Method for producing dried freshwater fishes by using microbial fermentation technology
A microbial fermentation and freshwater fish technology, applied in the direction of bacteria used in food preparation, application, food science, etc., can solve the problems of unstable product quality, strong seasonality of production, uneven pickling, etc., to slow down fat oxidation oyster effects of dehydration, accelerated dehydration process, and demand for safe food consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
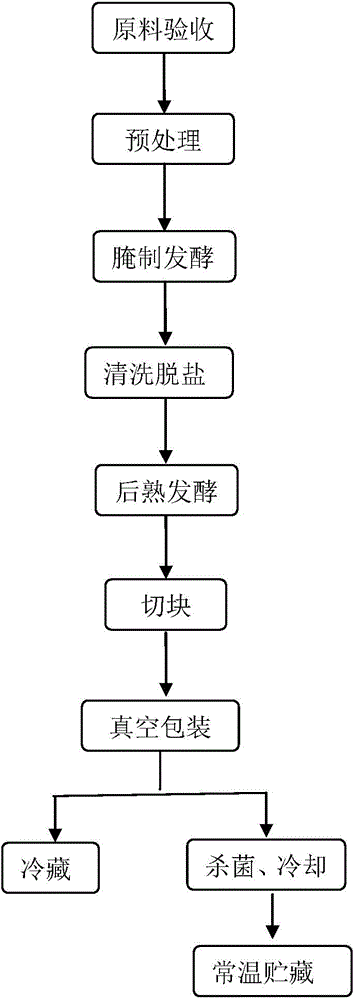
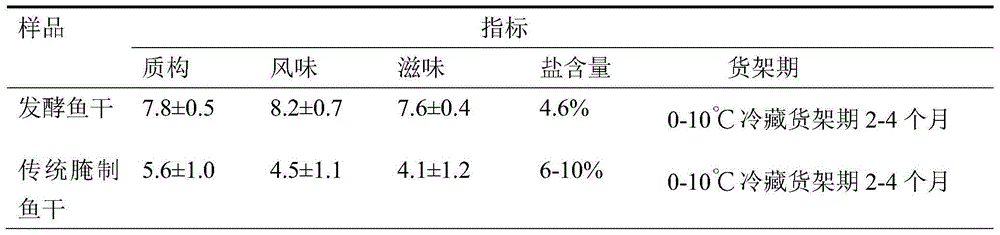
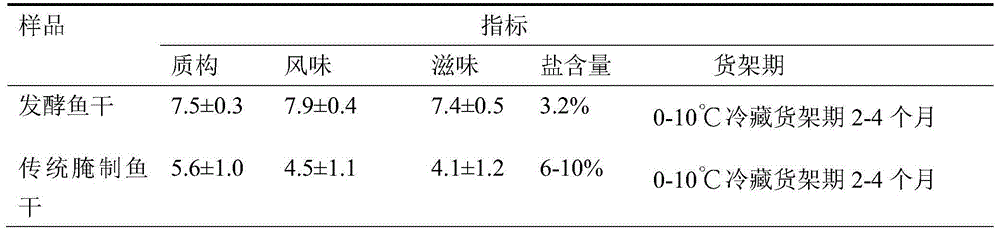
[0026] Fresh herring is dissected, viscera removed, cut open from the back, divided into two, washed with running water to remove dirt and mucus in the fish body; use a salt water injection machine to inject mixed fermentation strains on the back of the fish body, and inoculate the fermentation strains The amount accounts for 2% of the weight of the fish, and the fermentation strain is composed of bacteria with a concentration of 10 7 CFU / ml of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Pediococcus pentosaceae and Staphylococcus xylosus in equal proportions, then added 3% glucose and 5% salt; then salted with 8% salt, layered with salt Put it flat in the pickling pond; mix salt and then pickle and ferment at 15°C for 2 days; wash off the mucus, salt grains and fallen scales on the fish body with running water after leaving the pond; use spraying to inoculate the mixed fermentation bacteria species, the inoculum amount of the fermented strain accounts for 1% of the fish weight, and the fermente...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Fresh grass carp is dissected, viscera removed, cut open from the back, divided into two, washed with running water to remove dirt and mucus in the fish body; a salt water injection machine is used to inject mixed fermentation strains on the back of the fish body, and the fermentation strains are inoculated The amount accounts for 1% of the weight of the fish, and the fermentation strain is composed of bacteria with a concentration of 10 8 CFU / ml of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Lactobacillus plantarum and Staphylococcus xylosus in equal proportions and then added 2% glucose and 4% salt; Methods Put it flat in the pickling tank; mix salt and then pickle and ferment at 5°C for 4 days; wash off the mucus, salt grains and scales off the fish body with running water after leaving the tank; use spraying to inoculate the mixed fermentation strains , the inoculum amount of the fermented strain accounts for 2% of the fish weight, and the fermented strain is composed of a cell conce...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Fresh herring is dissected, viscera removed, cut open from the back, divided into two, washed with running water to remove dirt and mucus in the fish body; use a salt water injection machine to inject mixed fermentation strains on the back of the fish body, and inoculate the fermentation strains The amount accounts for 1% of the weight of the fish, and the fermentation strain is composed of bacteria with a concentration of 10 9CFU / ml of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Lactobacillus plantarum and Staphylococcus xylosus in equal proportions and then added 2% glucose and 3% salt; Methods Put it flat in the pickling tank; mix salt and then pickle and ferment at 5°C for 4 days; wash off the mucus, salt grains and scales off the fish body with running water after leaving the tank; use spraying to inoculate the mixed fermentation strains , the inoculum amount of the fermented strain accounts for 1.5% of the fish weight, and the fermented strain is composed of a cell concentration of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com