Polyphenylene sulfide composite fiber and non-woven fabric
A composite fiber and polyphenylene sulfide technology, applied in the direction of conjugated synthetic polymer artificial filament, textile, non-woven fabric, etc., can solve the problems of high mechanical strength, insufficient thermal adhesion, high fiber crystallinity, etc., to achieve Excellent thermal adhesion and excellent mechanical strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] (ingredient A)
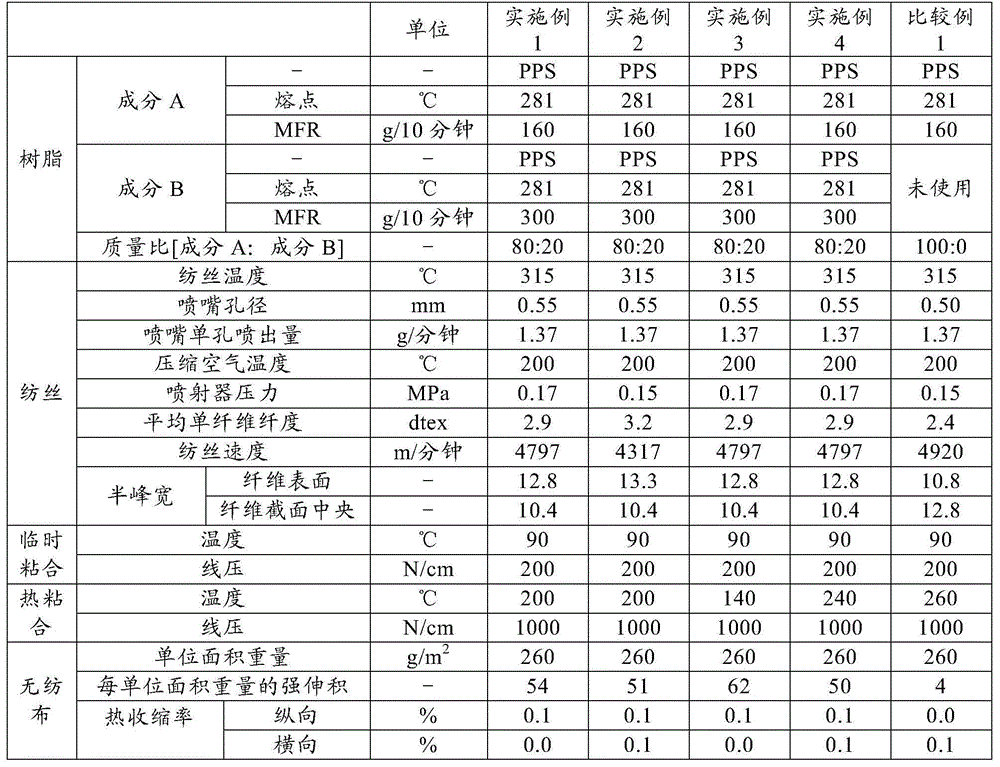
[0089] 100 mol% linear polyphenylene sulfide resin (manufactured by Toray Corporation, product number: E2280, MFR: 160 g / 10 minutes) was dried at a temperature of 160° C. for 10 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere, and used as component A.
[0090] (ingredient B)
[0091] 100 mol % linear polyphenylene sulfide resin (manufactured by Toray Corporation, product number: M2588, MFR: 300 g / 10 minutes) was dried at 160° C. for 10 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere, and used as component B.
[0092] (spinning and non-woven reticulation)
[0093] The above-mentioned component A was melted with the extruder for the core component, and the above-mentioned component B was melted with the extruder for the sheath component, and the mass ratio of component A and component B was measured in such a way that the mass ratio of component A and component B was 80:20. The filament temperature is 315°C, and the single-hole discharge rate is 1.37g / min from the hole diameter The co...
Embodiment 2
[0097] (ingredient A)
[0098] As component A, the same PPS resin as that used in Example 1 was used.
[0099] (ingredient B)
[0100] As component B, the same PPS resin as that used in Example 1 was used.
[0101] (spinning and non-woven reticulation)
[0102] Core-sheath composite spinning and nonwoven meshing were performed in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the injector pressure was 0.15 MPa. The average single fiber fineness of the obtained core-sheath type composite long fiber was 3.2 dtex, the spinning speed was 4,317 m / min, the crystallinity of the fiber surface was lower than that of the center of the fiber cross section, and there were 0 broken filaments during spinning for 1 hour. Good silkiness.
[0103] (Temporary Bonding · Thermal Bonding)
[0104] Next, the above-mentioned nonwoven web was temporarily bonded and thermally bonded in the same manner as in Example 1 to obtain a core-sheath composite long-fiber nonwoven fabric. The weight per unit ...
Embodiment 3
[0106] (ingredient A)
[0107] As component A, the same PPS resin as that used in Example 1 was used.
[0108] (ingredient B)
[0109] As component B, the same PPS resin as that used in Example 1 was used.
[0110] (spinning and non-woven reticulation)
[0111] In the same manner as in Example 1, core-sheath composite spinning and nonwoven reticulation were performed. The average single fiber fineness of the obtained core-sheath type composite long fiber was 2.9 dtex, the spinning speed was 4,797 m / min, the crystallinity of the fiber surface was lower than that of the center of the fiber cross section, and the number of broken filaments was 0 during spinning for 1 hour. Spinnability is good.
[0112] (Temporary Bonding · Thermal Bonding)
[0113] Next, except that the thermal bonding temperature was 140° C., temporary bonding and thermal bonding were performed on the above-mentioned nonwoven web in the same manner as in Example 1 to obtain a core-sheath type composite lon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com