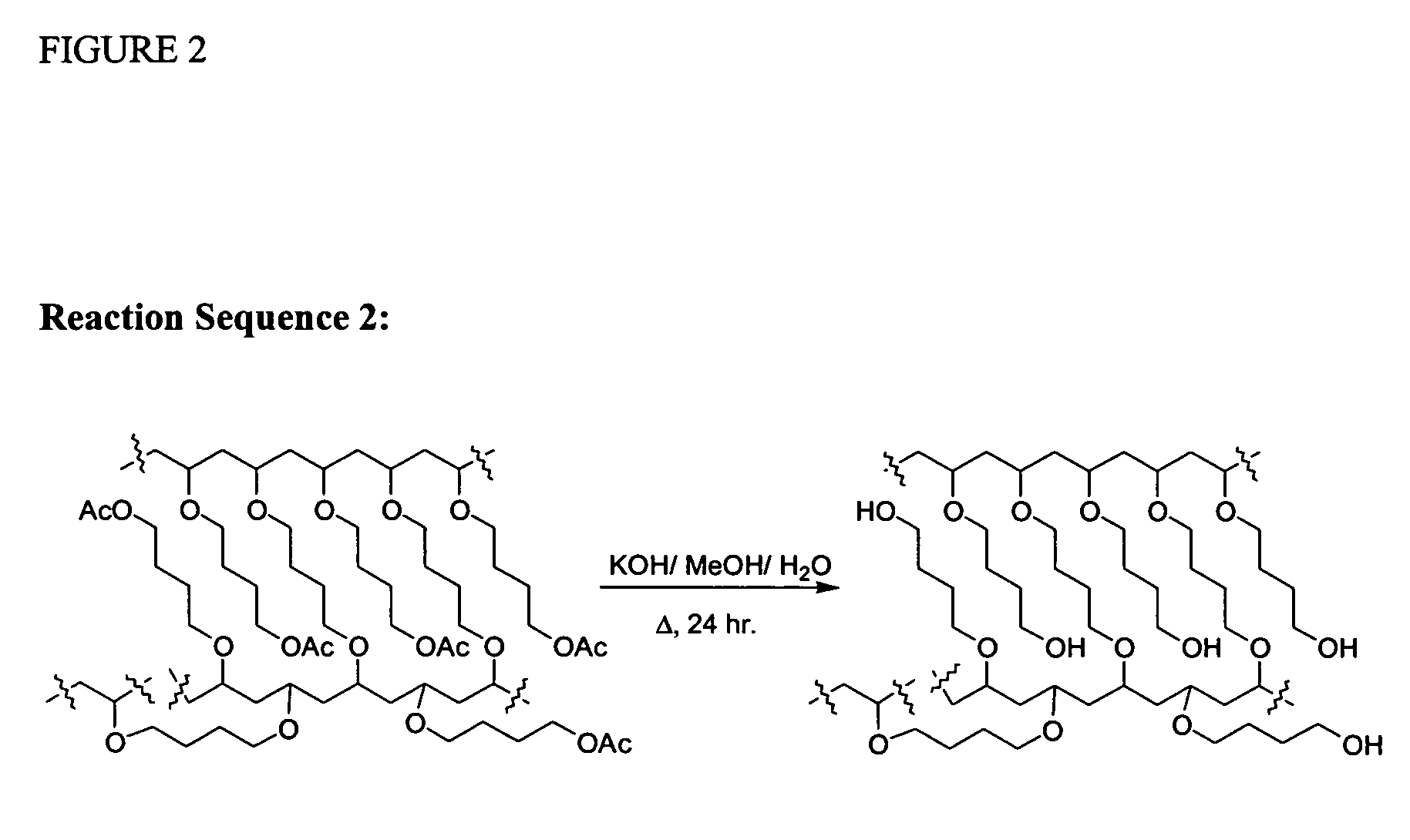
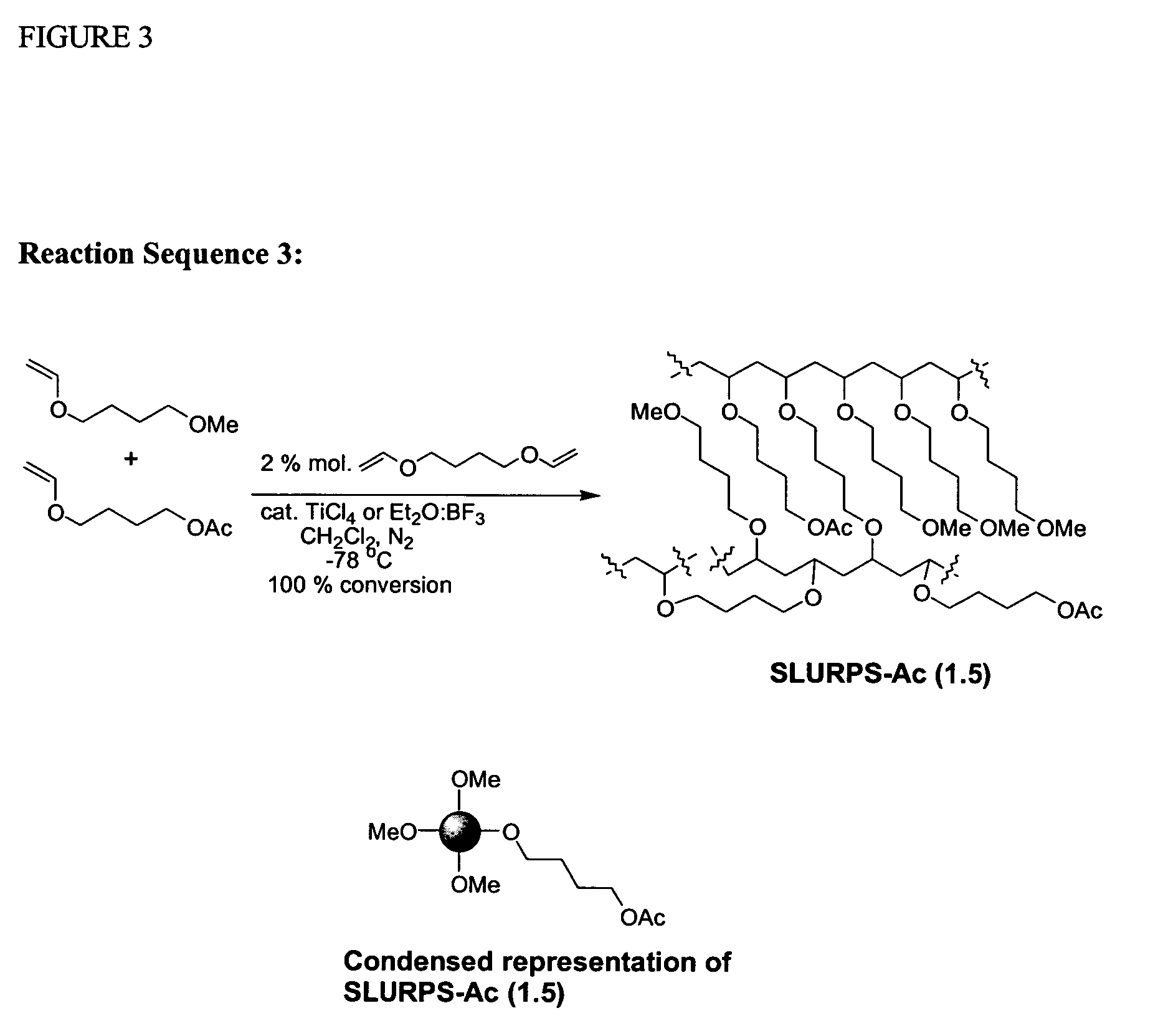
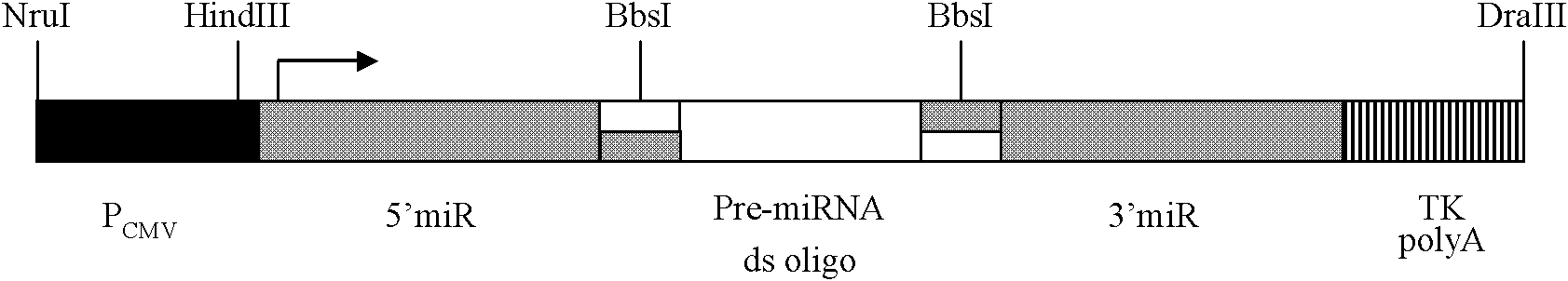
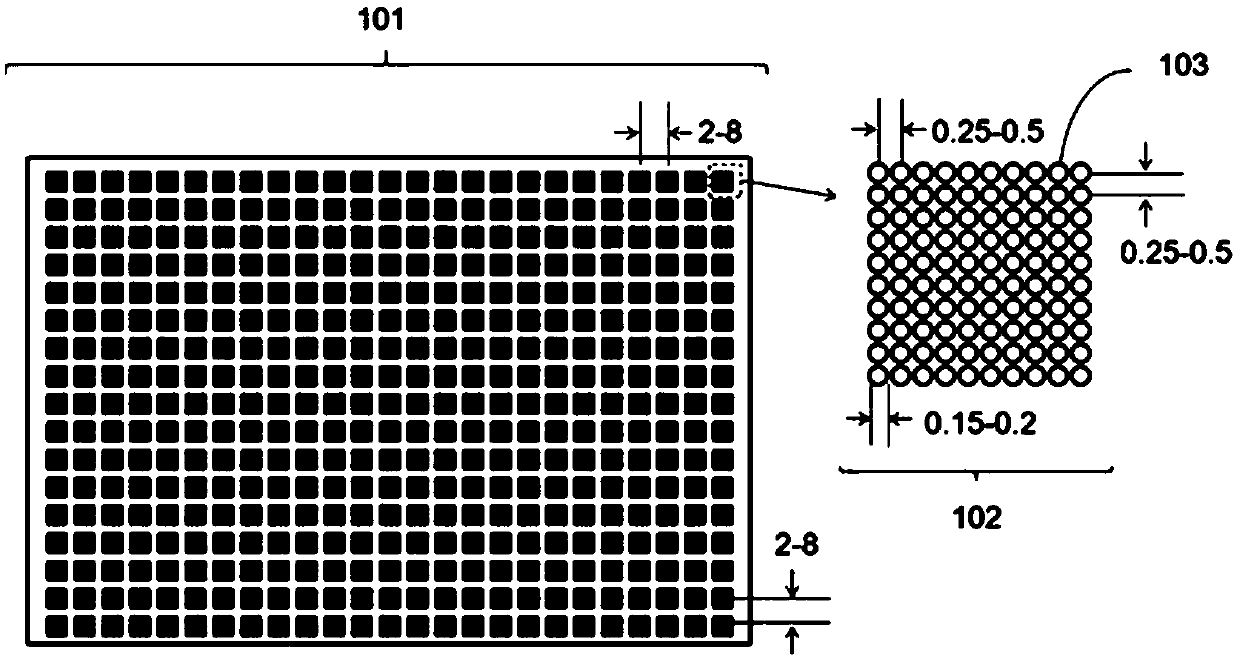
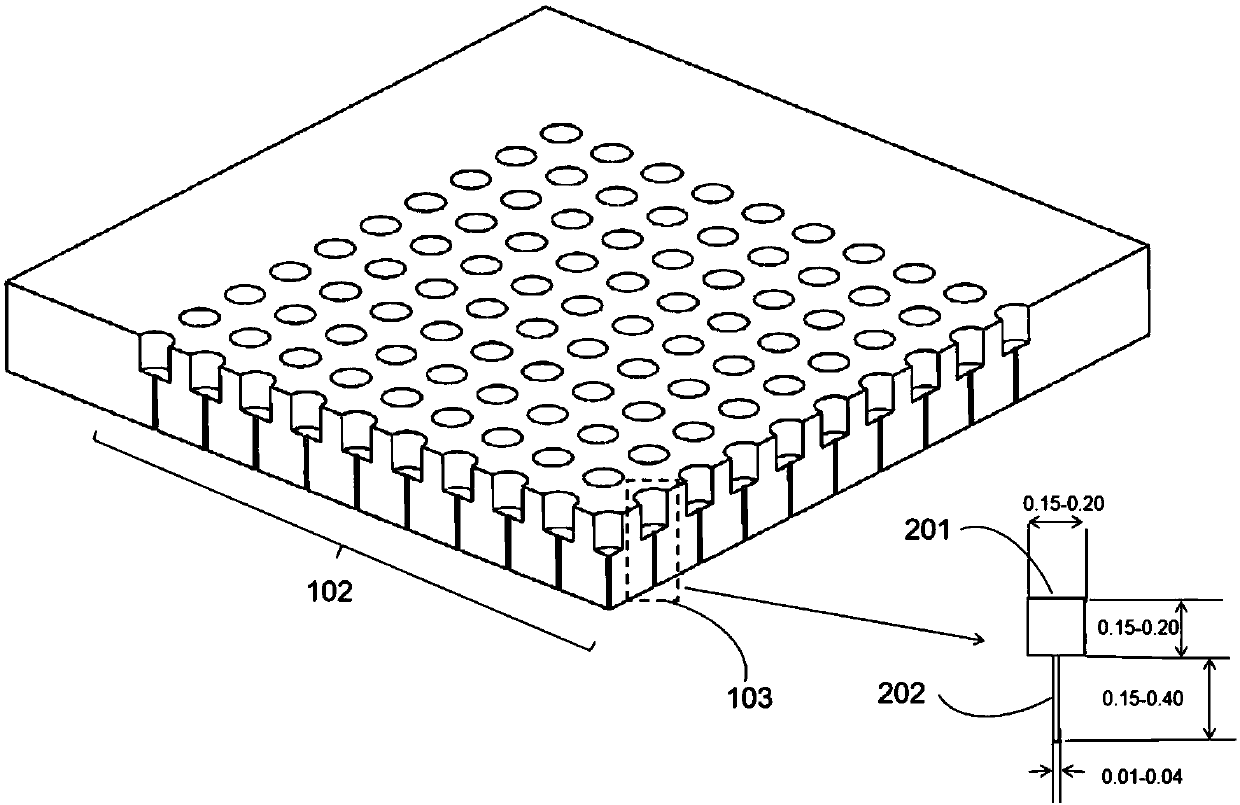
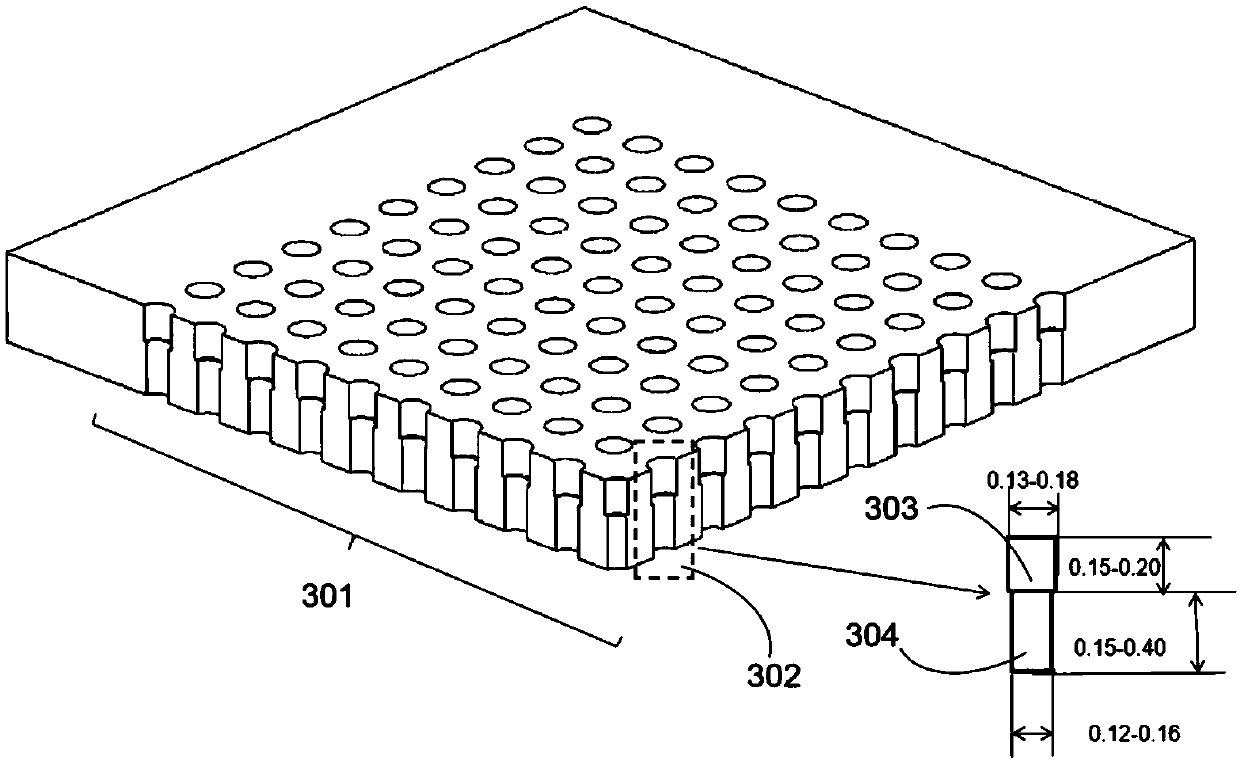
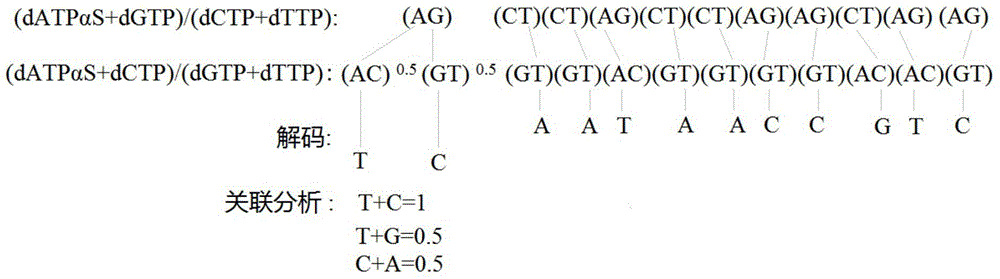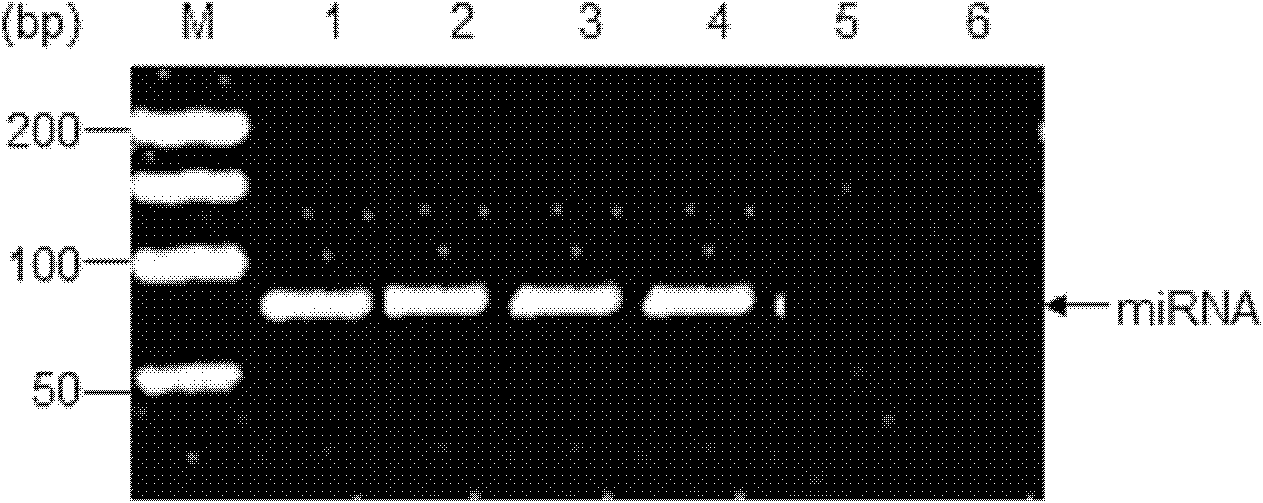Patents
Literature
95 results about "Nucleotide synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
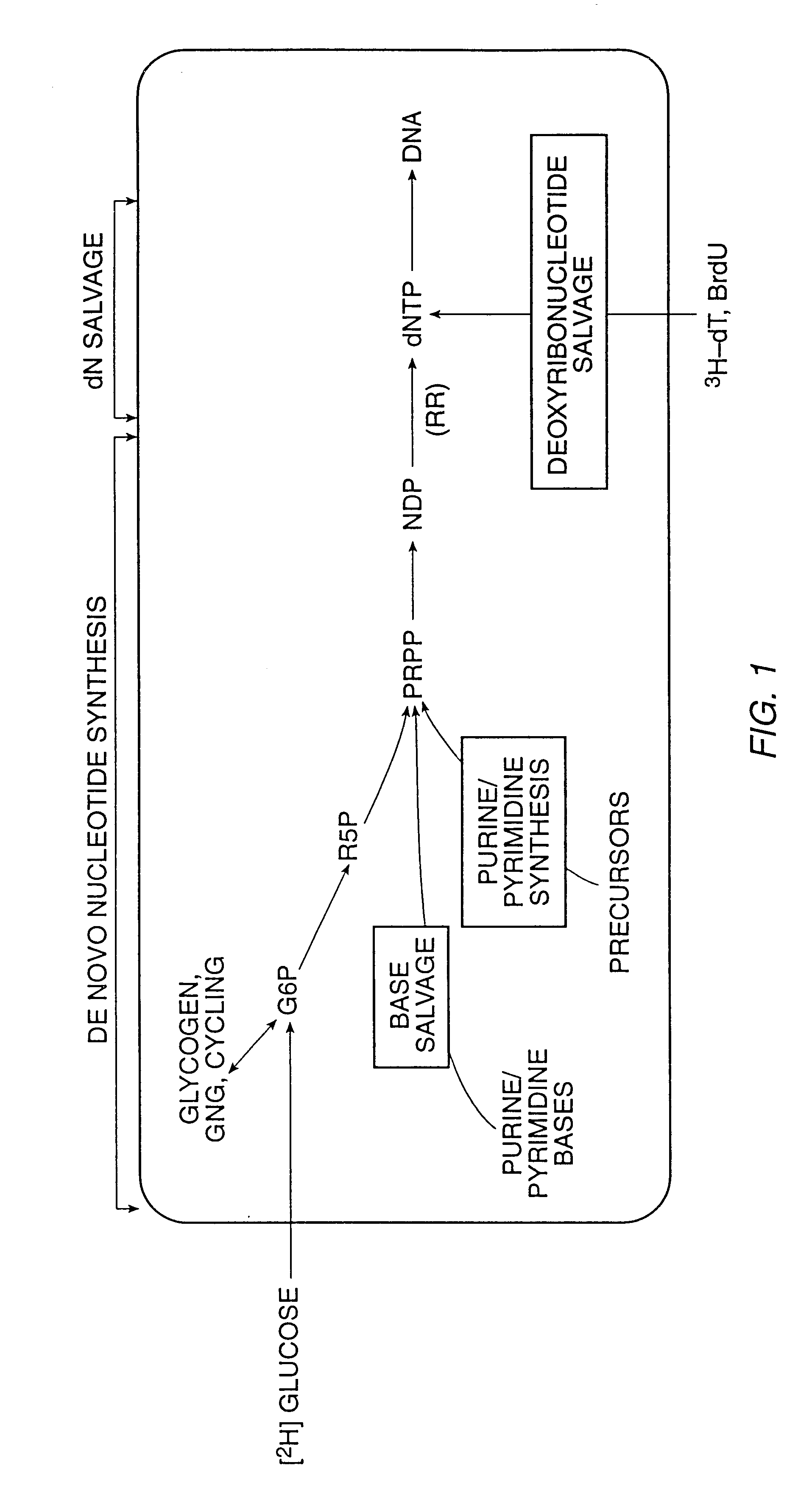
The components used in de novo nucleotide synthesis are derived from biosynthetic precursors of carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism, and from ammonia and carbon dioxide. The liver is the major organ of de novo synthesis of all four nucleotides. De novo synthesis of pyrimidines and purines follows two different pathways.
