Method for manufacturing silicon carbide semiconductor device
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurement, electric solid-state devices, etc., can solve problems such as increase in forward characteristic resistance, stacking fault expansion, etc., to prevent increase in manufacturing costs, The effect of good positive characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
[0019]
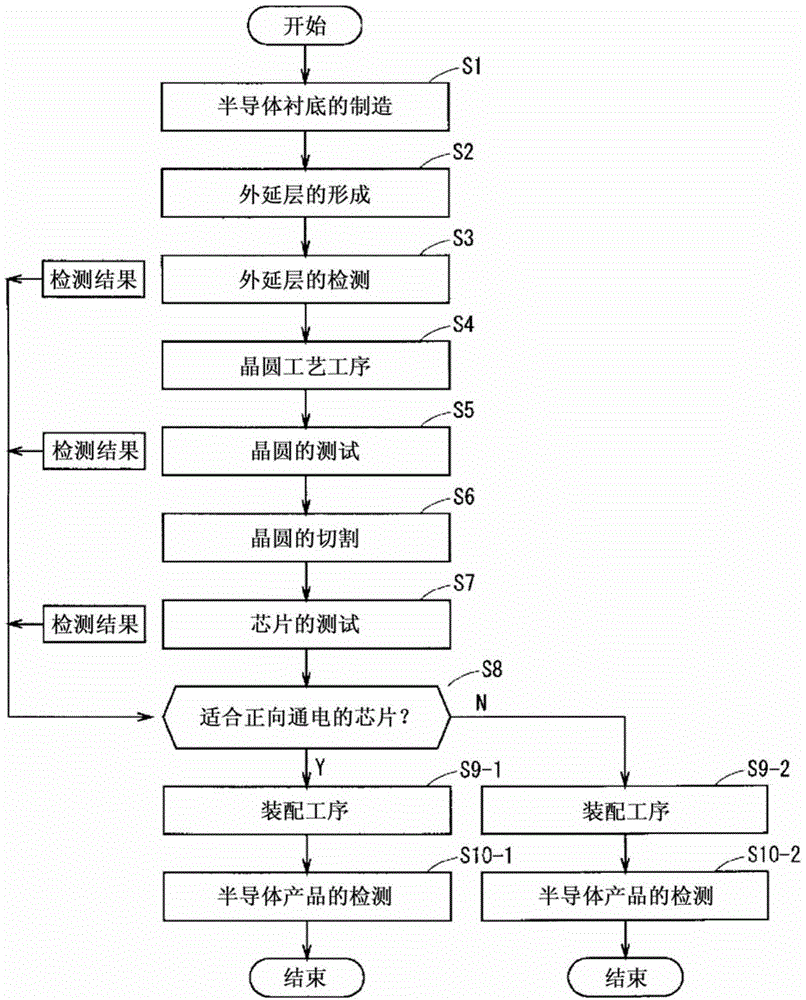
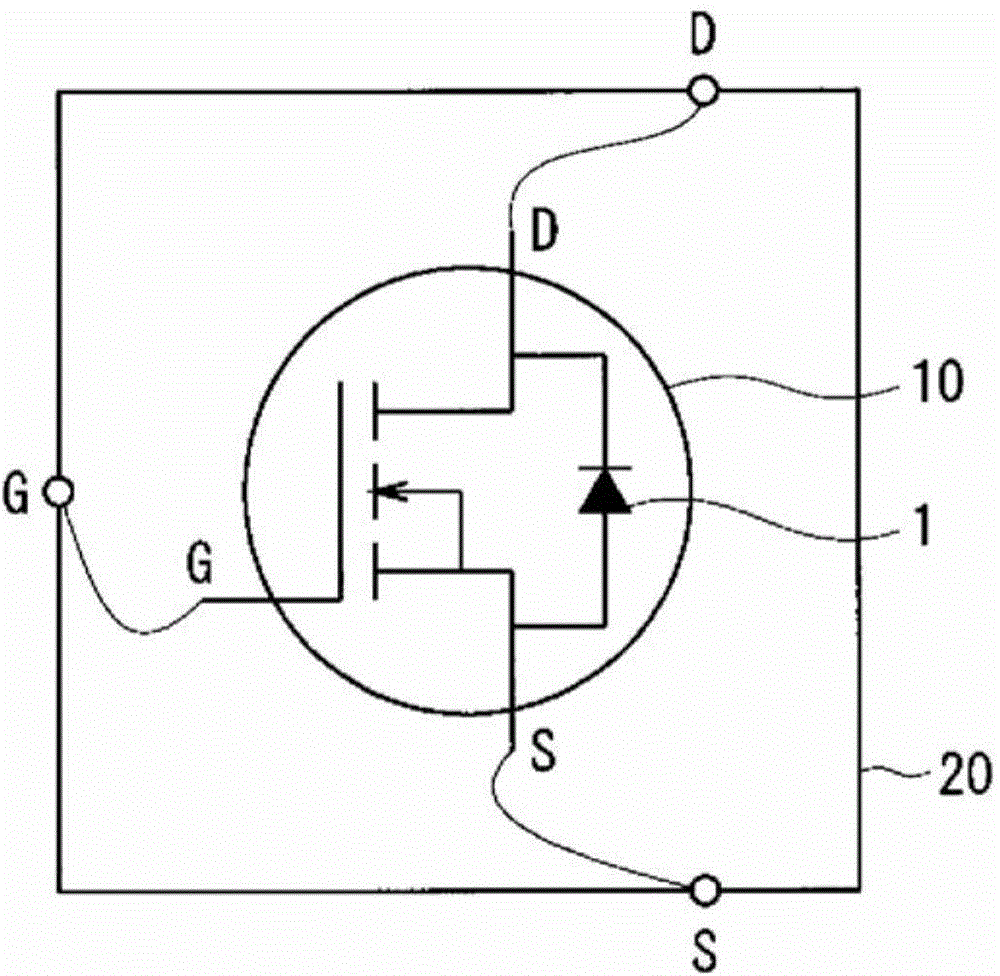
[0020] figure 1 It is a flowchart showing the outline of the method of manufacturing a silicon carbide semiconductor device according to the present embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, a silicon carbide semiconductor MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) is assumed as an example of a semiconductor device.
