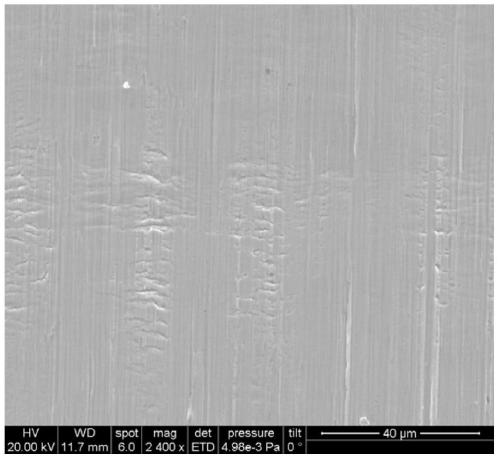
A kind of superhard austenitic stainless steel and its manufacturing method
A technology of austenitic stainless steel and its manufacturing method, which is applied in the field of ultra-hard austenitic stainless steel and its manufacturing, can solve problems such as surface quality problems, processing deformation defects, difficult control of plate shape, etc., and achieve hardness improvement and material orientation The effect of reducing the opposite sex and reducing the control of the shape
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0054] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with embodiment.
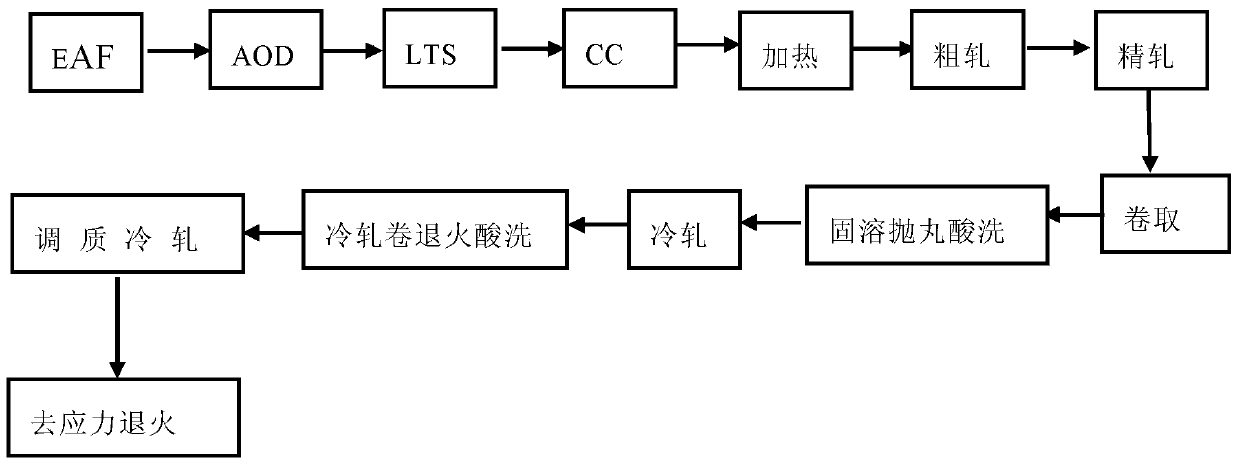
[0055] The technological process schematic diagram of the embodiment of the present invention is as figure 2 As shown, the details are as follows:
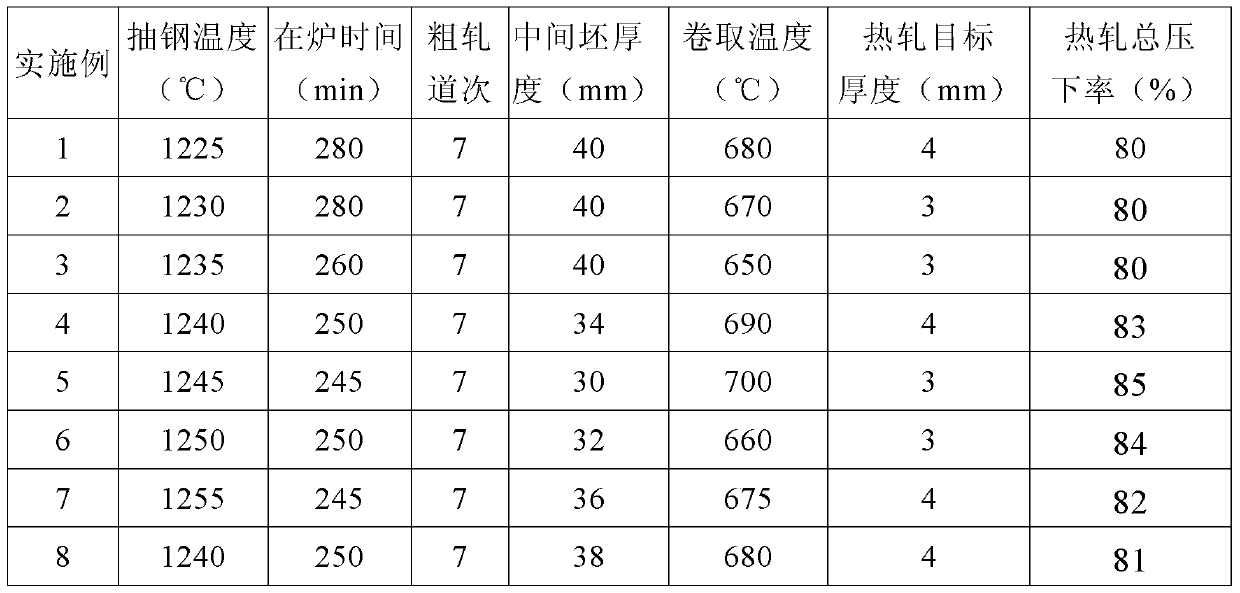
[0056] Pour the molten steel smelted by the electric furnace and AOD furnace into the baked ladle, hoist it to the refining station to fine-tune the composition, and ensure that the Md30 of the comprehensive effect of each composition is between 30 and 60°C. When the temperature of the ladle reaches the temperature required for casting, it is hoisted to the continuous casting platform and cast into a continuous casting slab with a thickness of 200mm. In order to ensure the surface quality of the continuous casting slab, try to ensure a stable casting speed, and slowly reduce the casting speed until the last 10 minutes. The chemical composition of steel examples 1-8 of the present invention is shown in Table 2.
[0057] The prepared s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com