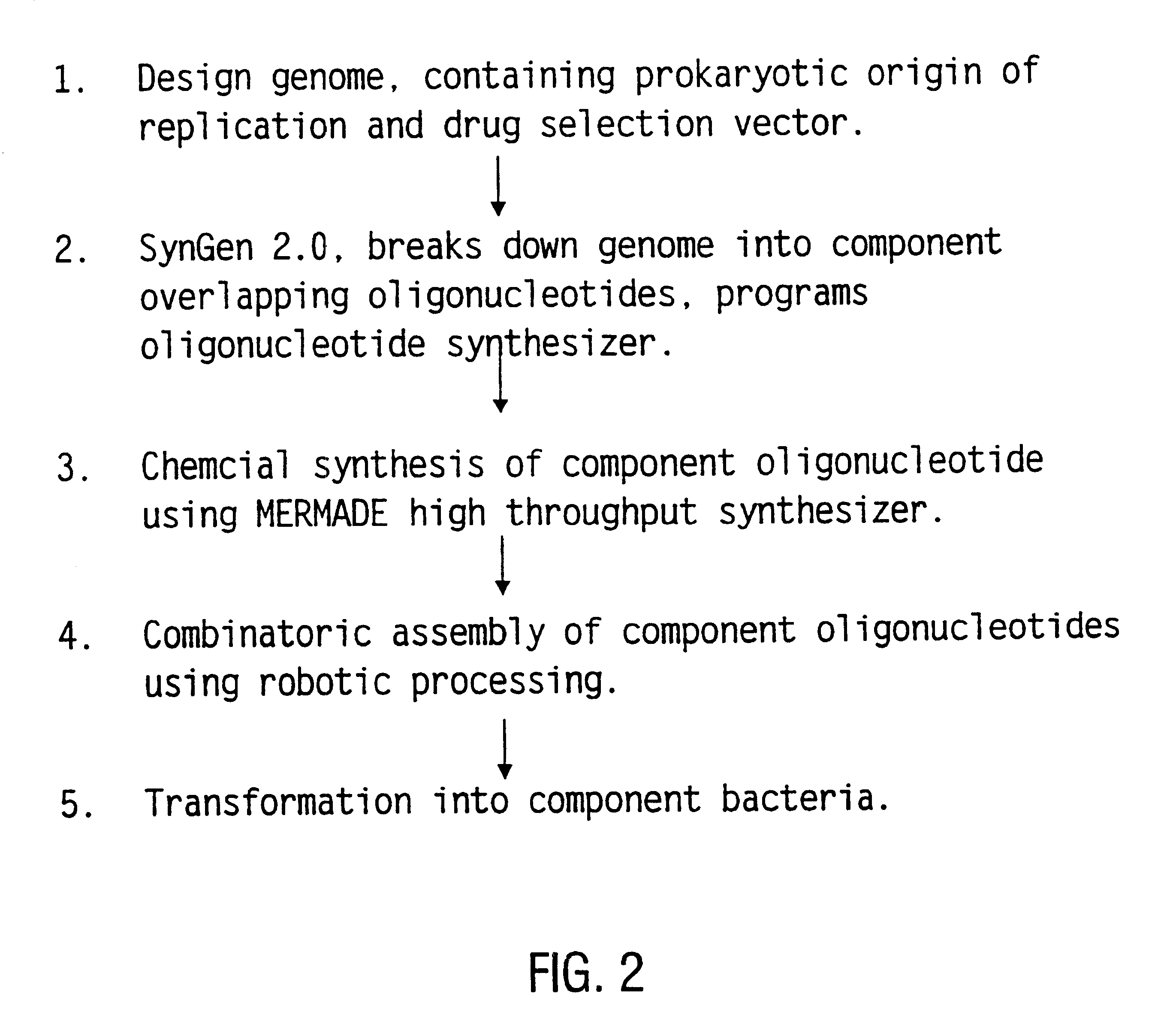
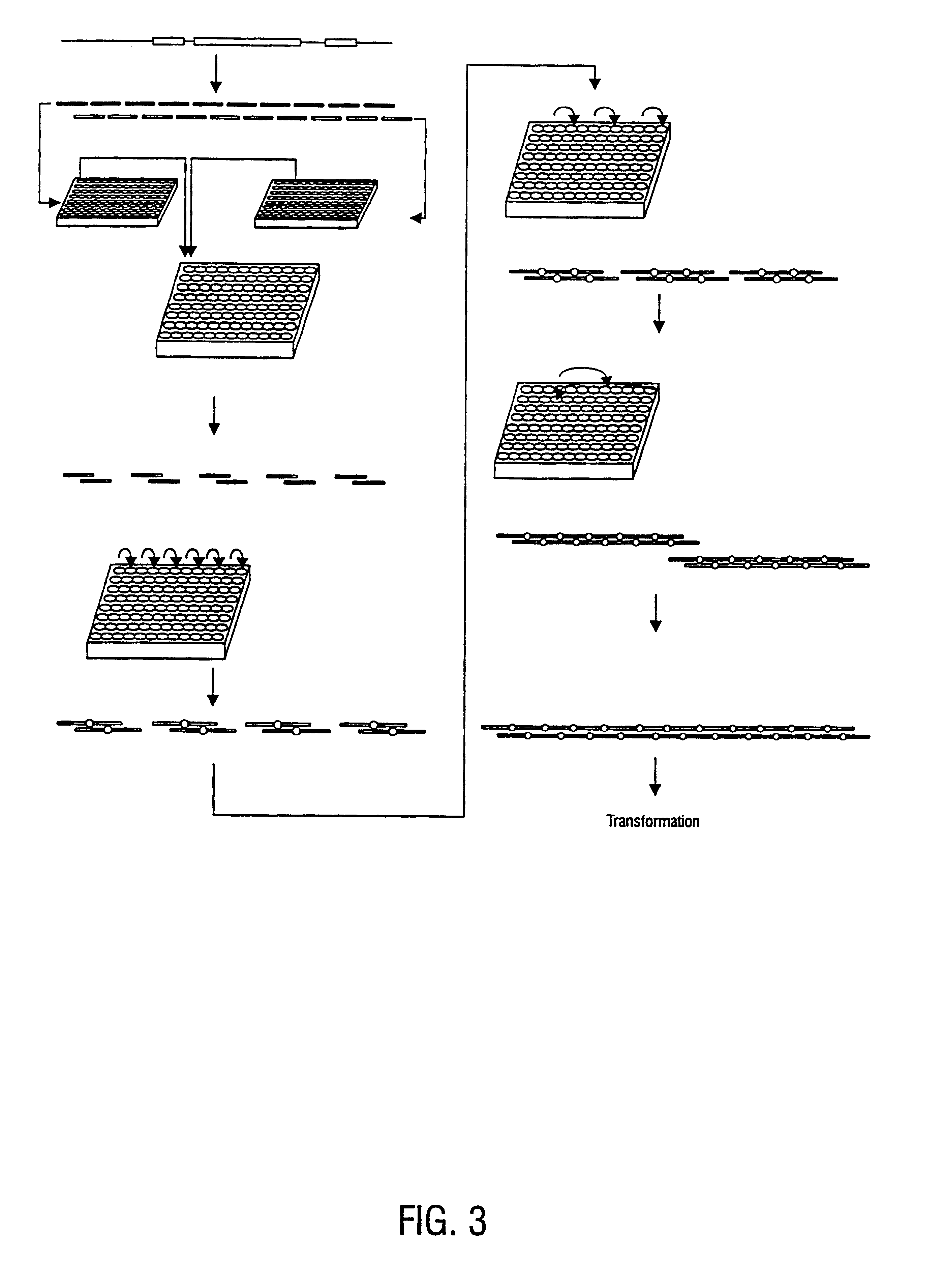
Method for the complete chemical synthesis and assembly of genes and genomes
InactiveUS6521427B1BiocideSequential/parallel process reactionsChemical synthesisHuman genome database
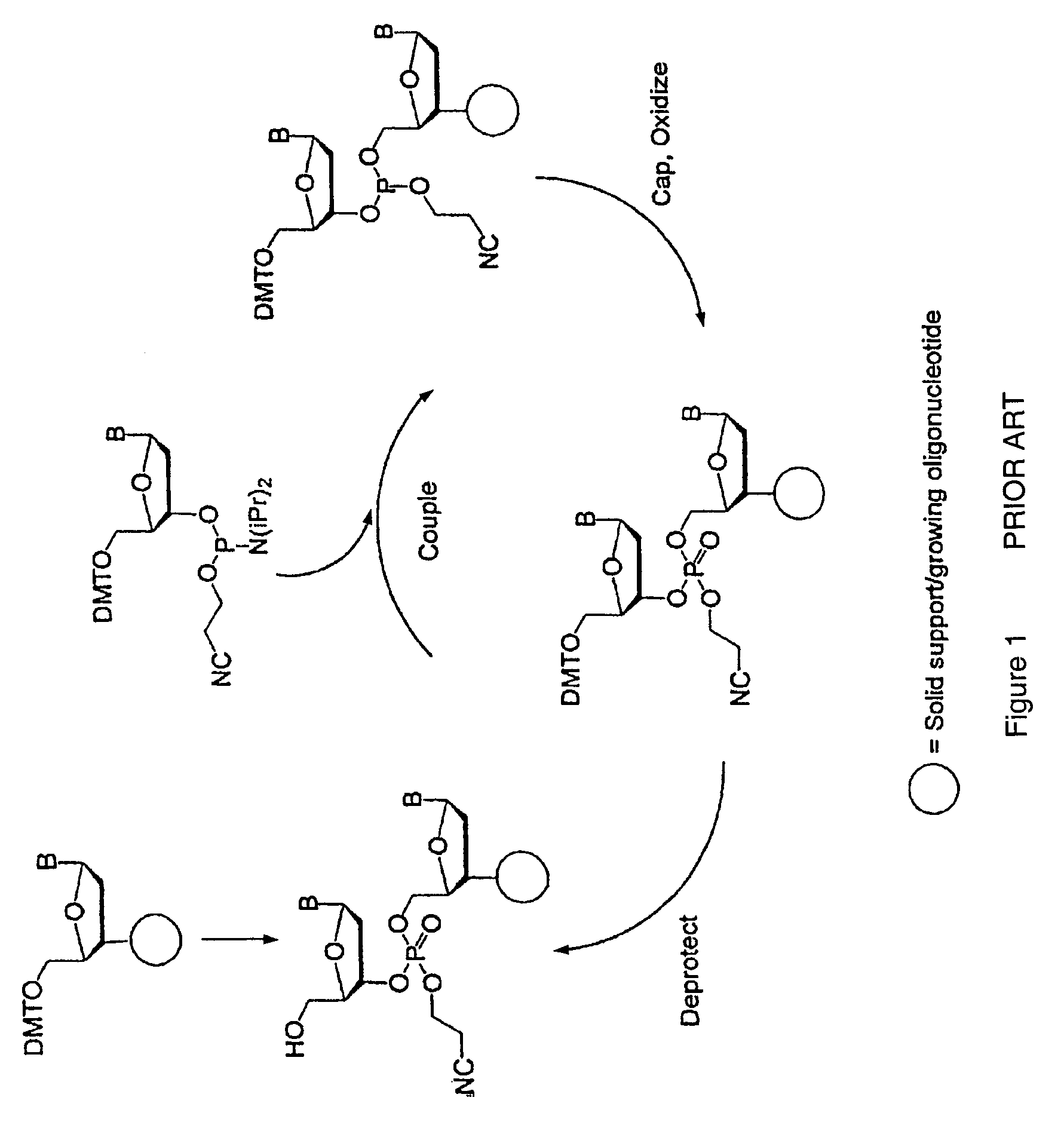
The present invention relates generally to the fields of oligonucleotide synthesis. More particularly, it concerns the assembly of genes and genomes of completely synthetic artificial organisms. Thus, the present invention outlines a novel approach to utilizing the results of genomic sequence information by computer directed gene synthesis based on computing on the human genome database. Specifically, the present invention contemplates and describes the chemical synthesis and resynthesis of genes defined by the genome sequence in a host vector and transfer and expression of these sequences into suitable hosts.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON INC (US) +3
Compounds and methods for the characterization of oligonucleotides
ActiveUS7427675B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide synthesisOrganic chemistry
The present invention relates to oligonucleotide synthesis. In particular, the present invention provides methods for characterizing samples useful for making oligonucleotides.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Programmable oligonucleotide synthesis
ActiveUS8173368B2Reduce yieldSynthesis is longSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsOligonucleotide synthesisSynthetic nucleic acid
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
Polymerase enzyme substrates with protein shield
ActiveUS20130316912A1Peptide librariesMethine/polymethine dyesPolymerase LSingle molecule real time sequencing
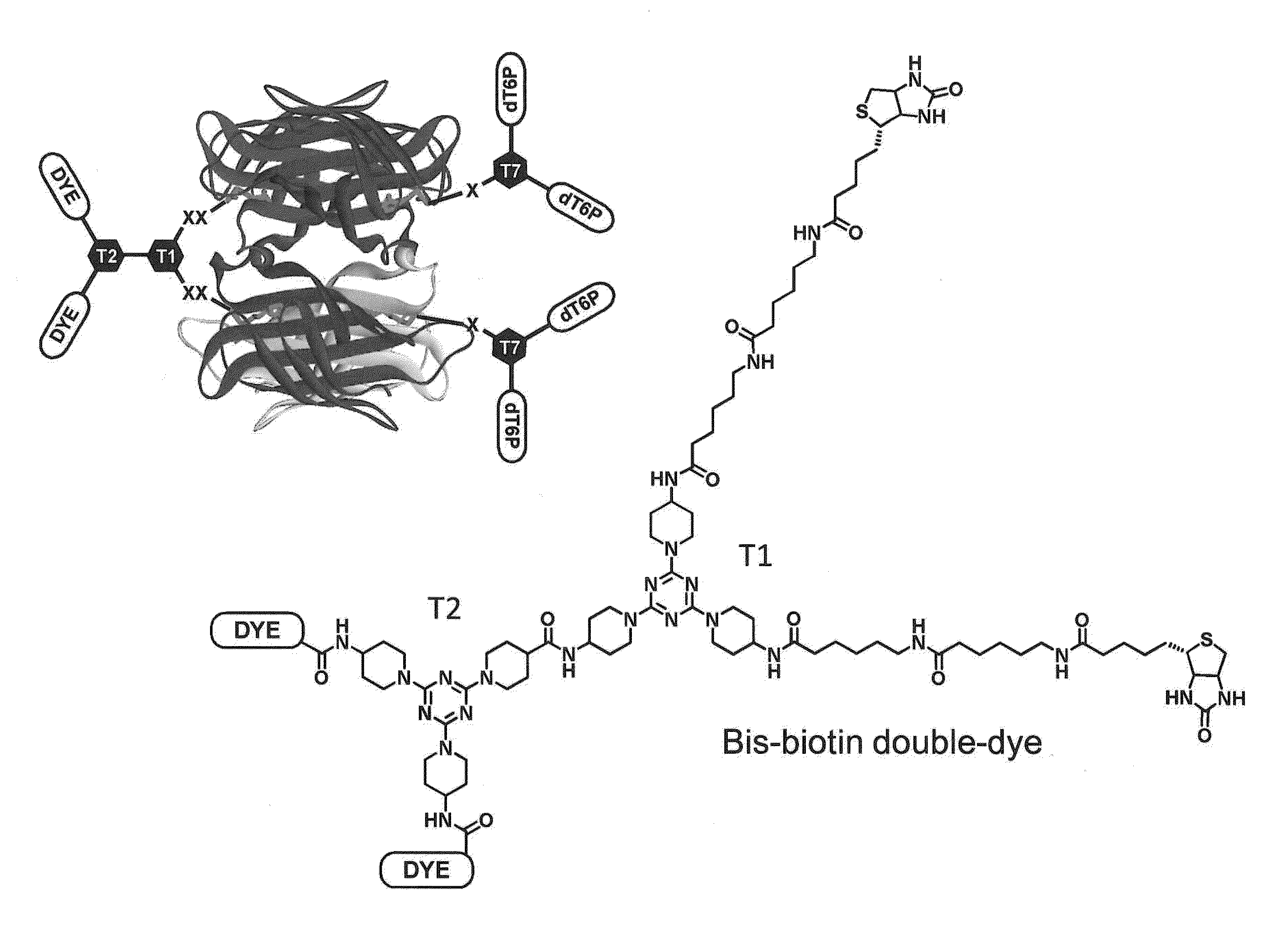
Compositions and methods are provided for nucleotide analogs comprising protein shields for improving enzyme photostability in single molecule real time sequencing. Nucleotide analogs of the invention have a protein shield between the dye moieties and nucleotide moieties of the analog. The protein prevents the direct interaction of the dye moiety with the enzyme carrying out nucleotide synthesis preventing photodamage to the enzyme. The nucleotide analogs of the invention can have multiple dyes and multiple nucleotide moieties.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Polymerase enzyme substrates with protein shield
