Negative electrode active material for non-aqueous electrolyte rechargeable battery, and non-aqueous electrolyte rechargeable battery using negative electrode active material
A negative electrode active material and non-aqueous electrolyte technology, which is applied in the field of non-aqueous electrolyte secondary batteries, can solve the problems such as the reduction of initial charge and discharge efficiency and capacity, and achieve the effect of improving the initial charge and discharge efficiency and cycle characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0050] The present invention will be described in more detail through specific examples below, but the present invention is not limited by the following examples, and can be implemented with appropriate changes within the scope of not changing its gist.
Embodiment 1
[0053] [Production of Negative Electrode]
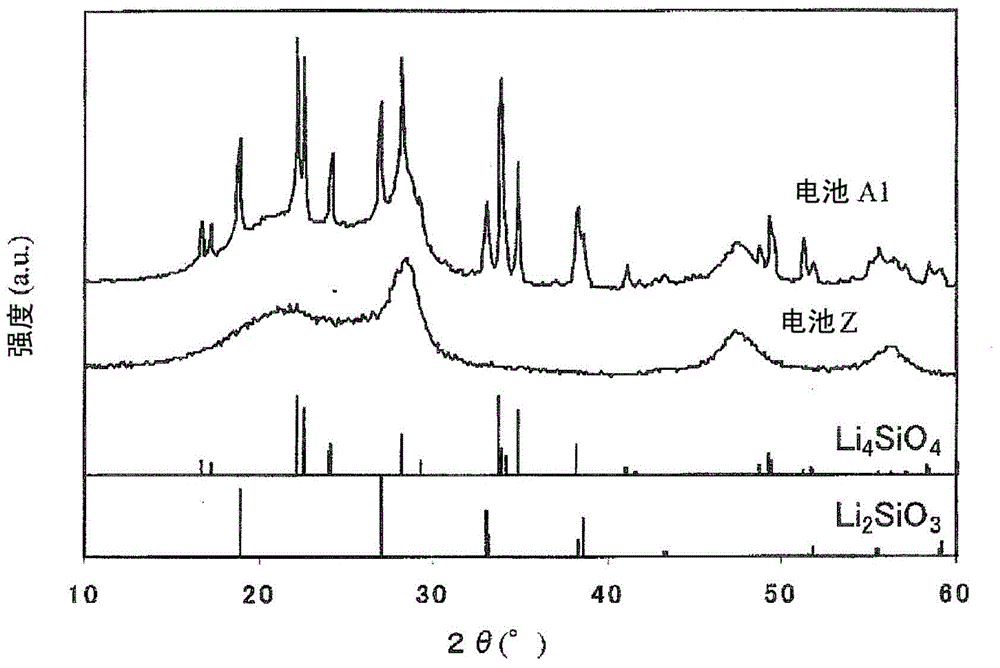
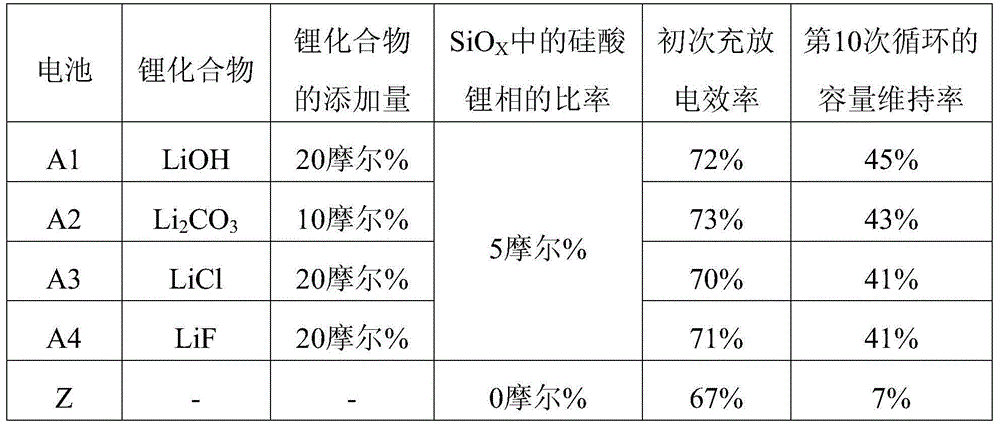
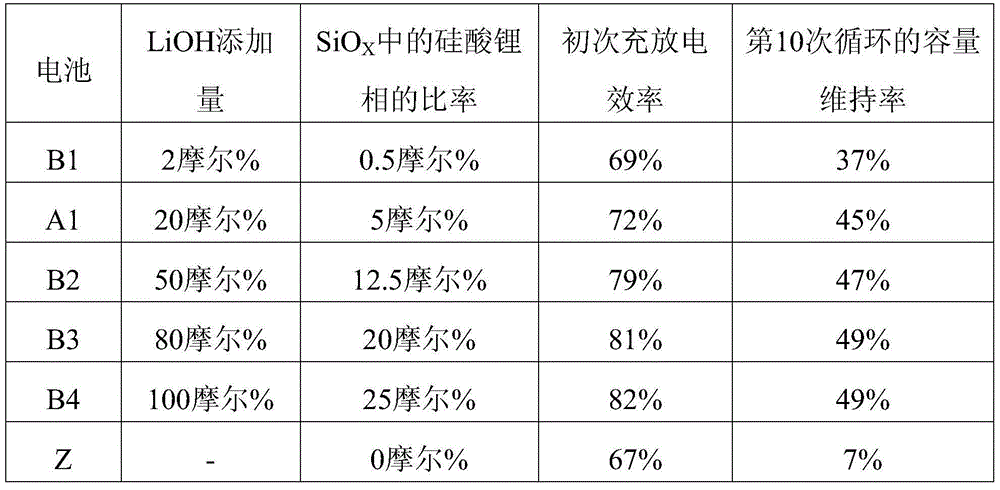
[0054] Preparation of SiO surface covered with carbon X (X=0.93, average primary particle diameter: 5.0 μm). It should be noted that the coating was carried out using the CVD method. In addition, the carbon relative to the SiO X The ratio is 10% by mass, SiO X The carbon coverage of the surface was set at 100%. 1 mole of the above SiO X , 0.2 mol of LiOH mixed in powder state (LiOH relative to SiO X The ratio is 20 mol%), in SiO X LiOH is attached to the surface. Then, it was heat-treated at 800°C for 10 hours in an Ar atmosphere to produce SiO with a lithium silicate phase formed inside. X . The heat-treated SiO X Analyzed by XRD (ray source is CuKα), the results are as follows figure 1 As shown, it was confirmed that Li as lithium silicate 4 SiO 4 and Li 2 SiO 3 peak. In addition, the number of moles of lithium silicate phase relative to SiO X The total number of moles (hereinafter referred to as SiO X The ratio o...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Lithium source and SiO X When mixing for heat treatment, use Li 2 CO 3 (Li 2 CO 3 relative to SiO X A battery was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 of the above-mentioned first example, except that LiOH was used as the lithium source instead of LiOH at a ratio of 10 mol%. It should be noted that the heat-treated SiO by XRD X As a result of analysis, it was confirmed that Li as lithium silicate 4 SiO 4 and Li 2 SiO 3 peak. In addition, SiO after heat treatment X The ratio of the lithium silicate phase in is 5 mol%. The battery produced in this way is hereinafter referred to as battery A2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com