Method for cooling yellow phosphorus furnace slags by air quenching
A cooling method, the technology of yellow phosphorus slag, which is applied in the chemical industry, can solve the problems of unutilized slag heat, high energy consumption and labor costs, and large production water consumption, so as to change water vapor pollution, reduce energy consumption and labor costs , The effect of reducing production water
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
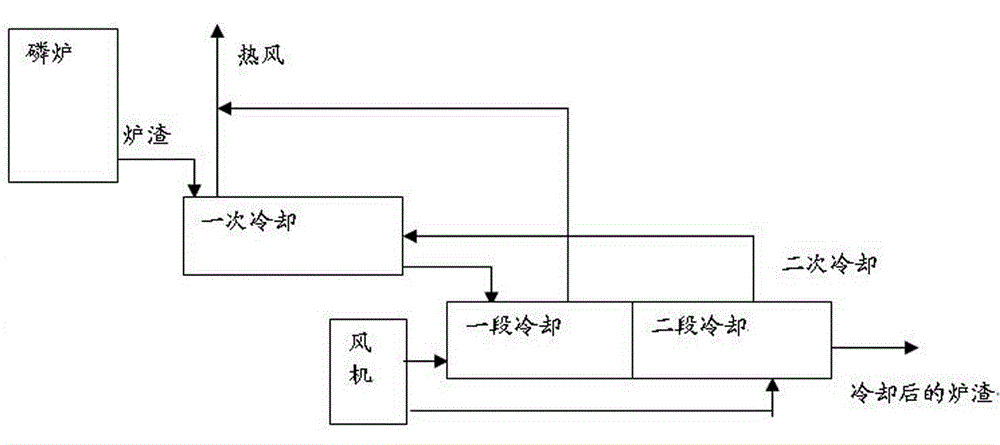
[0014] A method for cooling yellow phosphorus slag by air quenching, comprising the steps of:
[0015] (1) The high-temperature slag from the phosphorus furnace is firstly cooled, and the outlet air temperature is controlled at 700°C. The cooling air adopts the second-stage cooling air for secondary cooling, and then the slag enters the secondary cooling for further cooling;
[0016] (2) The material is in a semi-molten state when entering the secondary cooling, and the material temperature is about 900°C. The secondary cooling is divided into two stages for cooling, and the temperature of the cooling air in the first stage is controlled at 700°C. The hot air from the same cooling is sent to the boiler for production Steam, the second-stage cooling air temperature is controlled at 350°C, the secondary cooling outlet material temperature is 90°C, and the cooled slag goes downstream.
Embodiment 2
[0018] A method for cooling yellow phosphorus slag by air quenching, comprising the steps of:
[0019] (1) The high-temperature slag from the phosphorus furnace is firstly cooled, and the outlet air temperature is controlled at 600°C. The cooling air adopts the second-stage cooling air for secondary cooling, and then the slag enters the secondary cooling for further cooling;
[0020] (2) The material is in a semi-molten state when it enters the secondary cooling, and the material temperature is about 800°C. The secondary cooling is divided into two stages for cooling, and the temperature of the cooling air in the first stage is controlled at 600°C. The hot air from the same cooling is sent to the boiler for production Steam, the second-stage cooling air temperature is controlled at 200°C, the secondary cooling outlet material temperature is 65°C, and the cooled slag is sent downstream to produce superfine powder.
[0021] The hot air generated by the second-stage cooling and t...
Embodiment 3
[0023] A method for cooling yellow phosphorus slag by air quenching, comprising the steps of:
[0024] (1) The high-temperature slag from the phosphorus furnace is firstly cooled, and the outlet air temperature is controlled at 900°C. The cooling air adopts the second-stage cooling air for secondary cooling, and then the slag enters the secondary cooling for further cooling;
[0025] (2) The material is in a semi-molten state when entering the secondary cooling, and the material temperature is about 1100°C. The secondary cooling is divided into two stages for cooling, and the temperature of the cooling air in the first stage is controlled at 900°C. The hot air from the same cooling is sent to the boiler for production Steam, the second-stage cooling air temperature is controlled at 400°C, the secondary cooling outlet material temperature is 100°C, and the cooled slag is sent downstream to produce superfine powder.
[0026] The hot air generated by the second-stage cooling and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com