Compositions and methods are provided for nucleotide analogs comprising protein shields for improving enzyme photostability in single molecule real time sequencing. Nucleotide analogs of the invention have a protein shield between the dye moieties and nucleotide moieties of the analog. The protein prevents the direct interaction of the dye moiety with the enzyme carrying out nucleotide synthesis preventing photodamage to the enzyme. The nucleotide analogs of the invention can have multiple dyes and multiple nucleotide moieties.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Methods for measuring cellular proliferation and destruction rates in vitro and in vivo
InactiveUS6461806B1Organic active ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsStable Isotope LabelingDisease
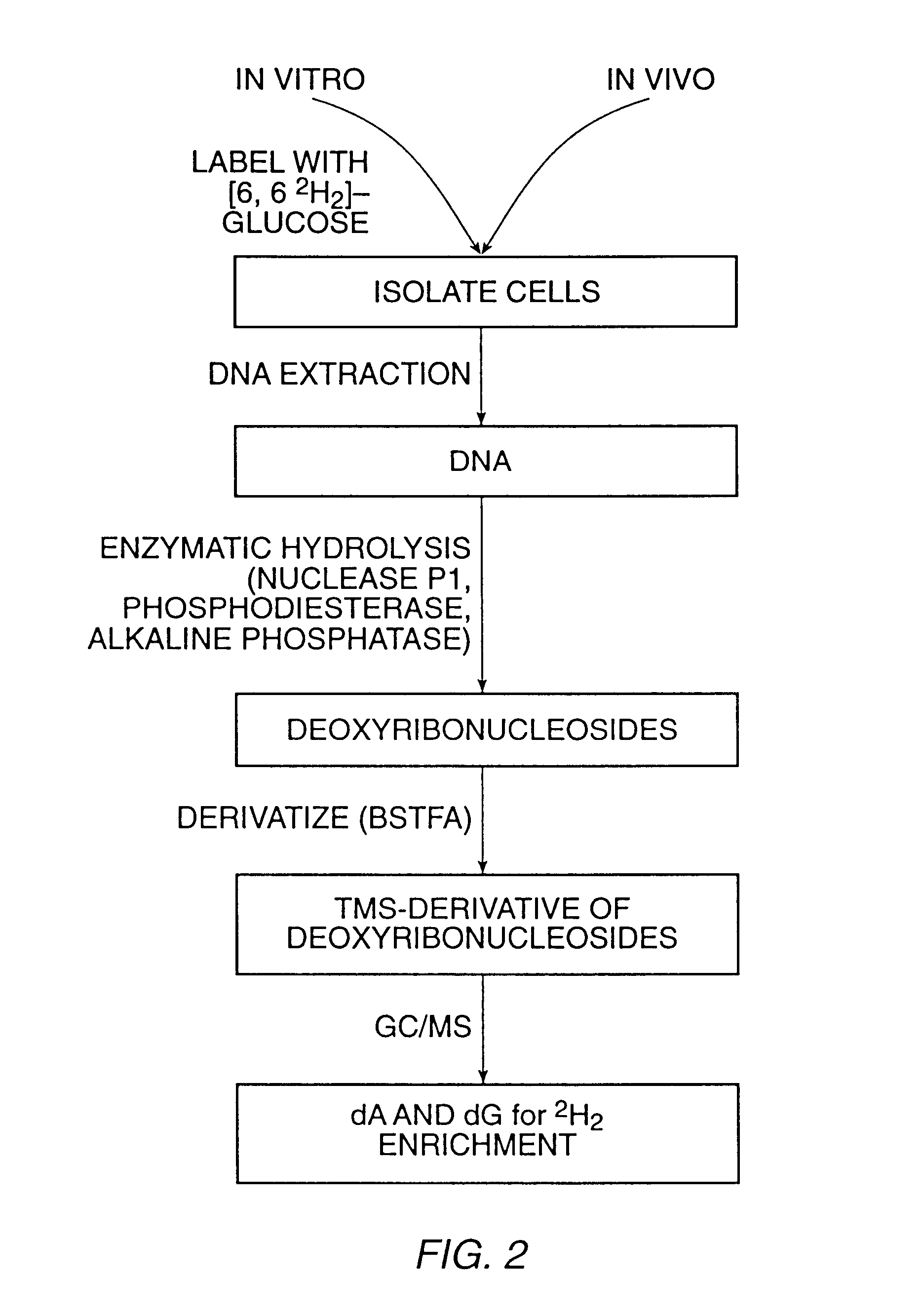
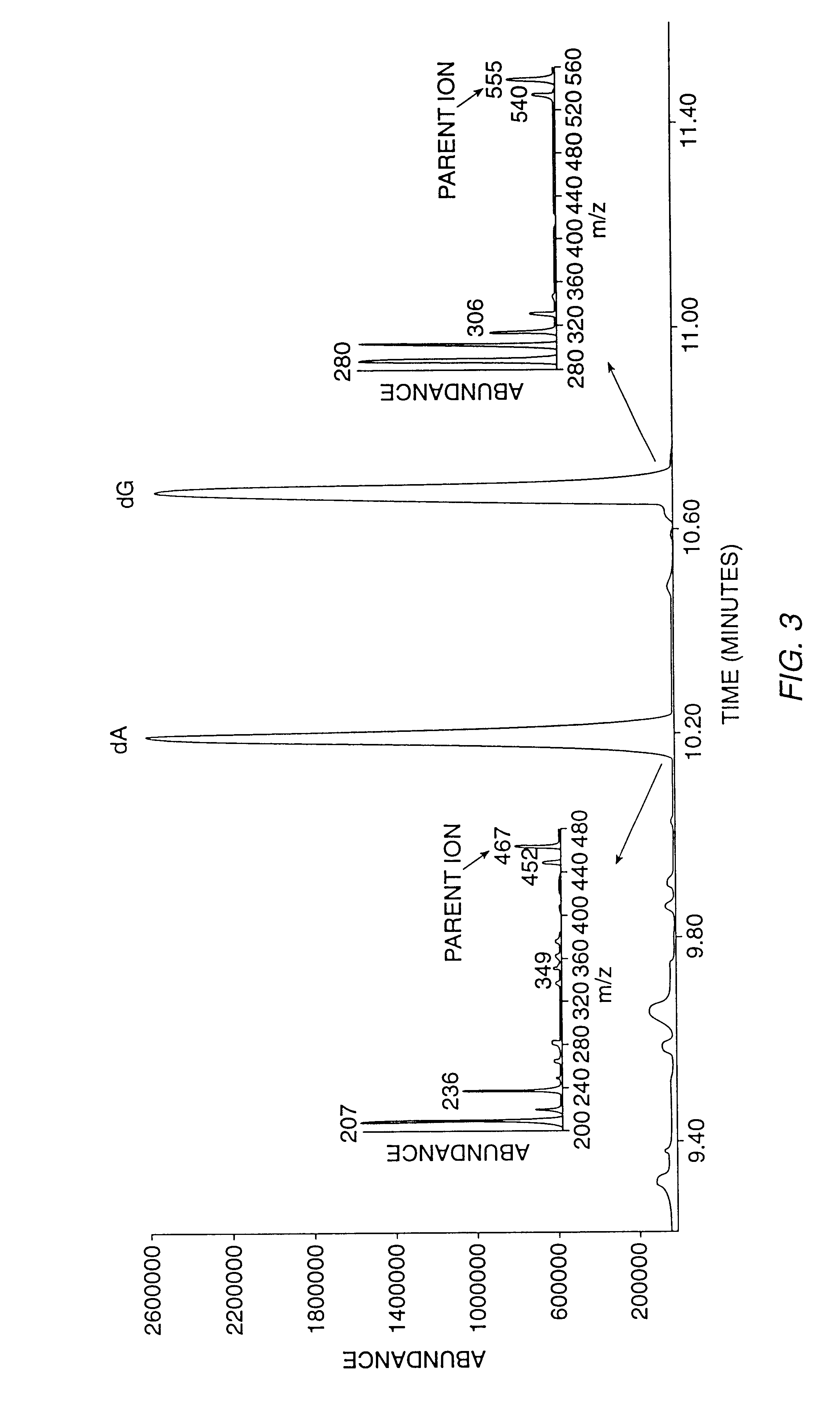
The present invention relates to methods for measuring the proliferation and destruction rates of cells by measuring deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis and / or destruction. In particular, the methods utilize non-radioactive stable isotope labels to endogenously label DNA synthesized through the de novo nucleotide synthesis pathway in a cell. The amount of label incorporated in the DNA is measured as an indication of cellular proliferation. The decay of labeled DNA over time is measured as an indication of cellular destruction. Such methods do not involve radioactivity or potentially toxic metabolites, and are suitable for use both in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, the invention is useful for measuring cellular proliferation or cellular destruction rates in humans for the diagnosis, prevention, or management of a variety of disease conditions in which cellular proliferation or cellular destruction is involved. The invention also provides methods for measuring proliferation or destruction of T cells in a subject infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and methods of screening an agent for a capacity to induce or inhibit cellular proliferation or destruction. In addition, the invention provides methods for measuring cellular proliferation in a proliferating population which utilize both radioactive isotope labels and stable isotopes to endogenously label DNA through the de novo nucleotide synthesis pathway.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