[0021] First, a substrate manufacturing step is performed in which a semiconductor substrate of the first conductivity type is manufactured (step S1). Specifically, a silicon carbide substrate was produced by a modified sublimation method (modified Lely method). In addition, it is also possible to purchase commercially available silicon carbide substrates that have already been manufactured and used in subsequent steps.
[0022] At this time, in order to suppress the expansion of stacking faults generated when the current flows to the pn junction in the forward direction (forward energization), it is desirable to produc...
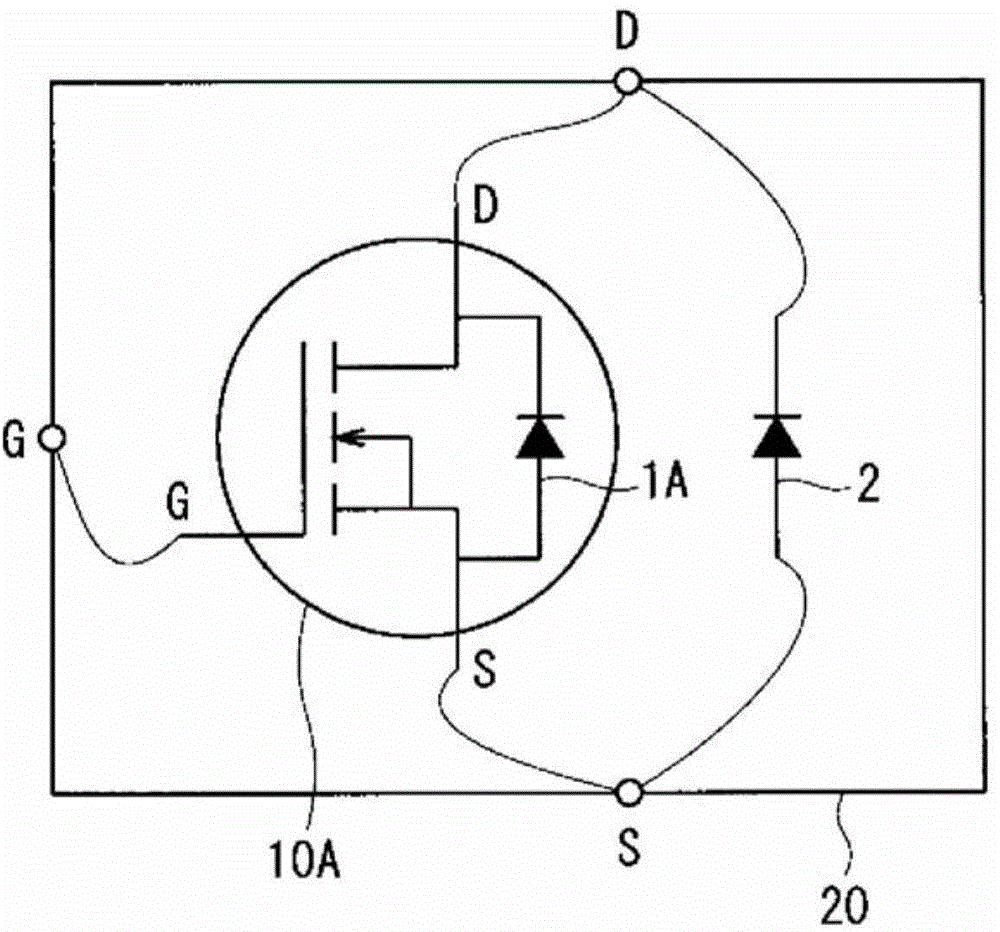
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0069]
[0070] Figure 4 It is a flowchart showing the outline of the method of manufacturing a silicon carbide semiconductor device according to this embodiment. exist Figure 4 Since steps S1 to S7 are the same as those in the first embodiment, detailed description thereof will be omitted.
[0071] After step S7, a mounting process is performed in which a semiconductor chip is fixed in a case or a module, and wiring is formed (step S9).
[0072] Then, a product inspection step is performed in which initial characteristics of the assembled silicon carbide semiconductor device (product) are inspected (step S10 ). The detection result is stored in a predetermined storage area as detection result data.
[0073] Then, a screening step is performed in which, in the silicon carbide semiconductor device (product), it is detected whether or not there is deterioration when the pn junction is forwardly energized (step S11 ). Specifically, the presence or absence of an increase i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com