Single-phase permanent magnet brushless direct-current motor with auxiliary teeth and auxiliary windings
A DC motor, single-phase permanent magnet technology, applied in the field of electric motors, can solve the problems of inability to start smoothly and smoothly, the vibration of the motor is large, and the vibration moment of the start is large, etc., and achieves the reduction of the combined torque ripple, the improvement of the motor efficiency, and the reduction of gas. The effect of gap flux density fluctuations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
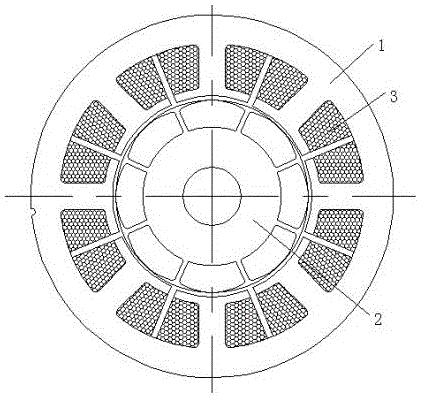
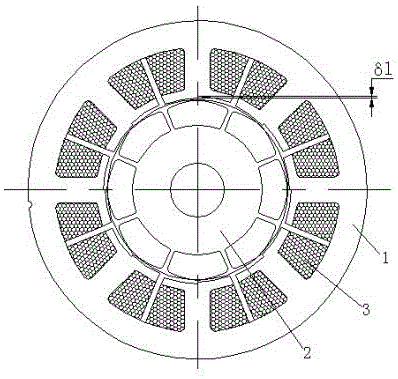
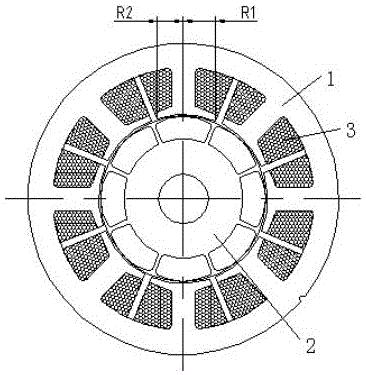
[0034] like Figure 6 to Figure 8 Show, the monoclon permanent magnetic non -brush -free DC motor of the auxiliary tooth and auxiliary winding of the present invention, including the stator and permanent magnet rotor 21; the maximum number of permanent magnet rotor is 2P;
[0035] The stator has multiple main polar teeth 15 and the stator auxiliary polar teeth 16, the main polar teeth 15 and the stator auxiliary polar teeth are settings;
[0036] Total altitude number of the main polar tooth 15 and the stator auxiliary polar teeth 16 is twice the number of motor permanent magnet rotor, that is, Z = 2 × 2P, P is extremely pair;
[0037] The width of the main polar teeth 15 is 1.55 to 2 times the width of the stator auxiliary polar teeth 16;
[0038] like Figure 8 Show, the stator main polar teeth 15 and the stator auxiliary polar teeth 16 are more width of the tooth width of the tooth of the stator in the statorThe ratio is 1 ~ 1.2;
[0039] The root of the main tooth 15 of the stat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com