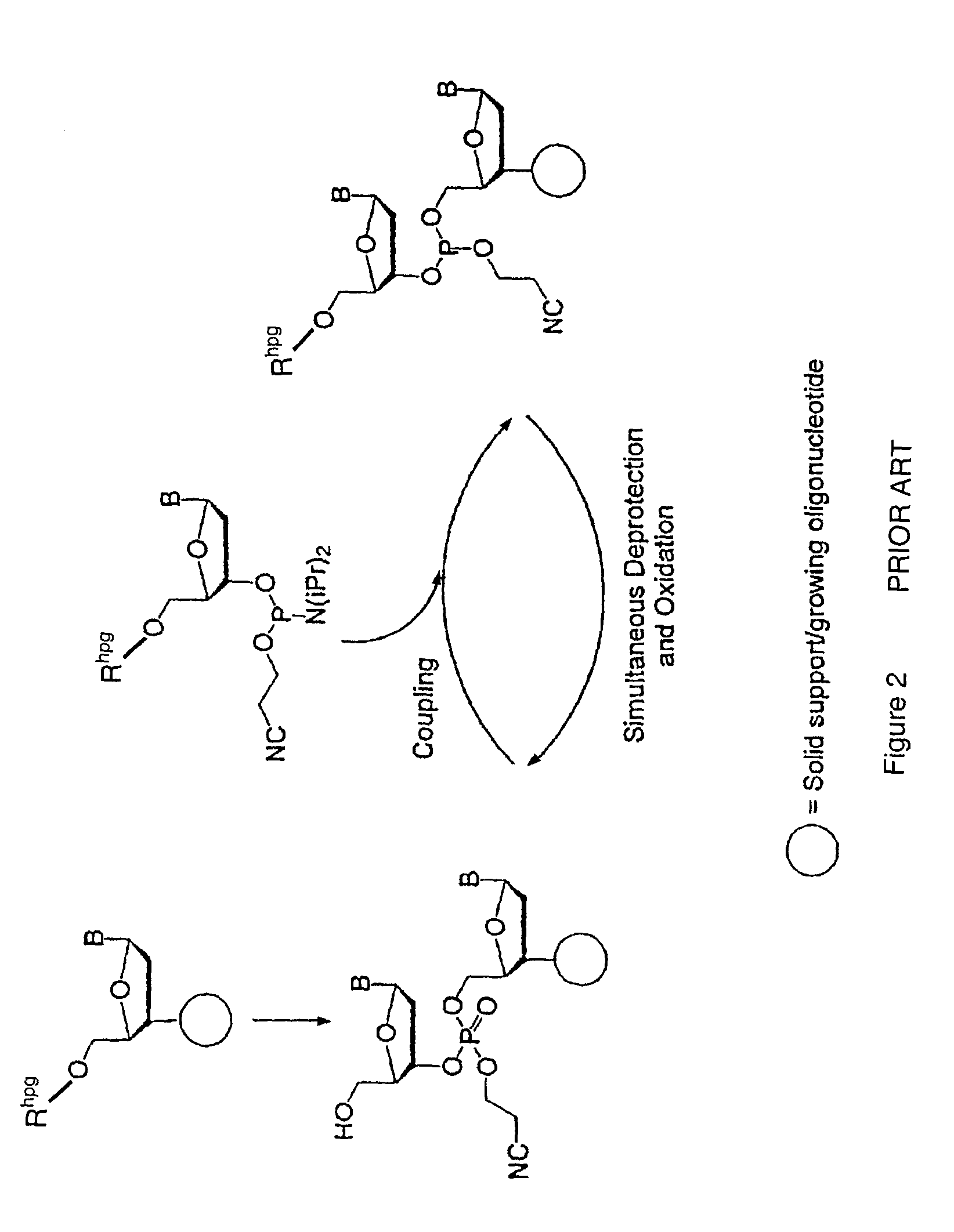
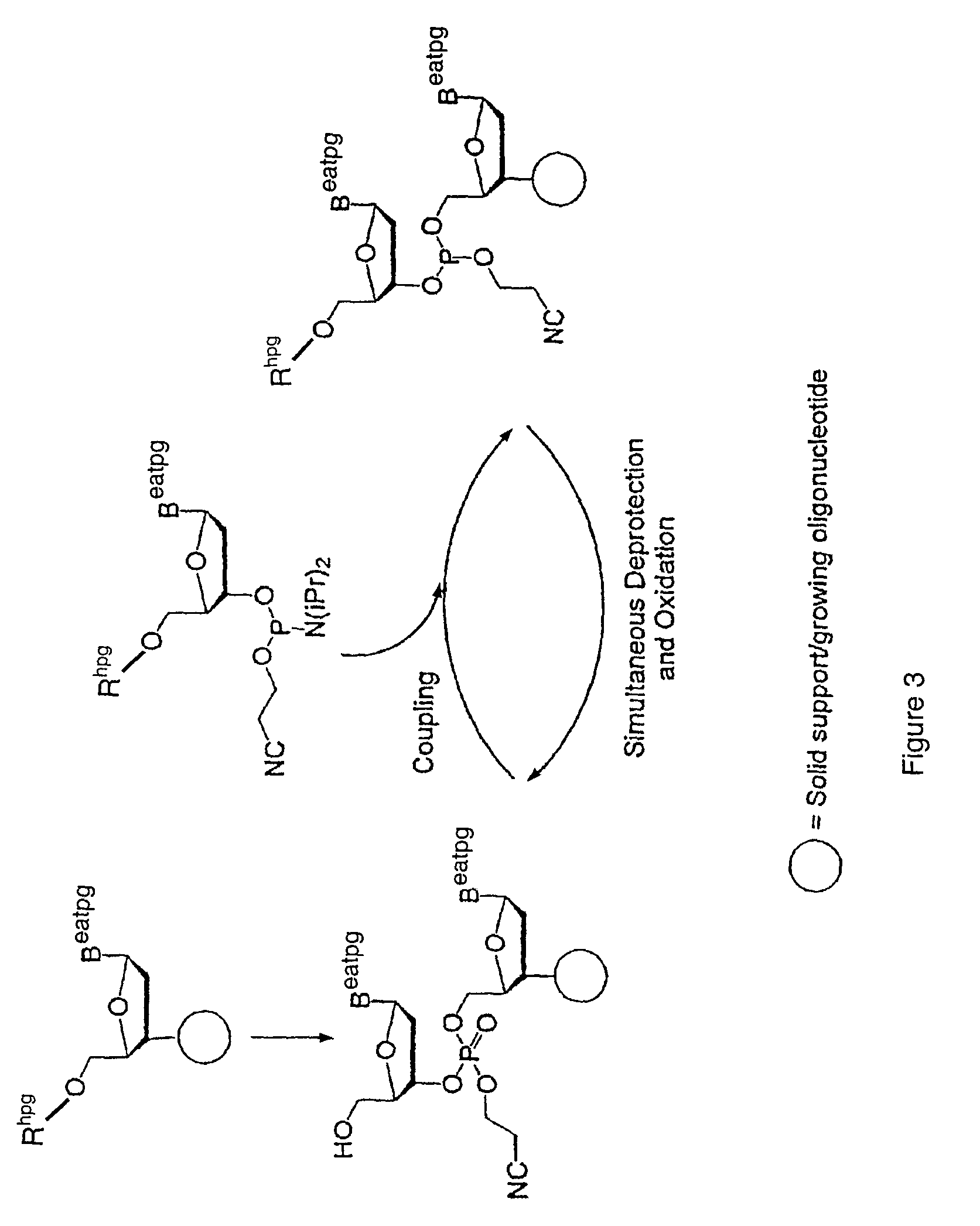
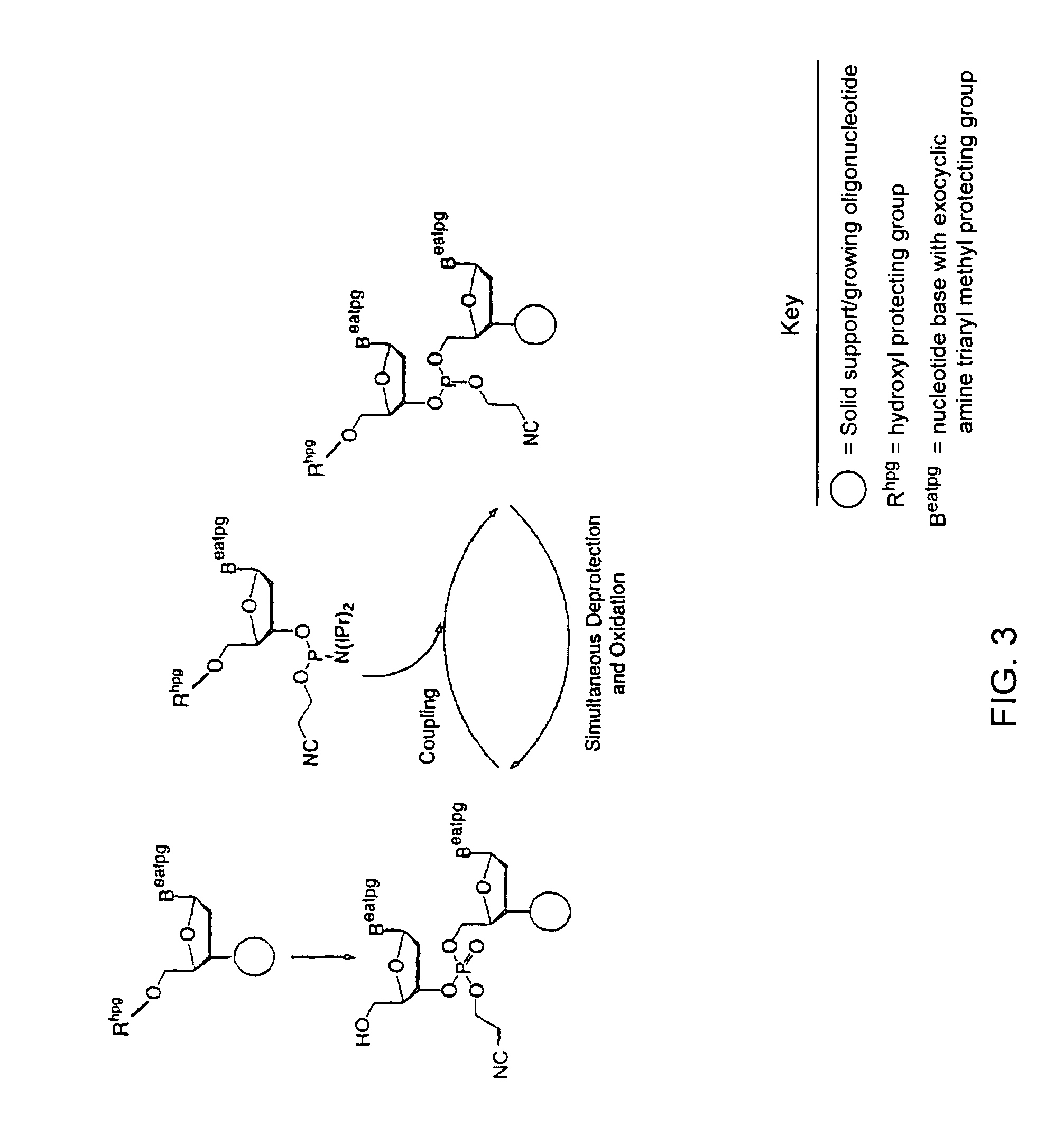
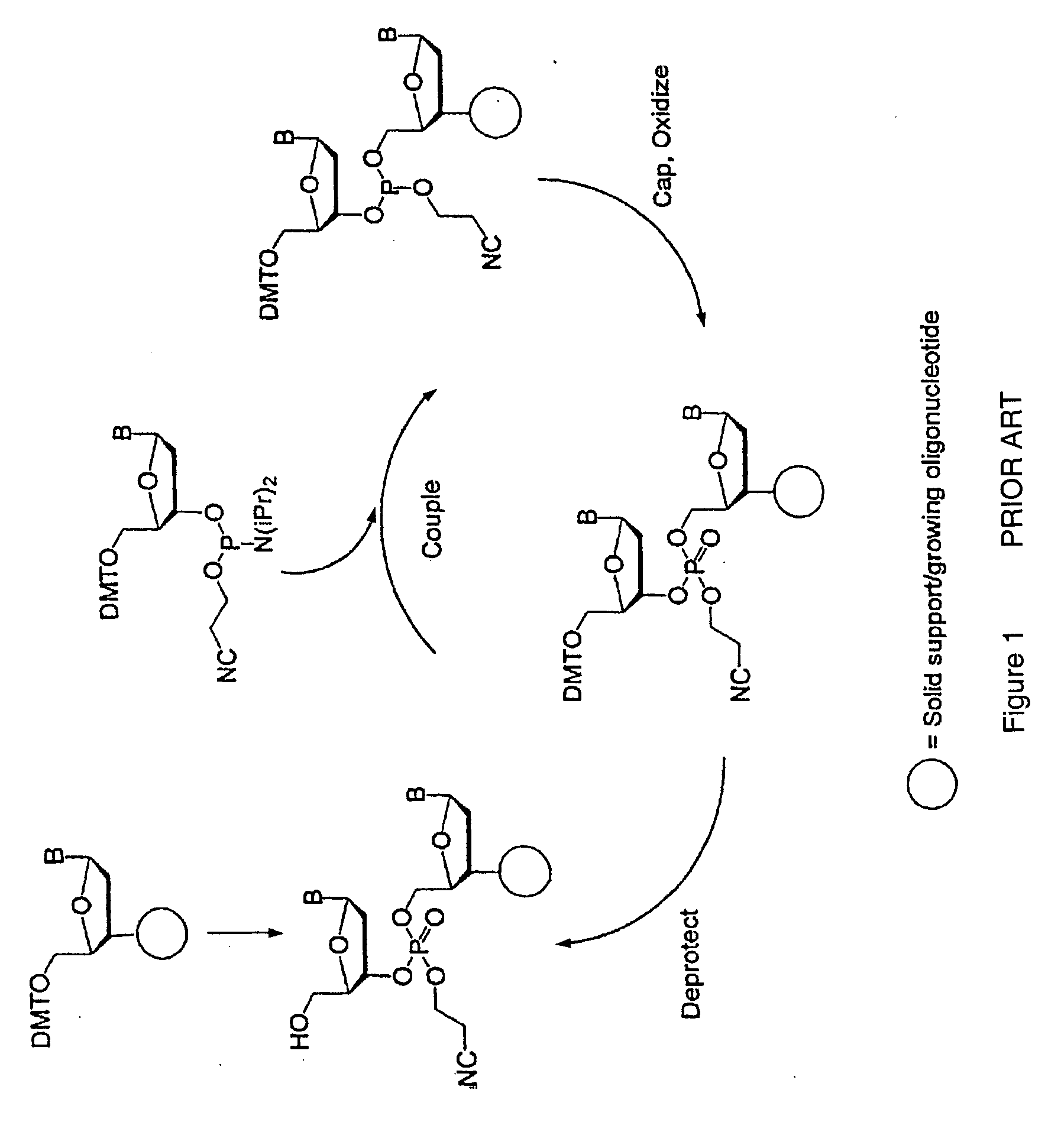
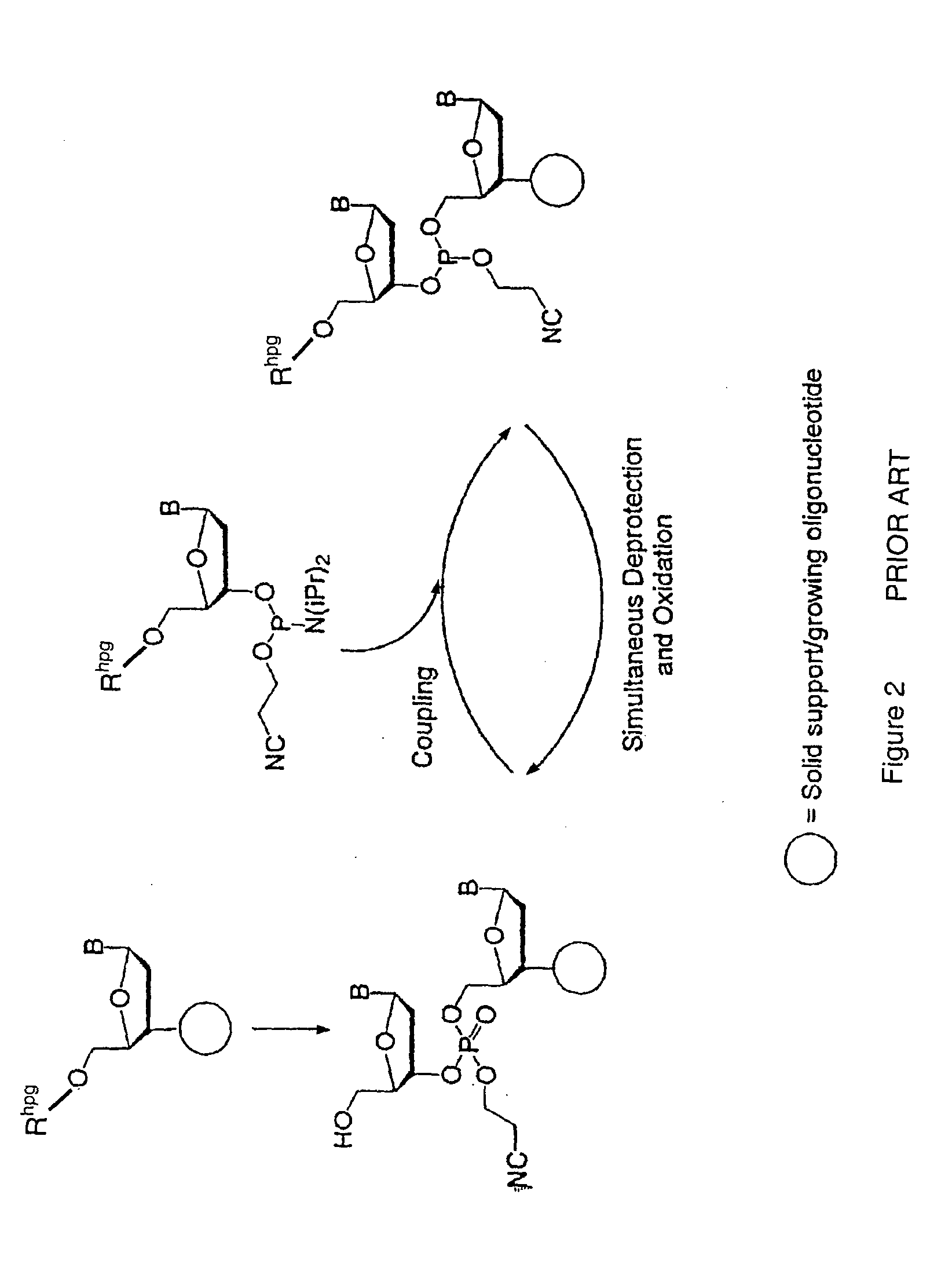
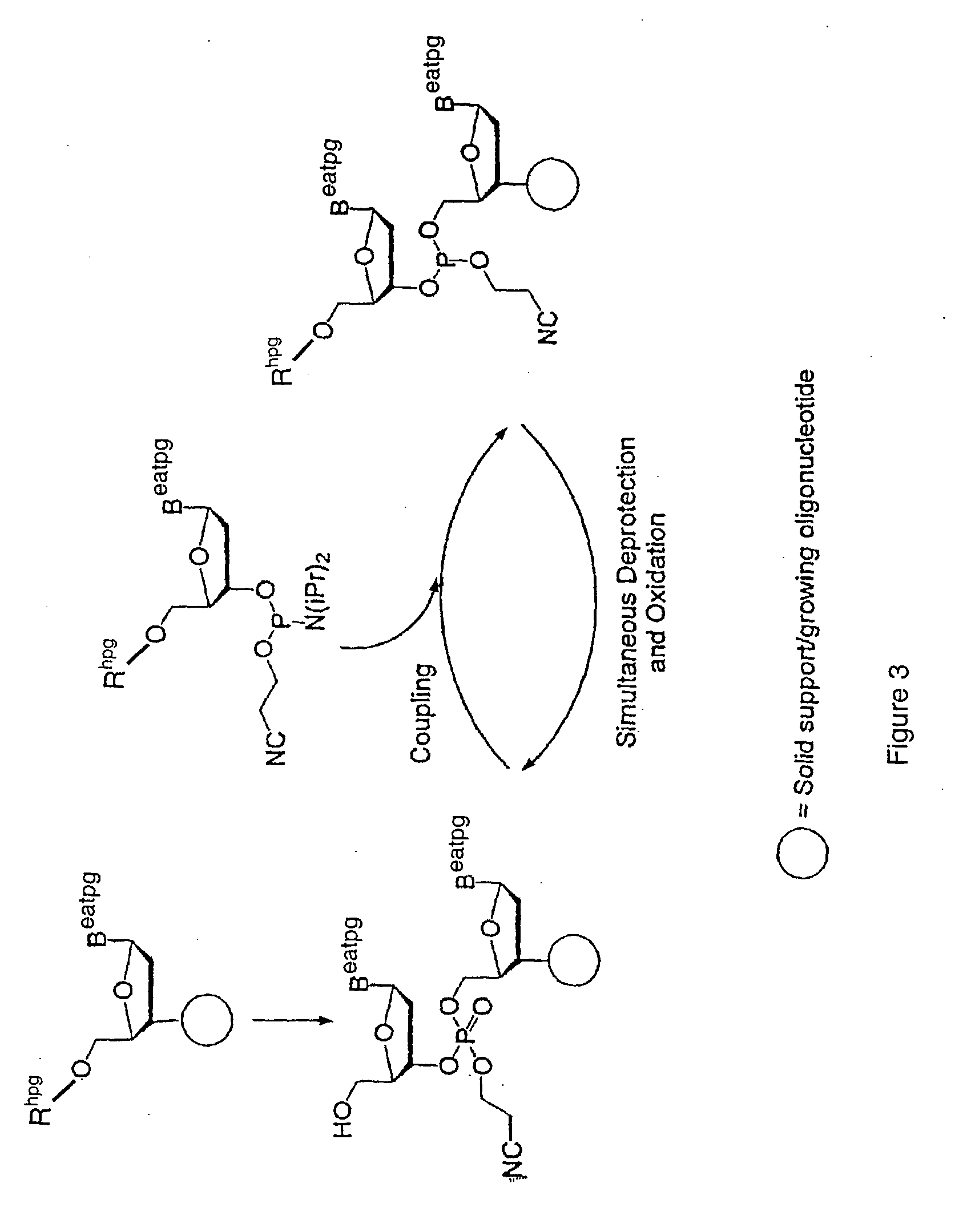
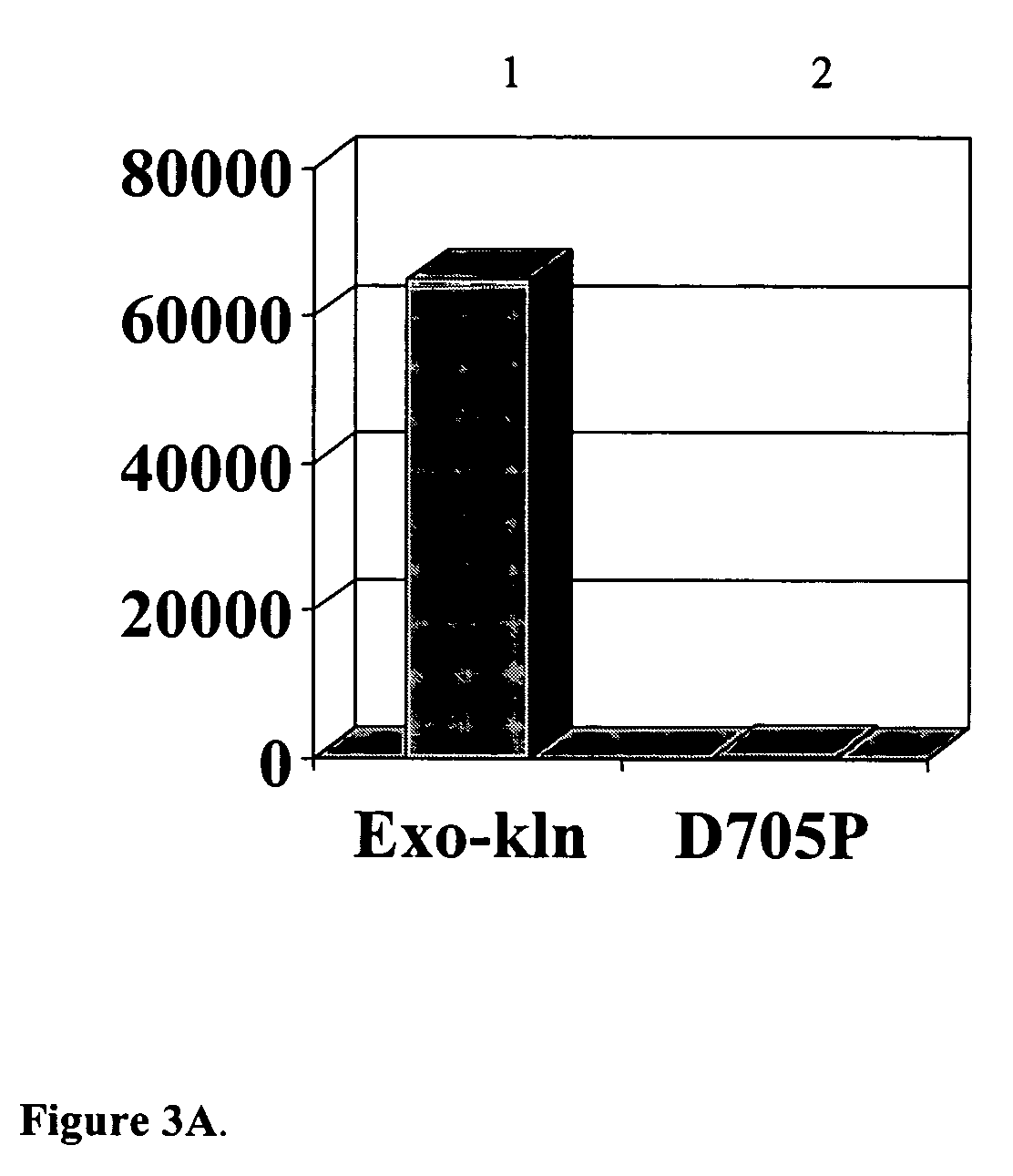
Exocyclic amine triaryl methyl protecting groups in two-step polynucleotide synthesis
Precursors for use in the synthesis of polynucleotides and methods of using the precursors in synthesizing polynucleotides are disclosed. The precursors include a heterocyclic base having an exocyclic amine group and a substituted or unsubstituted triaryl methyl protecting group bound to the exocyclic amine group.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC +1
Precursors for two-step polynucleotide synthesis
Precursors for use in the synthesis of polynucleotides are disclosed. The precursors include a heterocyclic base having an exocyclic amine group and a substituted or unsubstituted triaryl methyl protecting group bound to the exocyclic amine group. In particular embodiments, the precursor has the structure:wherein:O and H represent oxygen and hydrogen, respectively,R1 is hydrido, hydroxyl, protected hydroxyl, lower alkyl, modified lower alkyl, or alkoxy,one of R2 or R3 is a hydroxyl protecting group; and the other of R2 or R3 is a reactive group capable of reacting with a reactive site hydroxyl,Base is a heterocyclic base having an exocyclic amine group, andTram is a triaryl methyl group having the structure (V)wherein the broken line represents a bond to the amino nitrogen of the exocyclic amine group, and R4, R5 and R6 are independently selected from unsubstituted or substituted aryl groups, provided that at least one of R4, R5, and R6 is an aryl group other than phenyl and other than substituted phenyl.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC +1
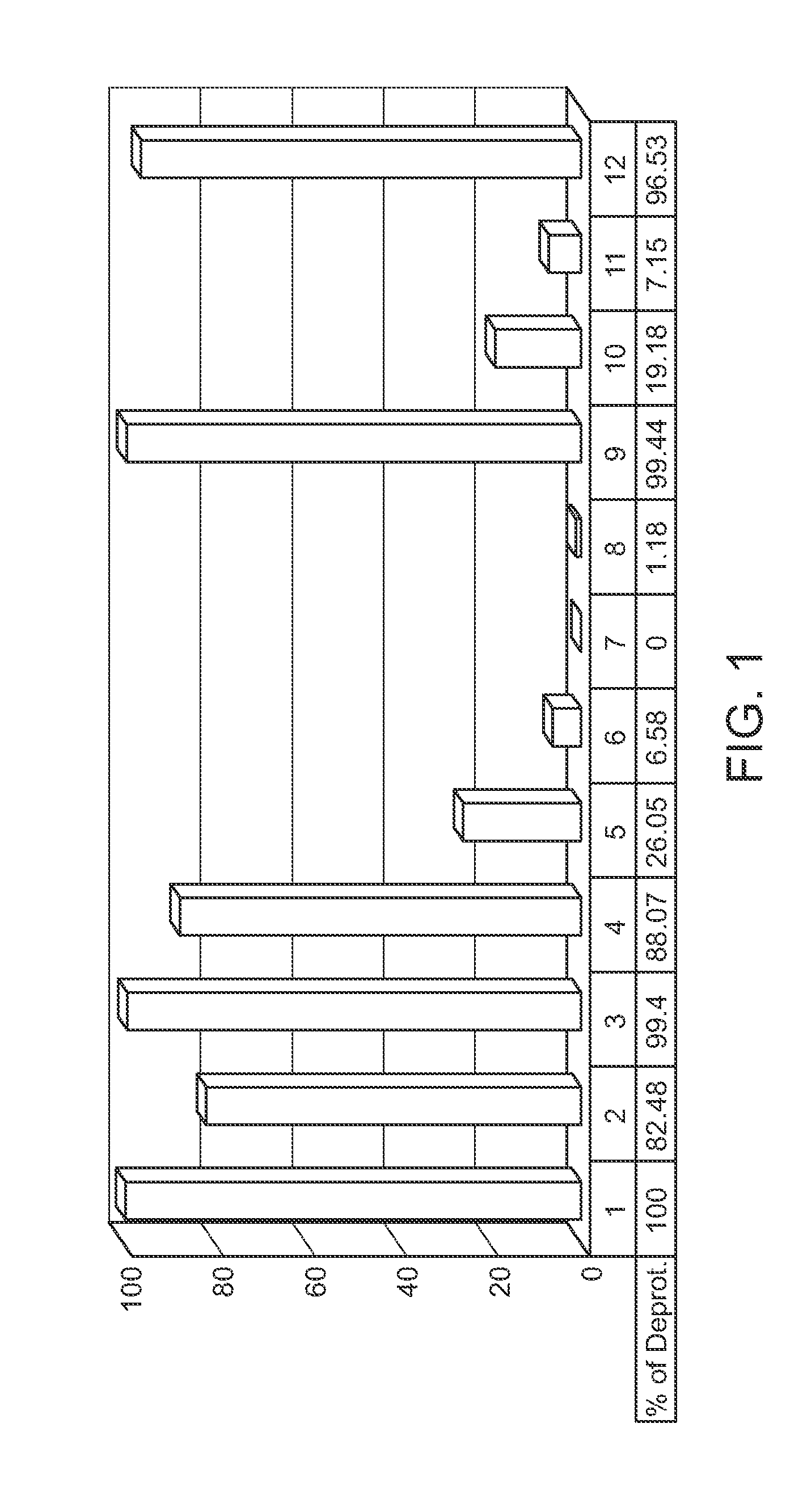
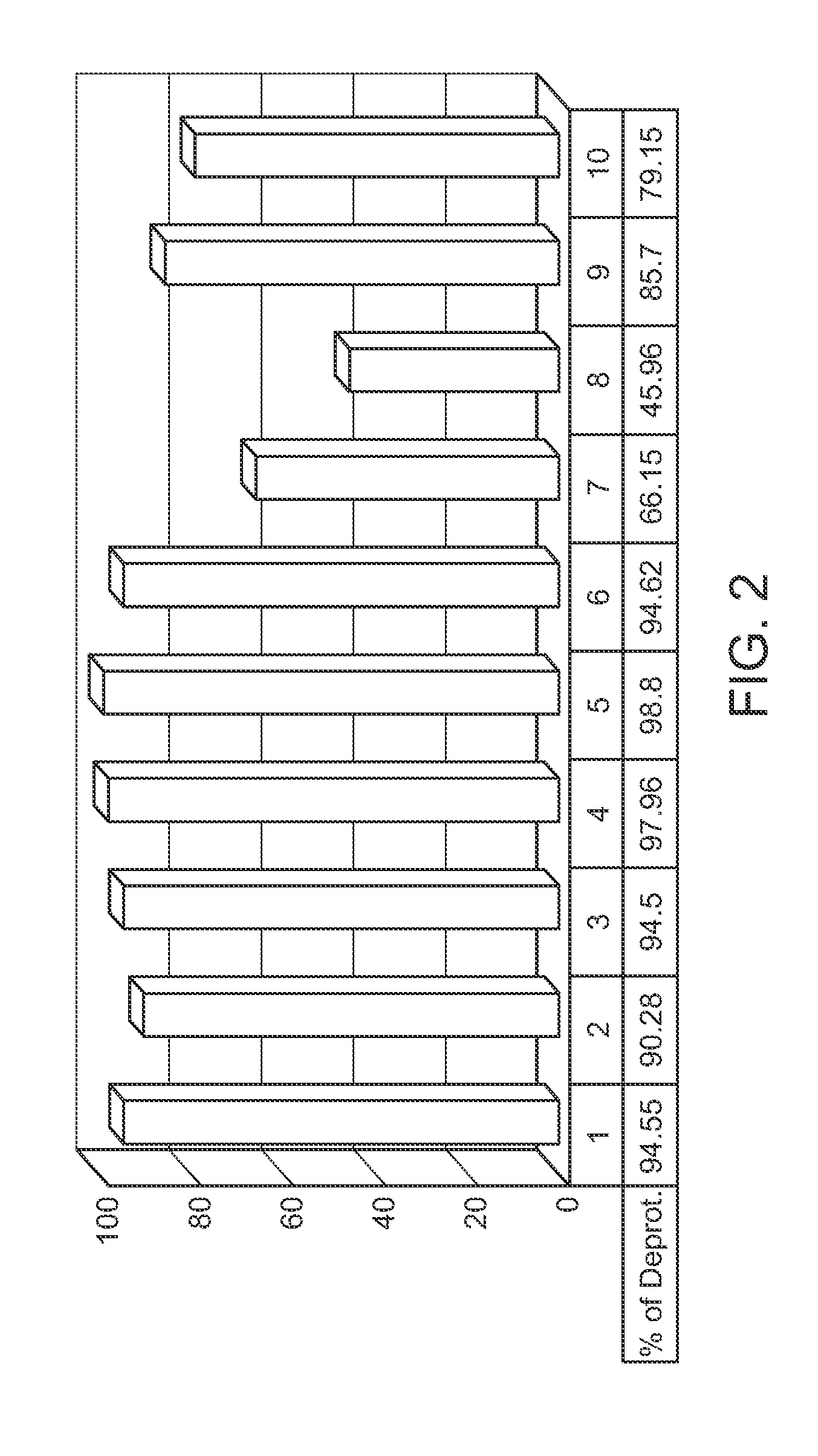
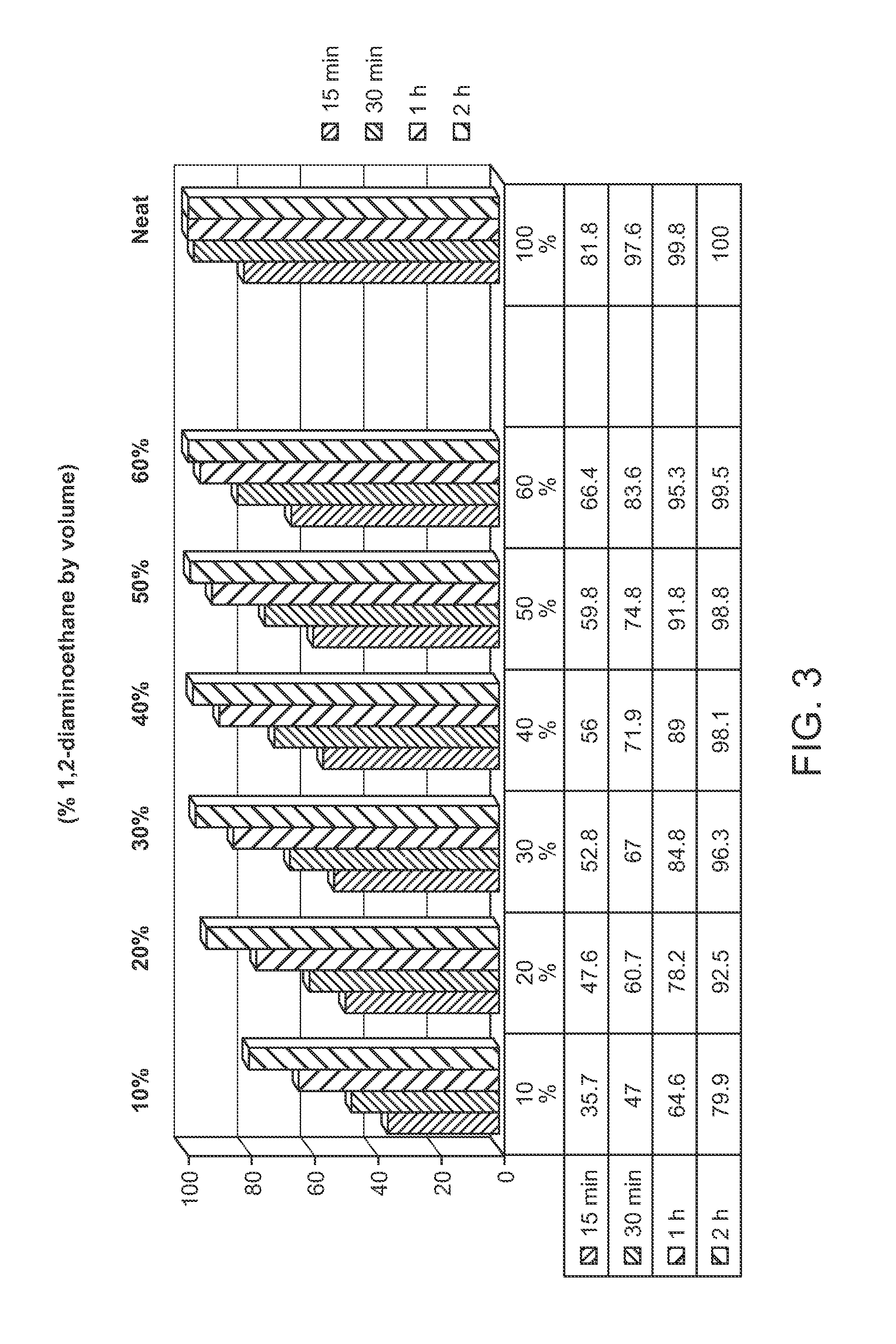
