Photosensitive component
A photosensitive element and nanohole array technology, applied in the field of photosensitive elements, can solve the problem that the sensitivity of the photosensitive element is not very high, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
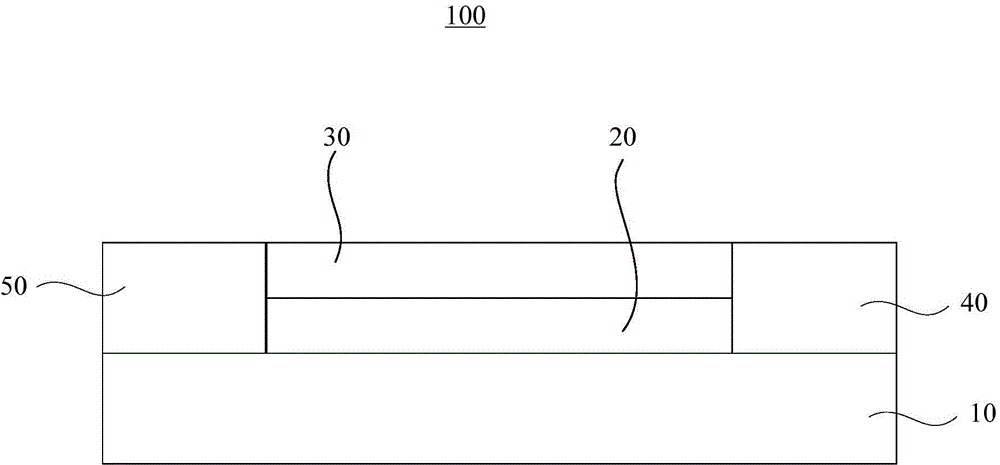
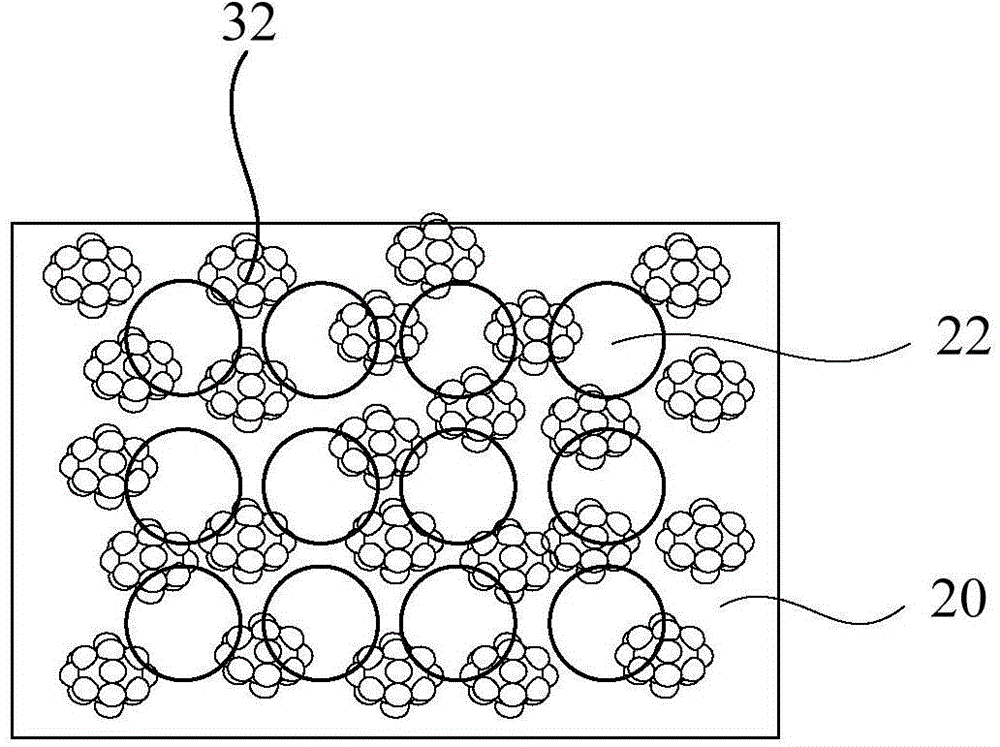
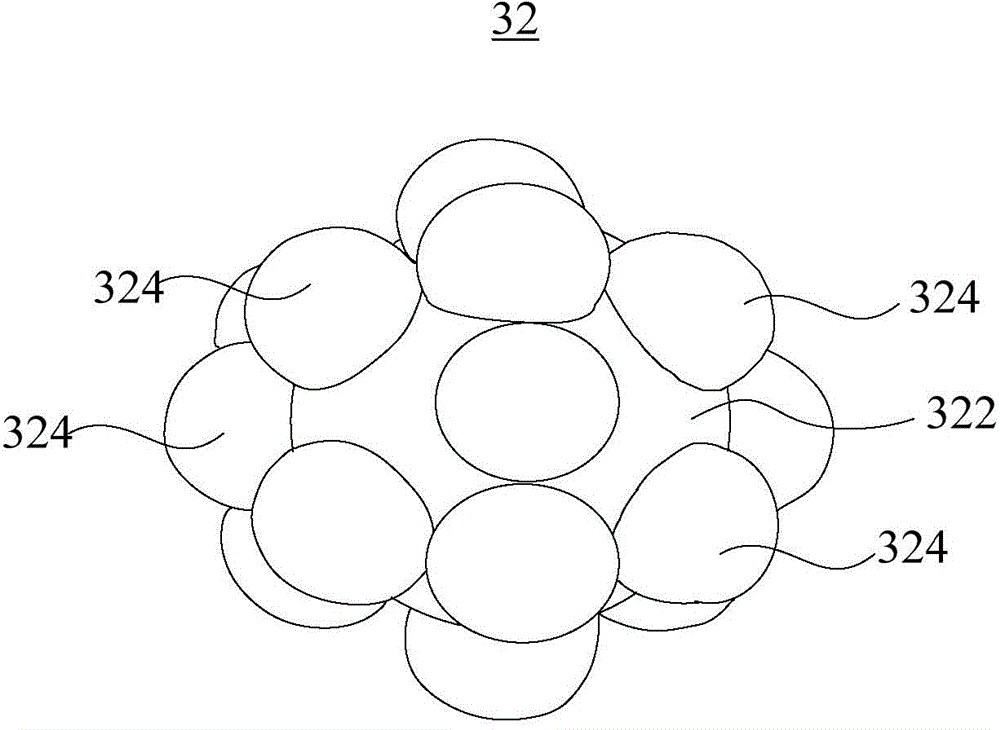
[0036] The photosensitive element I is prepared, and the photosensitive element I includes a semiconductor active layer, a nanohole array layer, a submicron particle layer, an anode and a cathode. Wherein the material of the semiconductor active layer is silicon. The diameter of the nanoholes in the nanohole array layer is 350 nm, the thickness of the nanohole array layer is 50 nm, and the distance between adjacent nanoholes is 100 nm. The material of the nanohole array layer is silver. The submicron particle layer is formed from submicron silver particles. The submicron silver particles include central silver nanoparticles with a diameter of 200nm and 18 surrounding silver nanoparticles with a diameter of 100nm protruding from the surface of the central silver nanoparticles. Both anode and cathode materials are silver.
[0037] Light with a wavelength of 700nm to 1600nm is irradiated onto the photosensitive element I from the side of the submicron particle layer, and the l...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The photosensitive element II was prepared, and the structure of the photosensitive element II was basically the same as that of the photosensitive element I in Example 1. The difference is that, in the photosensitive element II, a layer of spherical silver nanoparticles with a particle diameter of 100nm is stacked above the nanohole array layer instead of a submicron silver particle layer.
[0040] When light with a wavelength of 700nm-1600nm is irradiated from the side of the spherical silver nanoparticle layer onto the photosensitive element II, the enhancement factor of the obtained photocurrent is as follows: Figure 5 shown. As can be seen from the figure, compared with Example 1, the spherical silver nanoparticles in the photosensitive element II can also enhance the photocurrent intensity of the semiconductor active layer under the light condition with a wavelength greater than 1200nm, however, its enhancement effect is not as good as that of the photosensitive ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] The photosensitive element III was prepared, and the structure of the photosensitive element III was basically the same as that of the photosensitive element I in Example 1. The difference is that, in the photosensitive element III, a layer of spherical silver nanoparticles with a particle diameter of 200nm is stacked above the nanohole array layer instead of a submicron silver particle layer.
[0043] Irradiate light with a wavelength of 700nm to 1600nm from one side of the spherical silver nanoparticle layer onto the photosensitive element III, and the enhancement factor of the obtained photocurrent is as follows: Figure 5 As can be seen from the figure, compared with Example 1, the spherical silver nanoparticles in the photosensitive element III can also enhance the photocurrent intensity of the semiconductor active layer under the light conditions with a wavelength greater than 950nm, however, its enhanced The effect is not as good as the submicron particle layer o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com