Protected monomers and methods of deprotection for RNA synthesis
InactiveUS20120184724A1High premiumsIsotope introduction to sugar derivativesSugar derivativesThiocarbamateCarbamate
A nucleoside monomer that is protected by a thionocarbamate protecting group and contains one or more 2H, 13C, or 15N isotopes in the ribose and / or base part is provided, as well as a method for making a polynucleotide that uses the same. Also provided is a polynucleotide synthesis method that employs a diamine to deprotect a protected polynucleotide.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
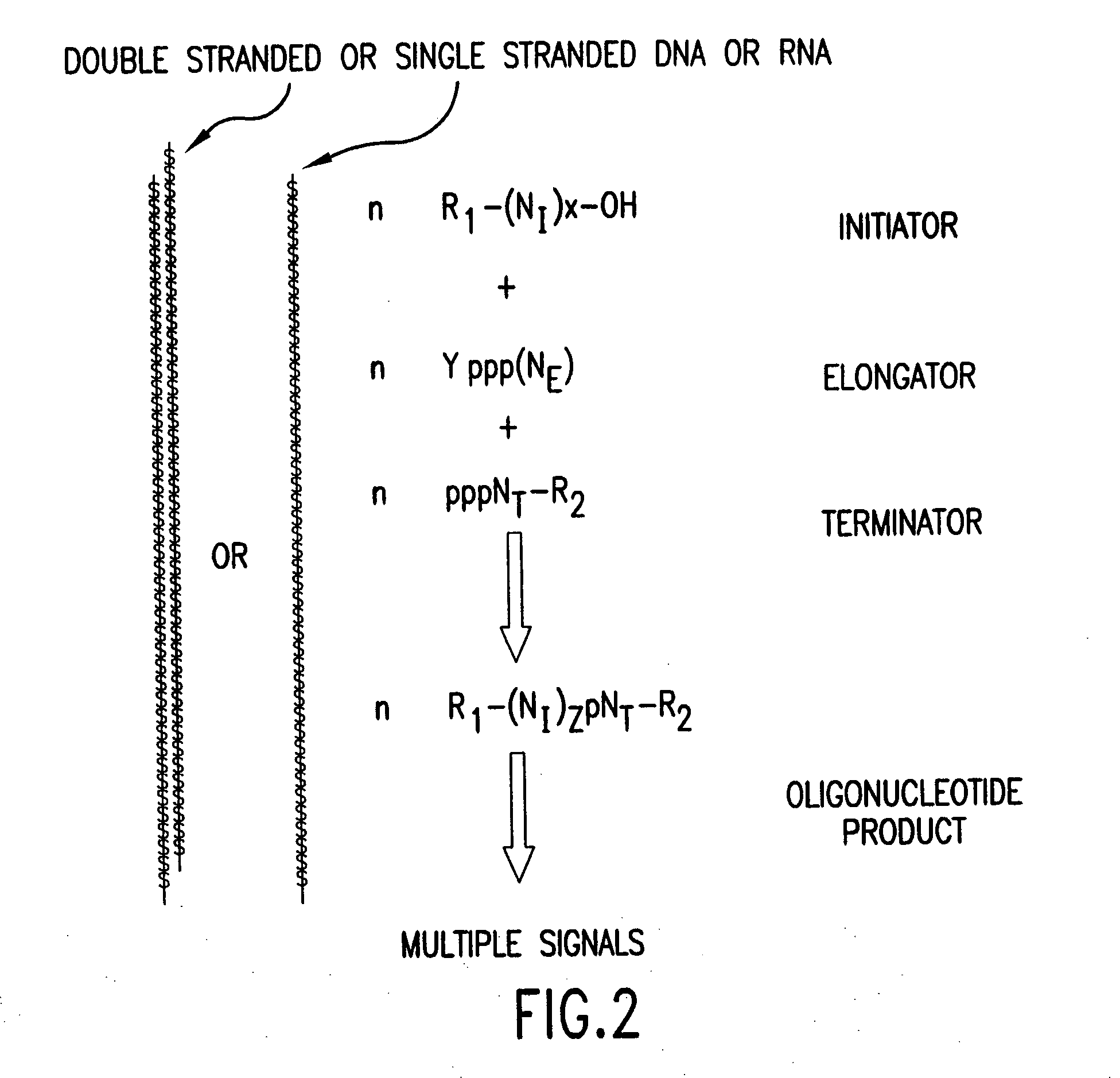
Molecular detection systems utilizing reiterative oligonucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS7045319B2Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationOligoribonucleotidesProtein target
Owner:RIBOMED BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
Multiplex polynucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS20060234264A1Solve low usageMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationChemical treatmentDna polymerasen
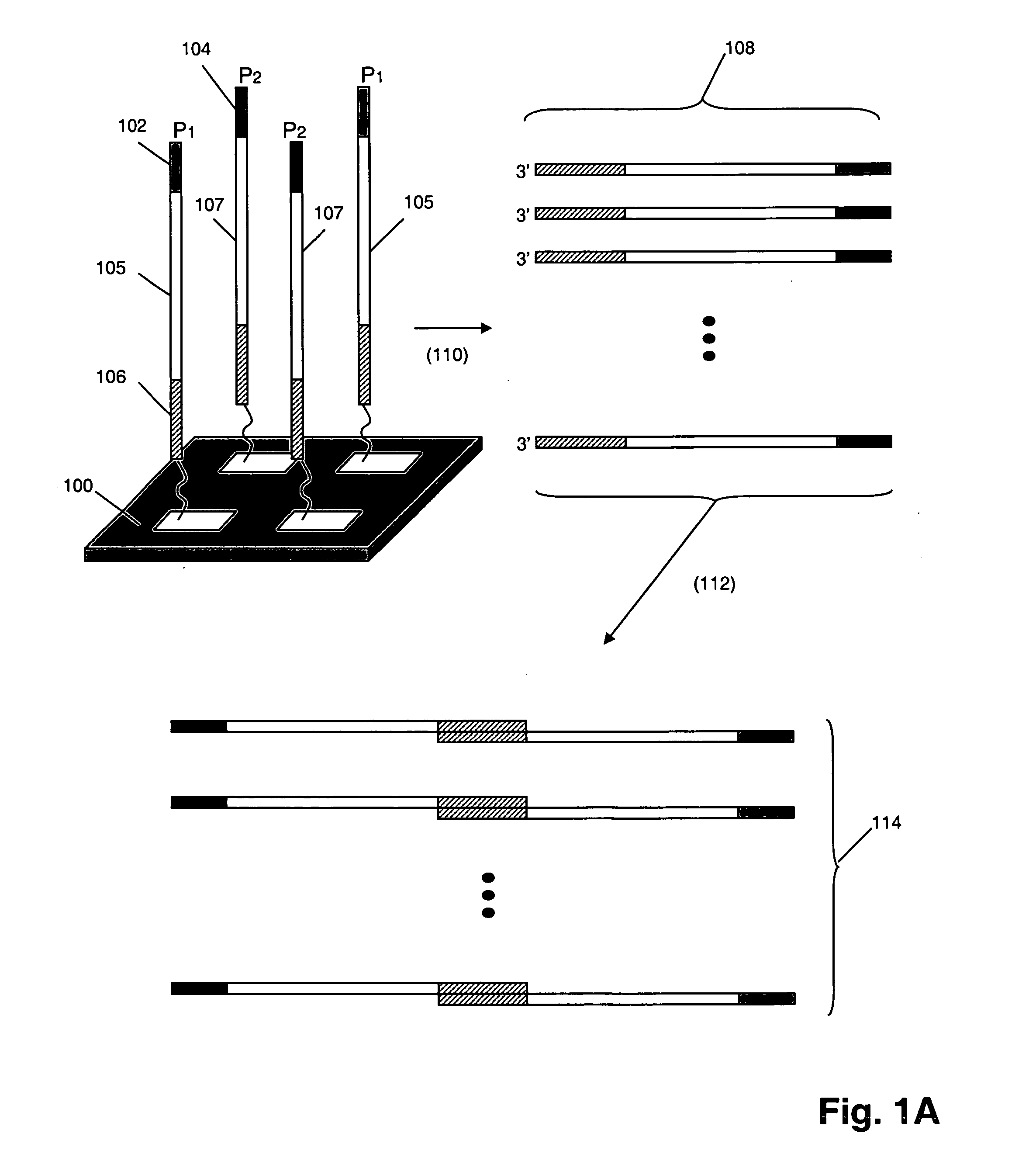
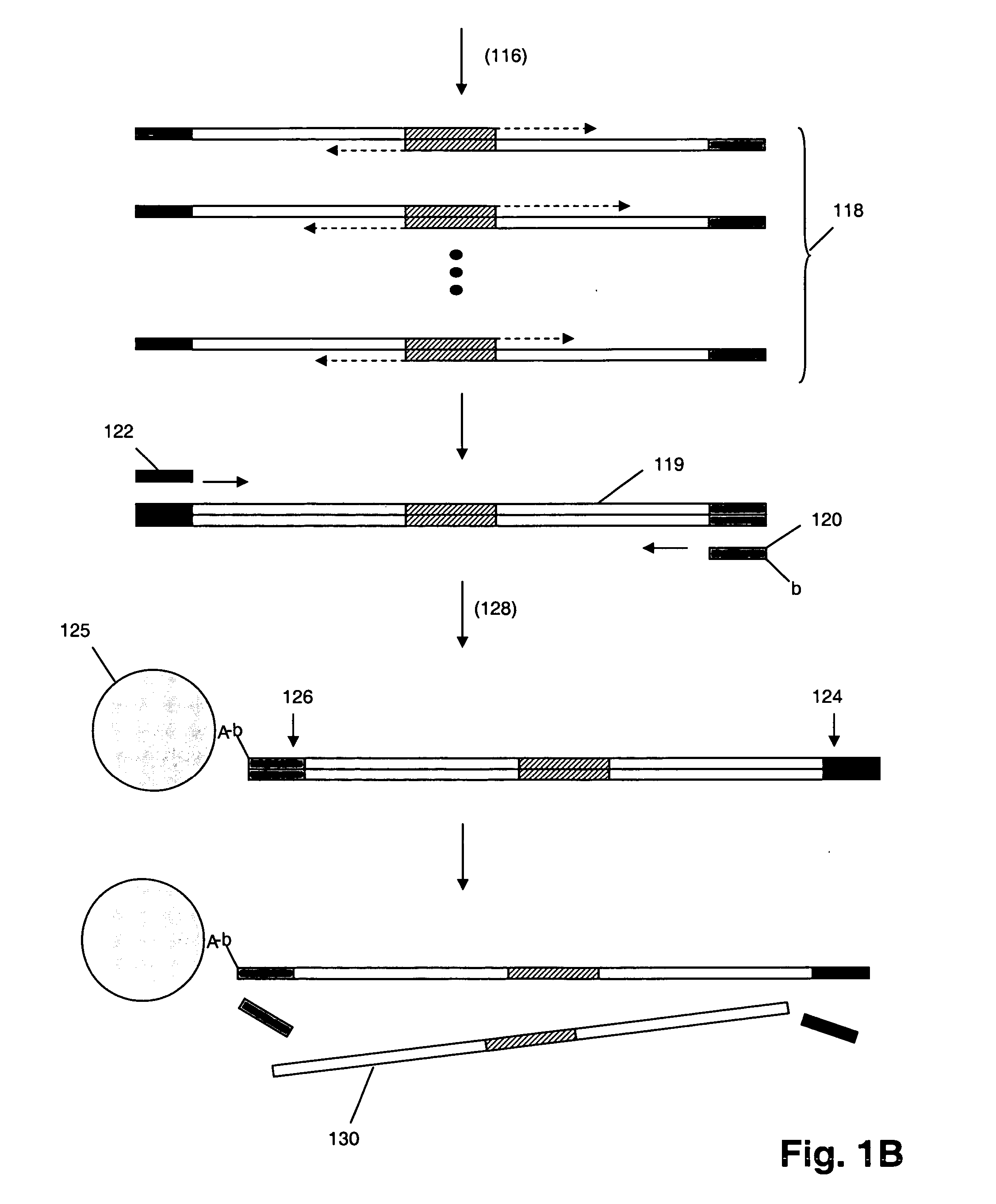
The invention provides a method of synthesizing complex mixtures of long polynucleotides by separately synthesizing and assembling shorter component oligonucleotides. In one aspect, pairs of oligonucleotides that form components of such polynucleotides are synthesized on one or more microarrays, or other large-scale parallel solid phase synthesis platforms, after which they are released. Members of each pair contain unique complementary barcode sequences that are used match-up pairs in a hybridization reaction to form duplexes. Such duplexes are then extended with a DNA polymerase and the resulting extension product is amplified to form an amplicon. The amplicon may be either used directly as the desired polynucleotide, or it may undergo further processing, such as capture on solid phase supports and / or additional enzymatic or chemical processing, to produce a desired polynucleotide product, such as a circularizing probe for multiplex analysis of genomic DNA, or the like.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Precursors for two-step polynucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS20050049407A1Undesirable side reactionSugar derivativesBulk chemical productionCombinatorial chemistryTwo step
Precursors for use in the synthesis of polynucleotides are disclosed. The precursors include a heterocyclic base having an exocyclic amine group and a substituted or unsubstituted triaryl methyl protecting group bound to the exocyclic amine group.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC +1
Exocyclic amine triaryl methyl protecting groups in two step polynucleotide synthesis
ActiveUS20050049411A1Undesirable side reactionSugar derivativesBulk chemical productionTwo stepProtecting group
Precursors for use in the synthesis of polynucleotides and methods of using the precursors in synthesizing polynucleotides are disclosed. The precursors include a heterocyclic base having an exocyclic amine group and a substituted or unsubstituted triaryl methyl protecting group bound to the exocyclic amine group.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC +1
Compositions, methods and detection technologies for reiterative oligonucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS20050214796A1MicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementDendrimerOligoribonucleotides
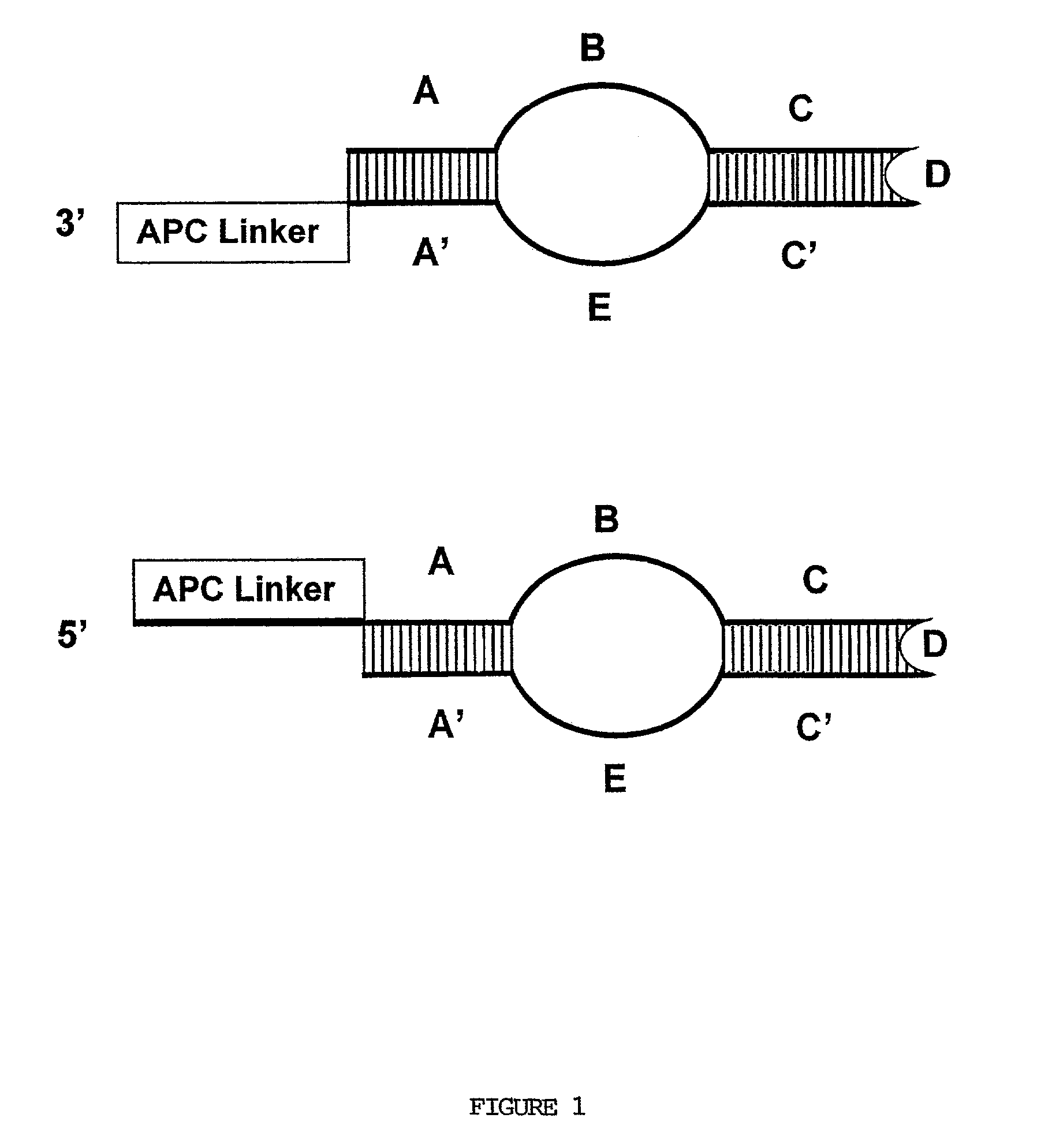
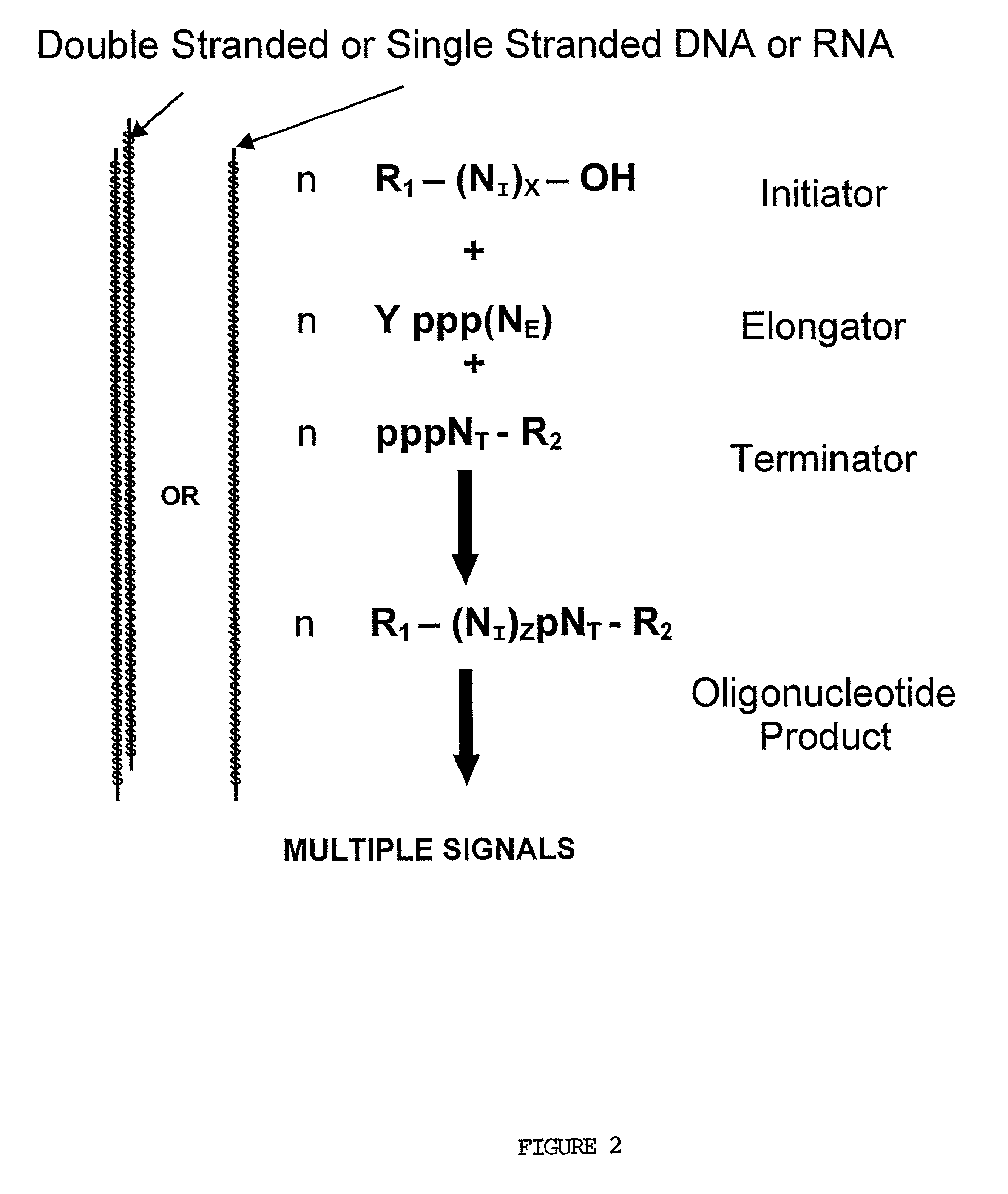
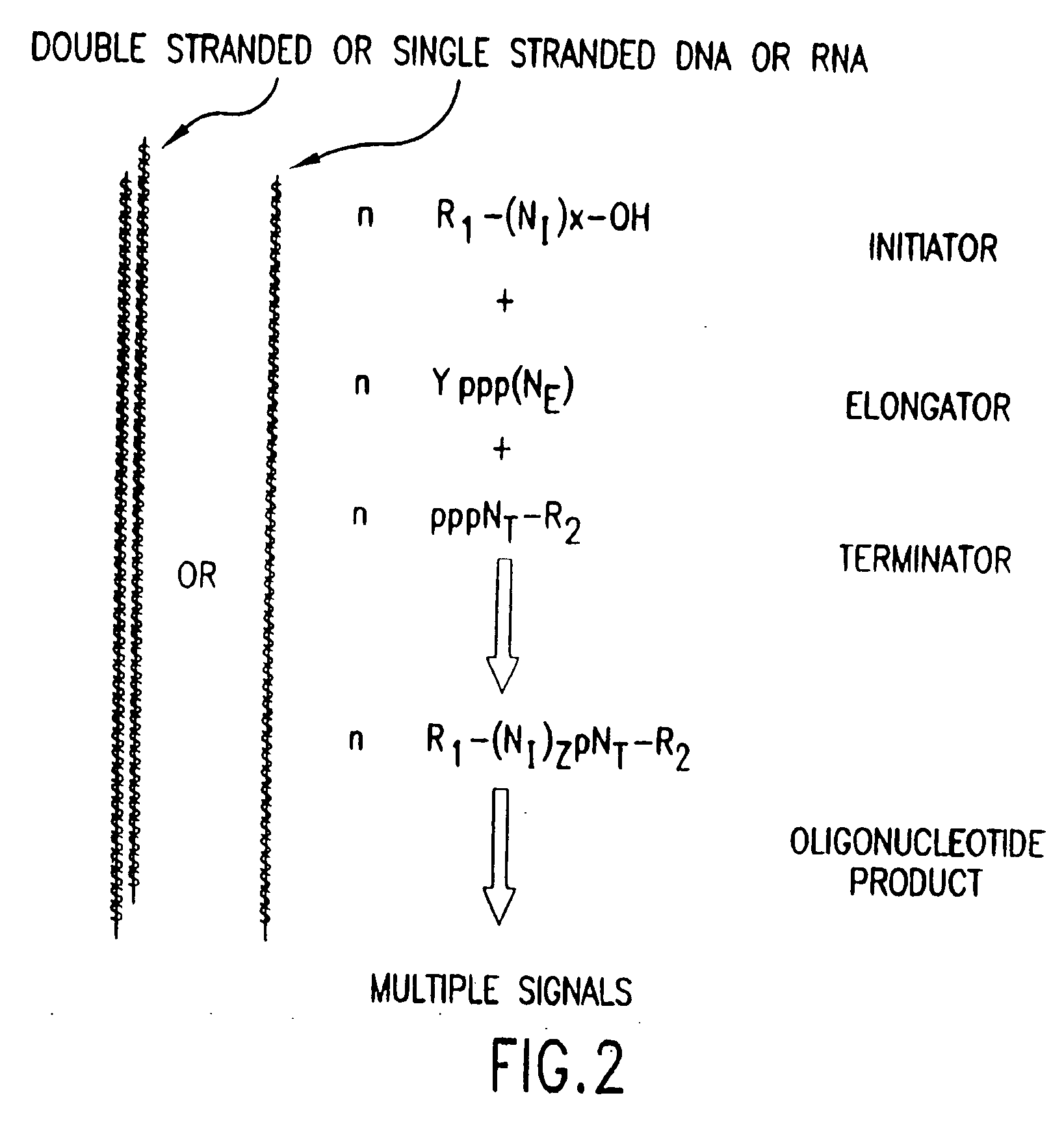
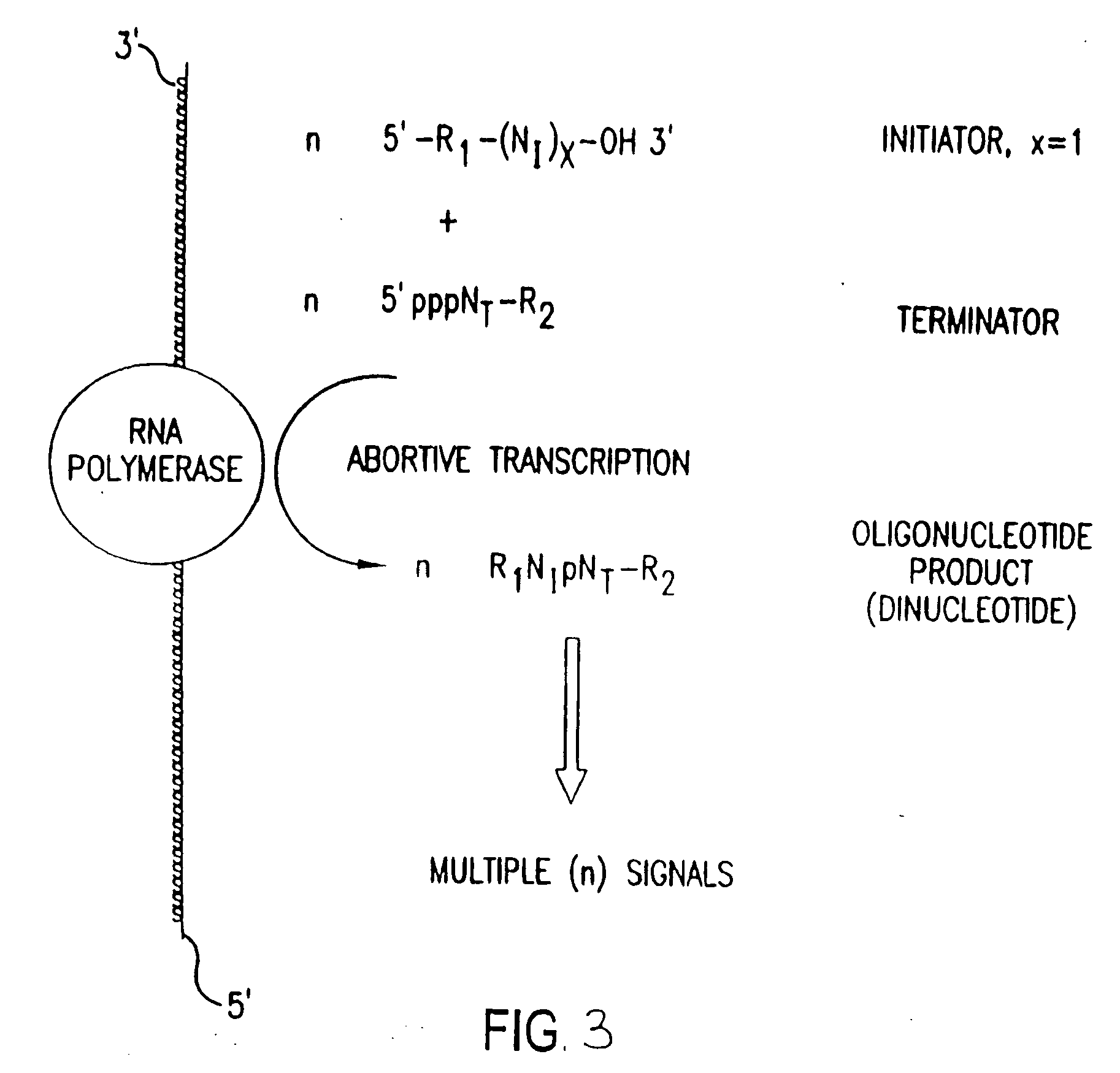
The present invention provides methods for detecting the presence of a molecule of interest by generating multiple detectable oligonucleotides through reiterative enzymatic oligonucleotide synthesis events on a polynucleotide sequence and detecting said products. The invention also provides for methods of multiplex abortive transcription. In a further aspect, the invention provides for the use of dendrimers containing abortive promoter cassettes. In one aspect, the invention provides for abortive promoter cassettes suitable for use in the present invention. In one aspect the products of abortive transcription are detected with the use of mass spectrometry. In another aspect, the invention provides a method for detecting a target protein, DNA or RNA by generating multiple detectable RNA oligoribonucleotides by abortive transcription that are detected, including by mass spectrometry.
Owner:RIBOMED BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
Method and system for polynucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS7164992B1Error minimizationMinimize incorrect joiningComputer controlRead-only memoriesSynthesis methodsTheoretical computer science
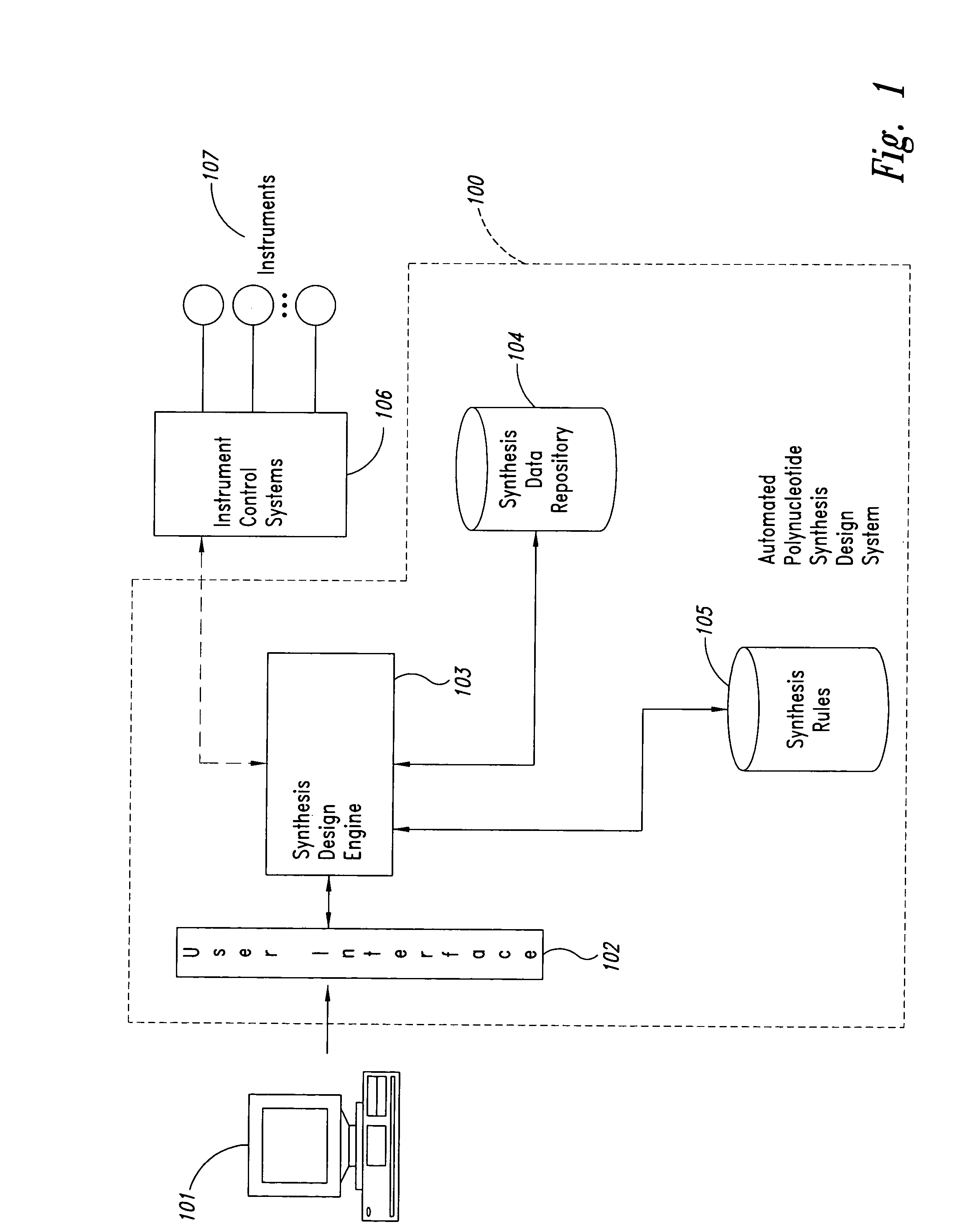
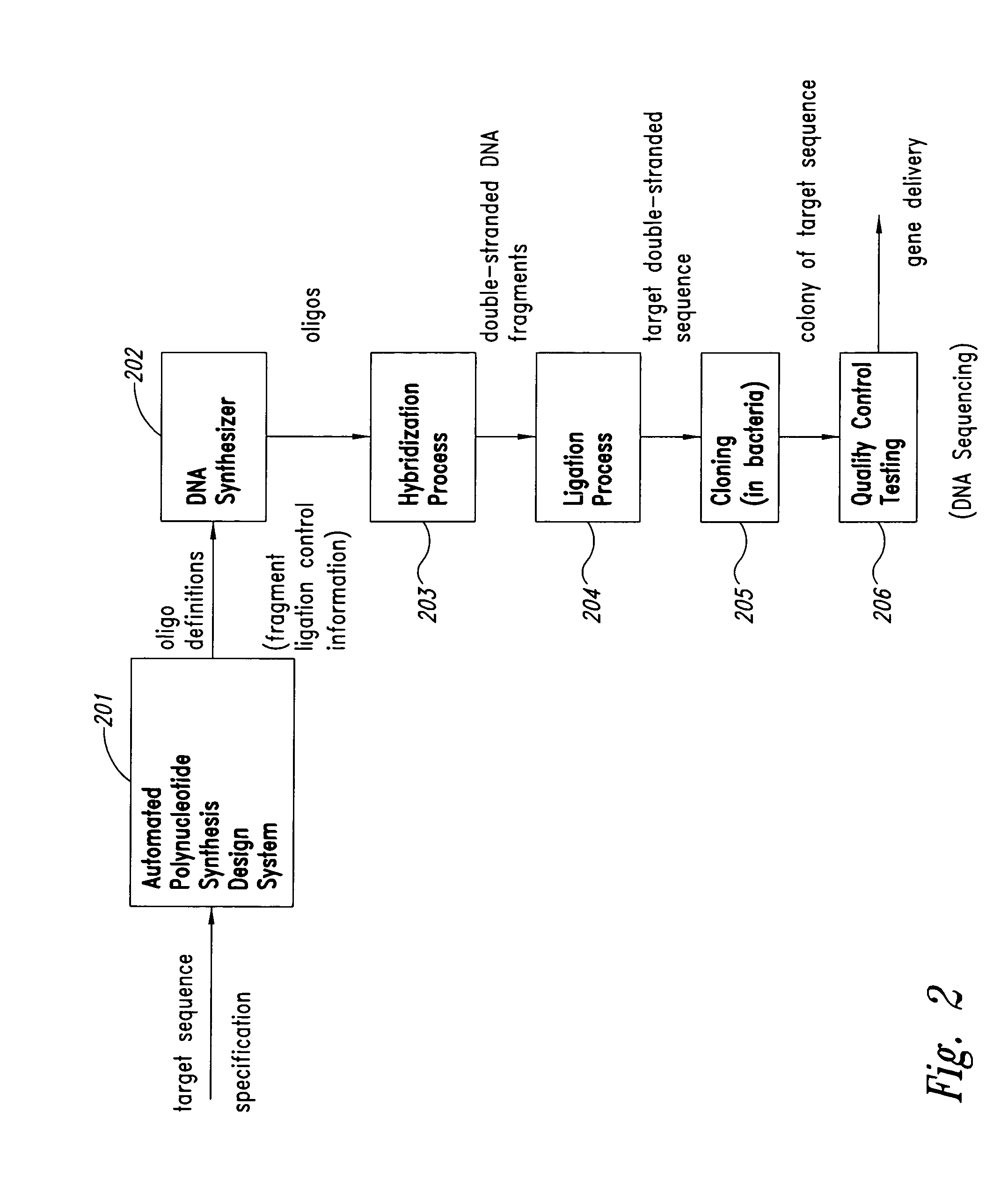
Methods and systems for automated polynucleotide synthesis design are provided. Example embodiments provide an Automated Polynucleotide Synthesis Design System (“APSDS”), which automatically generates a synthesis design for a designated target sequence specification. In one embodiment, the APSDS comprises a synthesis design engine, user interface support, a synthesis rules data repository, and a synthesis data repository. The APSDS automatically generates a synthesis design by receiving a target sequence(s) specification, generating a potential synthesis design, evaluating the potential design against synthesis rules, and when the evaluation indicates that the potential design is not successful according to the synthesis rules, adjusting the design to generate a new potential synthesis design and repeating the process of evaluating and adjusting until a potential synthesis design is found that satisfies the synthesis rules or until no solution is found.
Owner:BLUE HERON BIOTECH
Programmable Oligonucleotide Synthesis
ActiveUS20100015668A1Reduce yieldSynthesis is longSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsOligonucleotide synthesisNucleotide synthesis
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
Nanofluidic sorting system for gene synthesis and PCR reaction products
ActiveUS20150283514A1Reduce yieldIncrease the lengthSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementPolymerase LGene synthesis
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Hot start polymerase reaction using a thermolabile blocker
The invention relates to compositions, methods, and kits for hot start polynucleotide synthesis, including extension of primed polynucleotide templates and polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Hot start is provided by a thermally inactivated blocking polymerase protein that binds primed polynucleotide templates and prevents their access to a thermostable nucleic acid polymerase. High temperatures employed in the synthesis reaction cause the blocking polymerase to denature, thereby permitting the action of a thermostable processive polymerase. Compositions of the invention include a specific blocking polymerase protein which is a mutant of the Klenow fragment of E. coli DNA polymerase. The mutant is essentially devoid of polymerase activity, processivity, and 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity. Use of the thermally inactivated blocking polymerase together with a thermostable polymerase reduces non-specific priming and accumulation of unwanted amplification products, increasing the specificity and sensitivity of the synthesis reaction.
Owner:STRATAGENE INC US
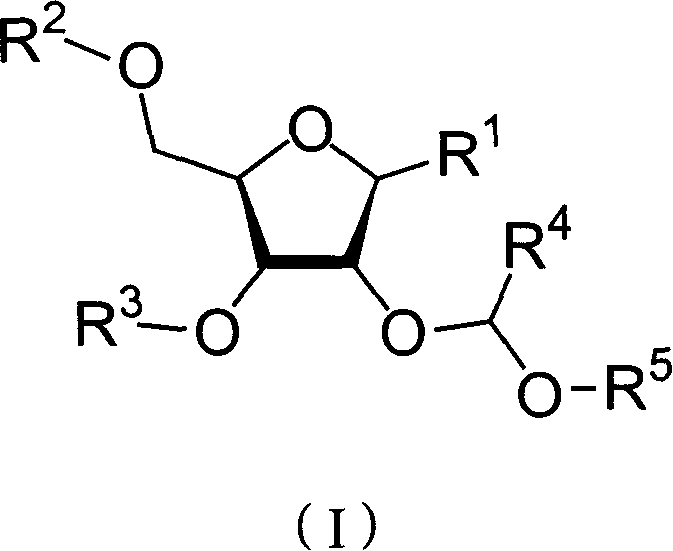
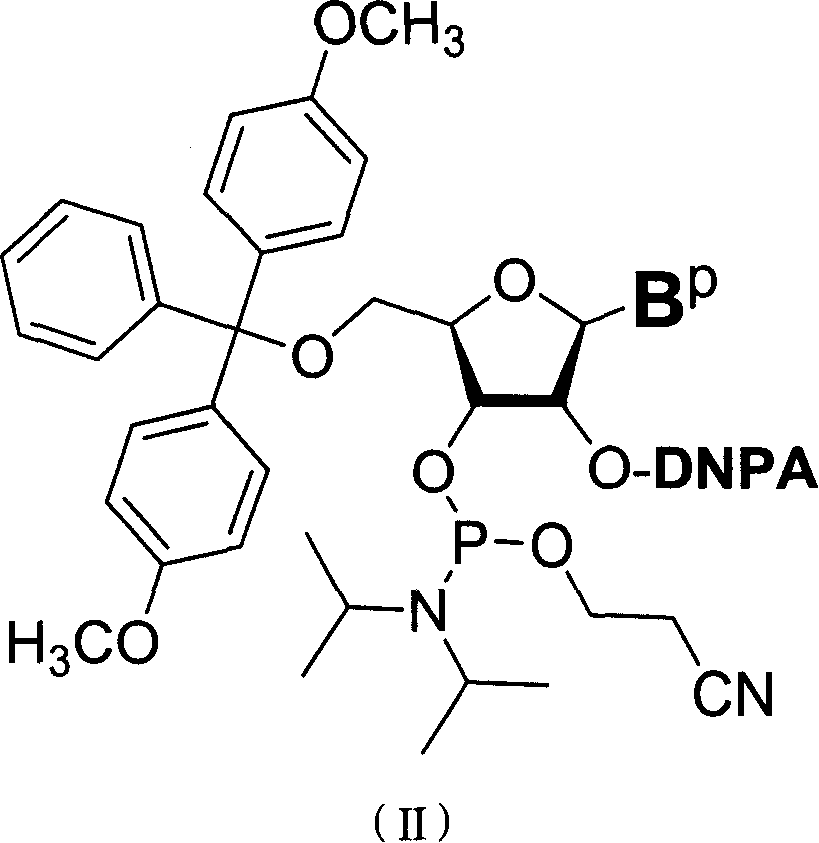
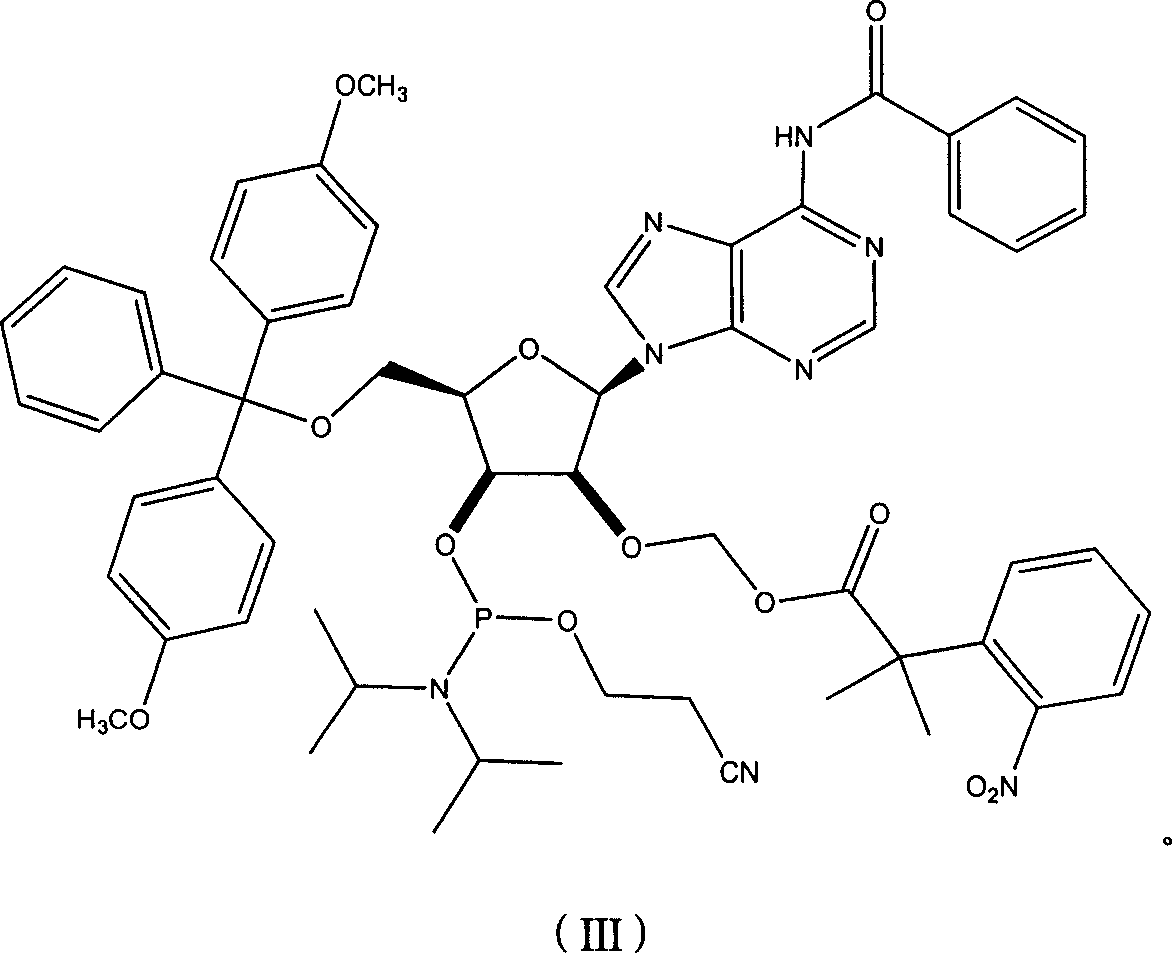
Nucleoside phosphoramidite used in RNA oligo-nucleotide synthesis and its synthesizing method
InactiveCN1900103AHigh purityDoes not affect the productSugar derivativesEtherCombinatorial chemistry
The present invention discloses a kind of nucleoside phosphoramidite for synthesizing RNA oligonucleotide and its synthesis. The present invention adopts [2, 2-dimethyl-2-(o-nitrophenyl) acetylmethoxy] ether (DNPA) as the 2'-hydroxy protecting radical. The protecting radical DNPA is compatible with convenient 5'-hydroxy protecting radical, and may be eliminated under mild condition, so that it can ensure the RNA integrality and is suitable for synthesis of RNA oligonucleotide. The present invention provides one new path for synthesizing RNA oligonucleotide and may be used for the RNA molecule synthesis of various kinds of natural nucleoside, non-natural nucleoside, labeling nucleoside or their derivatives.
Owner:张必良
Phosphoramidites for synthetic RNA in the reverse direction, efficient RNA synthesis and convenient introduction of 3'-end ligands, chromophores and modifications of synthetic RNA
ActiveUS8541569B2Efficient modificationClean oligo synthesisSugar derivativesPeptidesBiologyChromophore
The present invention provides building blocks and methods for synthesizing very pure RNA in a form that can efficiently be modified at the 3′ end. Reverse RNA monomer phosphoramidites have been developed for RNA synthesis in 5′→3′ direction, leading to very clean oligo synthesis that allows for the introduction of various modifications at the 3′-end cleanly and efficiently. Higher coupling efficiency per step have been observed during automated oligo synthesis with the reverse RNA amidites disclosed herein, resulting in a greater ability to achieve higher purity and produce very long oligonucleotides. The use of the reverse RNA phosphoramidites in the synthetic process of this invention leads to oligonucleotides free of N+1 species.
Owner:CHEMGENES CORP
Two-nucleotide synthetic sequencing analysis method for multi-template PCR product
ActiveCN104894246AEasy to findExpand the scope of analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisGenome sequence analysis
The invention discloses a two-nucleotide synthetic sequencing analysis method for a multi-template PCR product. The method comprises the steps of uniformly dividing the same PCR product into at least two parts, and carrying out two-nucleotide synthetic sequencing, wherein each sequencing reaction obtains sequencing encoding information containing two nucleotide kinds and nucleotide synthetic amount; selecting at least two groups of encoding information respectively obtained by at least two groups of different two-nucleotide synthetic circular sequencing in three groups to decode; and finally, determining the contents of different DNA templates of the PCR product through association analysis. The two-nucleotide synthetic sequencing analysis method can be used for widening the single-nucleotide synthetic sequencing analysis range, directly measuring the proportions of all the DNA templates in a sample and finding and screening nucleotide markers from large-scale samples, and is suitable for sequencing analysis of the multi-template PCR product and a mixed sample PCR product.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Molecular detection systems utilizing reiterative oligonucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS20050026150A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein targetPolymerase L
The present invention provides methods for detecting the presence of a target molecule by generating multiple detectable oligonucleotides through reiterative enzymatic oligonucleotide synthesis events on a defined polynucleotide sequence. The methods generally comprise using a nucleoside, a mononucleotide, an oligonucleotide, or a polynucleotide, or analog thereof, to initiate synthesis of an oligonucleotide product that is substantially complementary to a target site on the defined polynucleotide sequence; optionally using nucleotides or nucleotide analogs as oligonucleotide chain elongators; using a chain terminator to terminate the polymerization reaction; and detecting multiple oligonucleotide products that have been synthesized by the polymerase. In one aspect, the invention provides a method for detecting a target protein, DNA or RNA by generating multiple detectable RNA oligoribonucleotides by abortive transcription.
Owner:RIBOMED BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
Polyvinyl ethers
The present invention relates to polyvinyl ethers and to their use as supports for synthetic methods (organic synthesis, peptide synthesis, oligonucleotide synthesis, oligosaccharide synthesis or any other synthetic procedure) and to their use for chromatographic applications (such as affinity chromatography), immobilisation of enzymes, reagents or catalysts.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
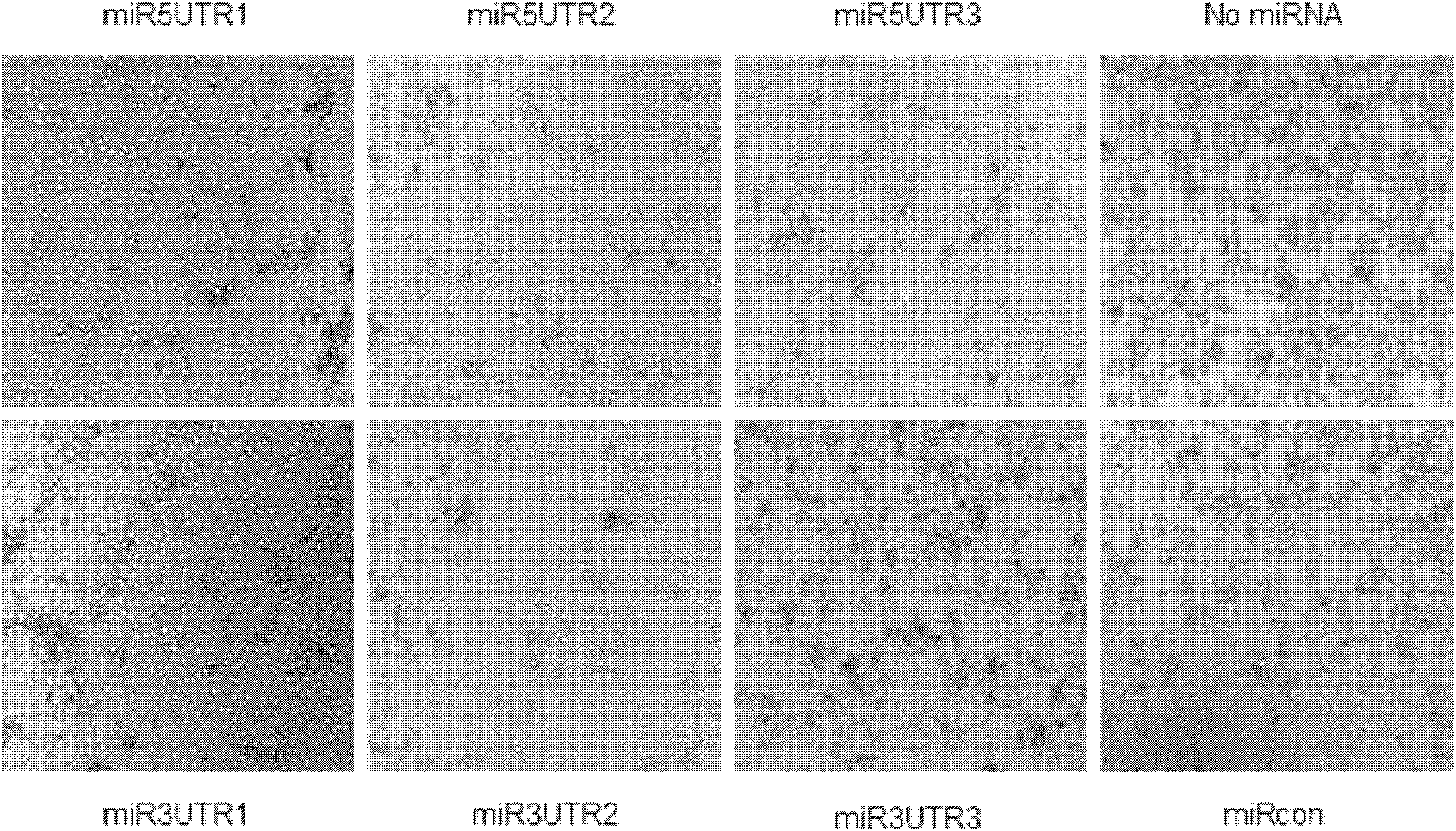
Untranslated region-specific artificial microRNAs that effectively inhibit the replication of different strains of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus
The invention designs an untranslated region specific artificial micro RNA (miRNA) capable of effectively inhibiting replication of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus strains, which belongs to the field of researches on gene engineering and biological products. The sequence of the miRNA is represented by one of SEQ ID No.1, SEQ ID No.2, SEQ ID No.3 and SEQ ID No.4. The invention also discloses the construction of an artificial miRNA expression vector based on RNA polymerase II, design of miRRNAi, synthesis and cloning of double-stranded oligo, detection of expression of miRNA and inhibition effect on replication of different PRRSV strains. Compared with siRNAs for genes of other PRRSVs, the artificial miRNA screened by the invention, according to the conservative sequence of the untranslated region, can inhibit the replication of homologous virus strains and heterologous virus strains and can be used in both the development of anti-PRRSV infection preparations and breeding transgenic pig disease resistance lines.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
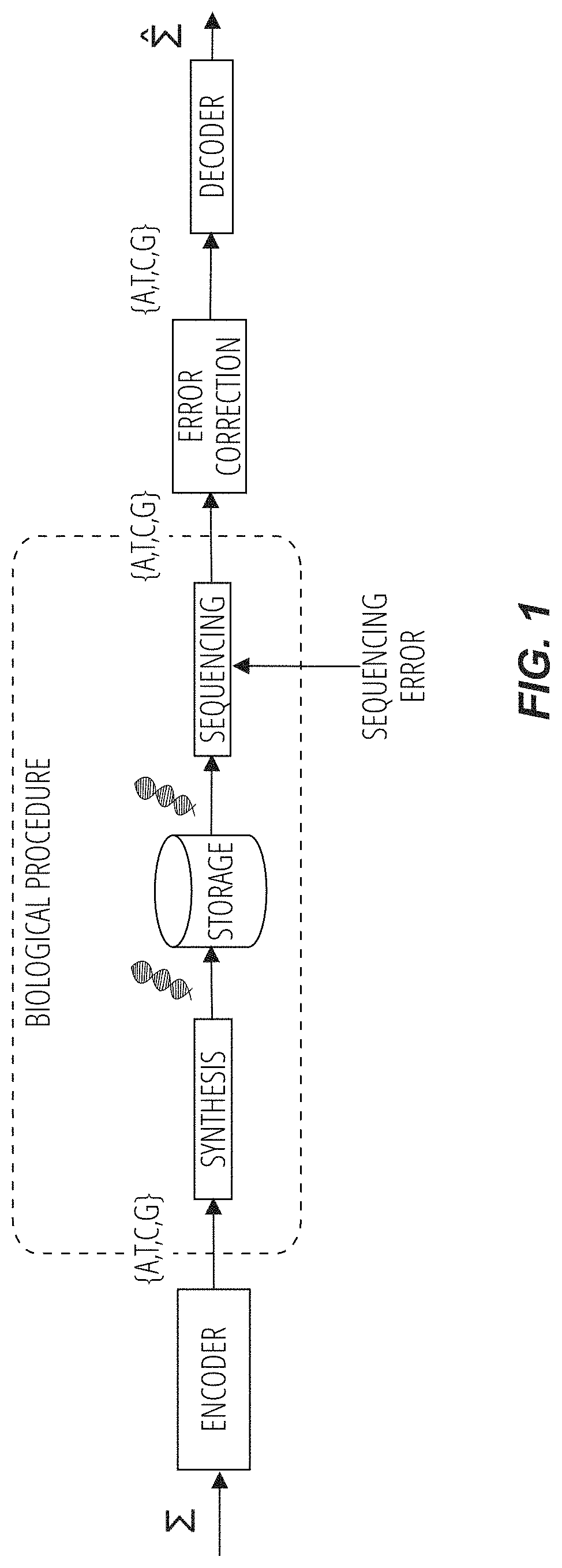
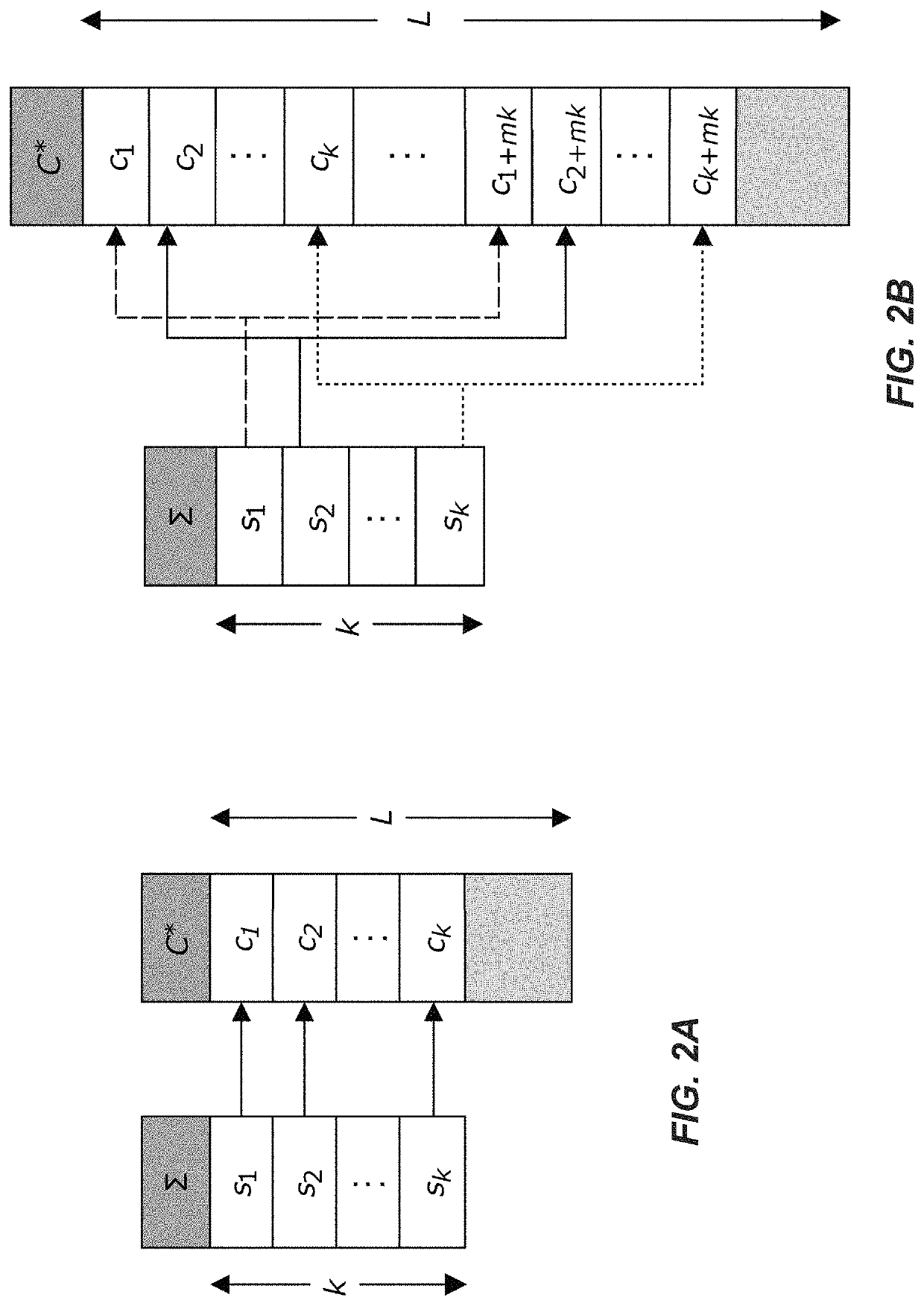
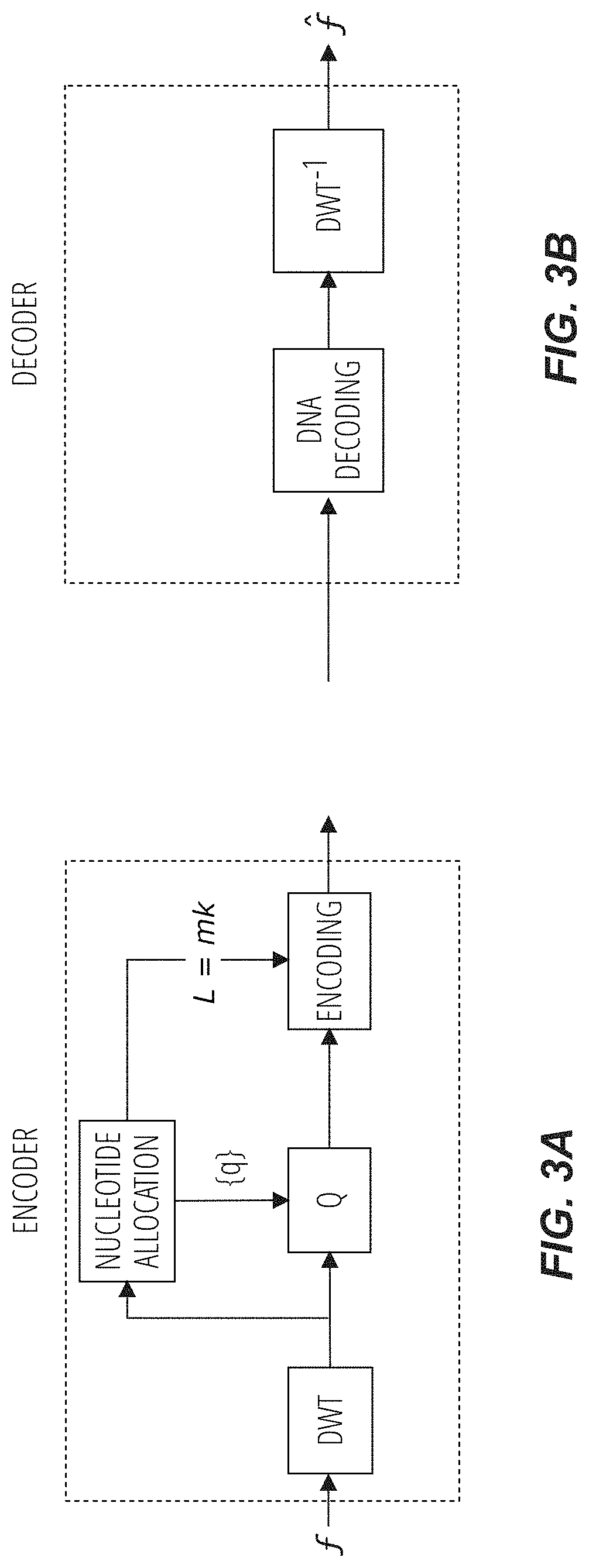
Methods for storing digital data as, and for transforming digital data into, synthetic DNA
Methods for encoding data in synthetic DNA include, for an input data sequence, constructing a codebook of a number of unique codewords, of a nucleotide length, which are constructed such that, for each codeword, the codeword is formed from a selection of nucleotide pairs from a first predefined dictionary of nucleotide pairs, and, if the nucleotide length of the codeword is odd, an additional selection of a nucleotide from a second predefined dictionary of individual nucleotides. For each symbol from the input data sequence, at least one codeword is designated as associable therewith, and each symbol is coded as one codeword selected from the designated at least one codeword associable with that symbol. A code is formed from the codewords, arranged in corresponding order to that of their respective symbols in the input data sequence. A DNA sequence is synthetized with nucleotides ordered to match the code.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Multiplex polynucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS20070087417A1Solve low usageFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionCombinatorial chemistrySingle strand
The invention provides a method of convergently synthesizing mixtures of either single stranded or double stranded polynucleotides. In one aspect, oligonucleotides that form components of such polynucleotides are synthesized on one or more microarrays, or other large-scale parallel solid phase synthesis platforms, after which they are amplified directly, or are released into solution and then amplified. At least two sets of such released and amplified oligonucleotides are produced, referred to herein as first and second amplicons. The first and second amplicons are cleaved and then ligated to different ends of a bridging duplex that is present in the reaction in limiting quantity to form a polynucleotide mixture of the invention. At the completion of the reaction, each polynucleotide in the mixture is present in substantially equal concentration, regardless of the starting concentrations of the first and second amplicons. That is, the invention provides a method for synthesizing a normalized mixture of polynucleotides.
Owner:PARALLELE BIOSCI
Recombinant bacterium for producing L-histidine, construction method of recombinant bacterium and method of producing L-histidine
ActiveCN110117568AImprove synthesis abilityShort fermentation cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAdenosineSuccinic acid
The invention relates to a recombinant bacterium for producing L-histidine, a construction method of the recombinant bacterium and a method of producing the L-histidine. Compared with an original strain, the recombinant bacterium for producing the L-histidine has the improved expression and / or activity of adenosine succinic acid synthetase PurA, and the original strain is a strain capable of accumulating the L-histidine. According to the recombinant bacterium and the construction method of the recombinant bacterium, based on the pioneering principle, by enhancing AMP synthesis in the synthesispath of nucleotide and improving the synthesis capacity of a bacterial strain ATP, enough precursor substances and energy carriers ATP are provided for efficient histidine synthesis, and the histidine synthesis capacity of the recombinant bacterium strain is significantly improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coated polymer article and its use
InactiveUS6420028B1Reduce the amount requiredSignificant selectivityLiquid surface applicatorsComponent separationTO-18Hydrogen
A polymer article having structure (I), where P comprises the basic polymer and groups -L-CH(-X(R1)p)-CH2(-Y(R2)p); L is a part of a pending group utilized for introducing -X(R1)p and -Y(R2)p; X and Y are halogen, N, S and O; R1 is hydrogen, alkyl, acyl or R2 when X is N, O or S; R2 is hydrogen, alkyl, alkylaryl or arylalkyl in which the alkyl part may contain 1-18 carbons, or -R3(-NH-CR4=O)q or -R3(-NH2)q, -CR4=O or poly alkyloxy that may have been terminally acylated or alkylated; p is an integer 0-3, with the provisos a) p depends on X being halogen, O, S or N, and b) that if several groups R2 are present they may be identical or different; R3 is alkyl, -O-alkyl, hydroxyalkyl, phenylalkyl, with up to 18 carbon atoms in the alkyl part, and R4 is C1-18 alkyl. q is an integer>O representing that one or more hydrogens in R3 may have been replaced with -NH2 or -NH-CR4=O. The polymer article may be used as a chromatography separation medium or in solide phase oligonucleotide synthesis.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIOPROCESS R&D
Oligonucleotide synthesis chip system and use method thereof
ActiveCN109603704ASimple processing technologySimple processSequential/parallel process reactionsChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsOligonucleotide synthesisEngineering
The invention discloses an oligonucleotide synthesis chip system. The oligonucleotide synthesis chip system comprises an oligonucleotide synthesis chip and a synthetic carrier particle size screeningchip, wherein the high-throughput oligonucleotide synthesis chip comprises a micro-funnel structure with two ends open, an upper end opening is located in the upper surface of the high-throughput oligonucleotide synthesis chip, a lower end opening is located in the lower surface of the high-throughput oligonucleotide synthesis chip, and the caliber of the upper end opening is larger than that of the lower end opening. The synthetic carrier particle size screening chip comprises screen holes, wherein the upper surface opening diameter of the screen holes is smaller than the upper end opening aperture of the oligonucleotide synthesis chip, the lower surface opening diameter of the screen holes is obvious larger than the lower end opening diameter of the oligonucleotide synthesis chip, and the lower surface opening diameter of the screen holes is slightly smaller than the upper surface opening diameter of the screen holes.
Owner:杭州原合生物科技有限公司
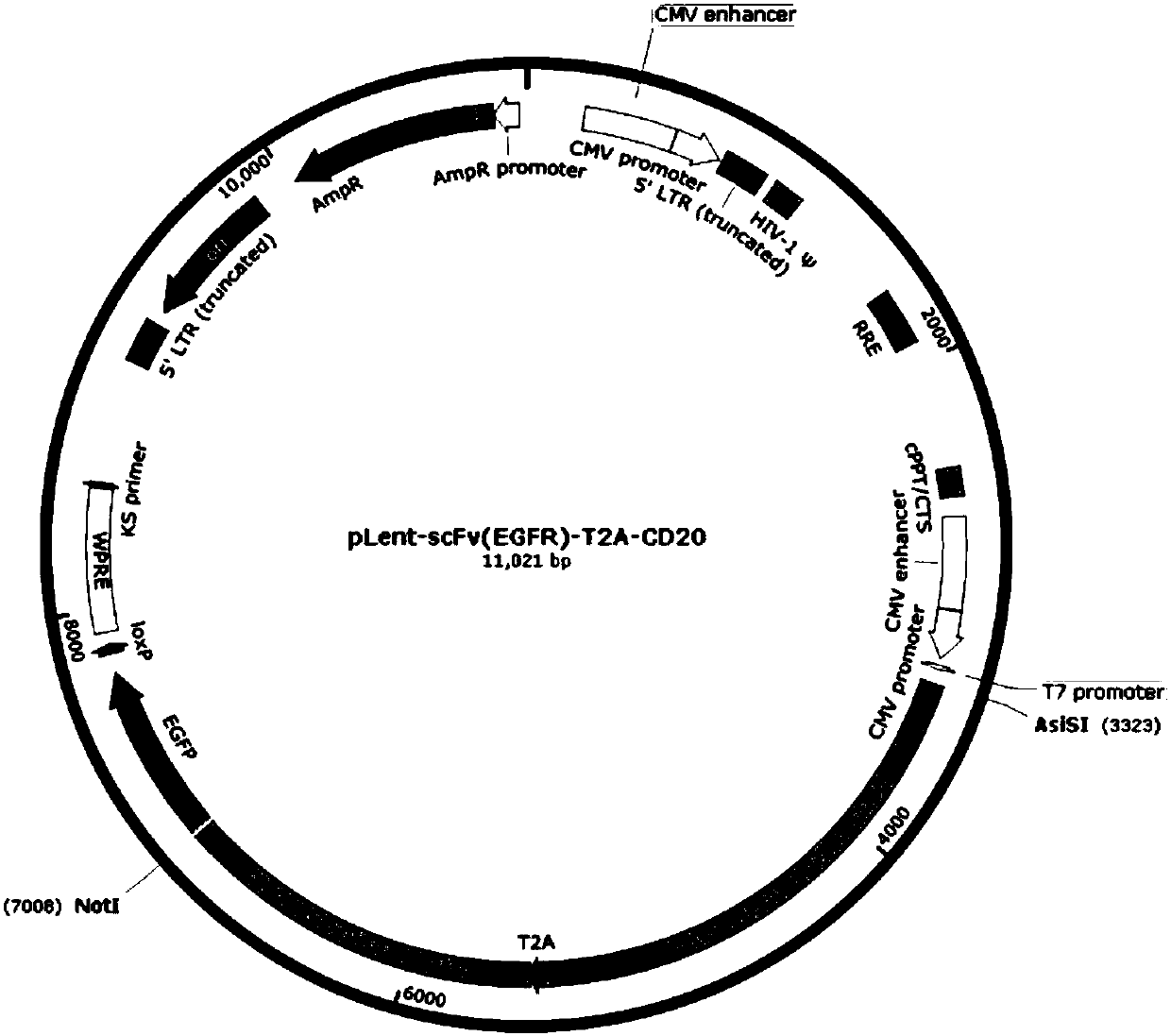
Method for preparing anti-EGFR safe chimeric antigen receptor modified immune cell and application thereof
ActiveCN107557392AReduce side effectsImprove securityMammal material medical ingredientsFermentationCD20CD33
The invention discloses a method for preparing an anti-EGFR safe chimeric antigen receptor modified immune cell and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing scFv(EGFR)-CD8-CD137-CD33 zeta-T2A-Leader-CD20-CD8-CD3 zeta-nucleotide; inserting a fusion gene fragment into a lentivirus expression vector, and packaging into a lentivirus carrying scFv(EGFR)-CD8-CD137-CD3zeta-T2A-Leader-CD20-CD8-CD3 zeta coding genes, and infecting a monocyte induced immune cell to obtain the anti-EGFR safe chimeric antigen receptor modified immune cell. According to the method, the safety of chimeric antigen receptor modified immune cell can be improved, toxic and side effect can be controlled, and occurrence of adverse response can be avoided.
Owner:山东省成体细胞产业技术研究院有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com